Authorities play a crucial role in maintaining public safety and enforcing laws that protect communities. Their decisions and actions impact daily life, shaping social order and justice systems. Discover how understanding the responsibilities and challenges faced by authorities can empower you to engage more effectively with your community in the full article.
Table of Comparison
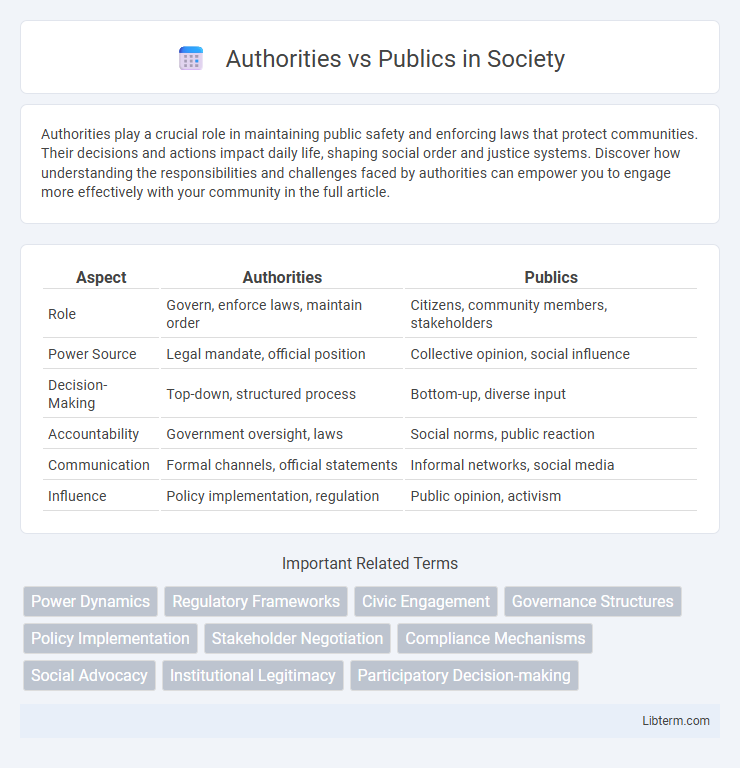
| Aspect | Authorities | Publics |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Govern, enforce laws, maintain order | Citizens, community members, stakeholders |
| Power Source | Legal mandate, official position | Collective opinion, social influence |
| Decision-Making | Top-down, structured process | Bottom-up, diverse input |
| Accountability | Government oversight, laws | Social norms, public reaction |
| Communication | Formal channels, official statements | Informal networks, social media |
| Influence | Policy implementation, regulation | Public opinion, activism |
Defining Authorities and Publics
Authorities represent structured organizations or individuals vested with official power to enforce laws, make decisions, and regulate societal functions. Publics consist of diverse groups or communities of individuals who share common interests, concerns, or identities but lack formal power or governance authority. Understanding the distinction between authorities and publics is essential for analyzing power dynamics, decision-making processes, and civic engagement within social and political contexts.
Historical Context of Authorities vs Publics
Authorities vs publics has historically evolved through shifting power dynamics shaped by political revolutions, social movements, and governance reforms. The Enlightenment era catalyzed challenges to absolute authority, promoting public sovereignty and individual rights as seen in documents like the Magna Carta and the U.S. Constitution. Industrialization and mass media further transformed public engagement, enabling more widespread participation and accountability in modern democratic systems.
Power Dynamics Between Authorities and Publics
Power dynamics between authorities and publics often shape governance and social order, where authorities wield institutional power to enforce laws and policies. Publics exercise power through collective actions such as protests, voting, and advocacy to influence or resist authority decisions. The balance of power depends on legitimacy, transparency, and accountability mechanisms within political and social systems.
Communication Channels: Top-Down vs Bottom-Up
Authorities typically rely on top-down communication channels, disseminating information through formal media, official statements, and institutional platforms to control messaging and maintain order. In contrast, publics engage in bottom-up communication via social media, community forums, and grassroots networks, enabling feedback, dialogue, and decentralized information flow. Understanding the dynamics between these channels is crucial for effective governance, crisis management, and fostering public trust.
Trust and Credibility Issues
Authorities often struggle with trust and credibility issues when publics perceive a lack of transparency or accountability, undermining effective communication. Public skepticism increases when authorities fail to address concerns or provide inconsistent information, leading to diminished cooperation and engagement. Building trust requires transparent actions, consistent messaging, and genuine responsiveness to public needs and feedback.
Public Participation in Decision-Making
Public participation in decision-making enhances transparency and accountability by involving diverse community members in policy formulation and implementation processes. Authorities benefit from integrating stakeholder feedback to create more effective and equitable regulations that reflect public needs and priorities. Empowering publics through inclusive engagement mechanisms fosters trust, improves governance outcomes, and strengthens democratic legitimacy.
Case Studies: Conflicts Between Authorities and Publics
Case studies of conflicts between authorities and publics reveal patterns of power struggles rooted in social, political, and economic grievances. Instances such as the Arab Spring uprisings, Hong Kong protests, and the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe's opposition to the Dakota Access Pipeline demonstrate how public mobilization challenges government policies perceived as unjust or oppressive. These conflicts highlight the importance of transparent communication, respect for human rights, and inclusive governance to mitigate tensions and foster mutual understanding.
The Role of Media in Shaping Perceptions
Media plays a critical role in shaping the relationship between authorities and publics by framing narratives that influence public opinion and trust in governance. Through selective coverage, emphasis on particular events, and framing of information, media can amplify or mitigate tensions between authorities and citizens, impacting social cohesion and policy acceptance. The rise of digital platforms has further democratized information flow, enabling publics to challenge authoritative discourse and participate actively in the construction of societal narratives.
Building Collaborative Relationships
Building collaborative relationships between authorities and publics requires transparent communication, mutual trust, and shared goals that address community needs effectively. Engaging stakeholders early in decision-making processes enhances legitimacy and fosters cooperative problem-solving initiatives. Collaborative frameworks that emphasize accountability and responsiveness lead to sustained partnerships and improved social outcomes.
Future Trends in Authority-Public Interaction
Emerging digital platforms and AI-driven communication tools are reshaping authority-public interactions, enhancing transparency and real-time engagement. Authorities are increasingly leveraging data analytics to tailor public services and anticipate citizen needs, fostering more responsive governance. Social media trends predict a rise in decentralized dialogue, enabling diverse public voices to influence policy-making processes directly.
Authorities Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com