Behavioral assimilation refers to the process by which individuals adopt the behaviors, values, and norms of a different group, often to fit in or be accepted. This phenomenon plays a crucial role in social integration, influencing how people navigate new cultural or organizational environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover how behavioral assimilation impacts your interactions and social dynamics.
Table of Comparison
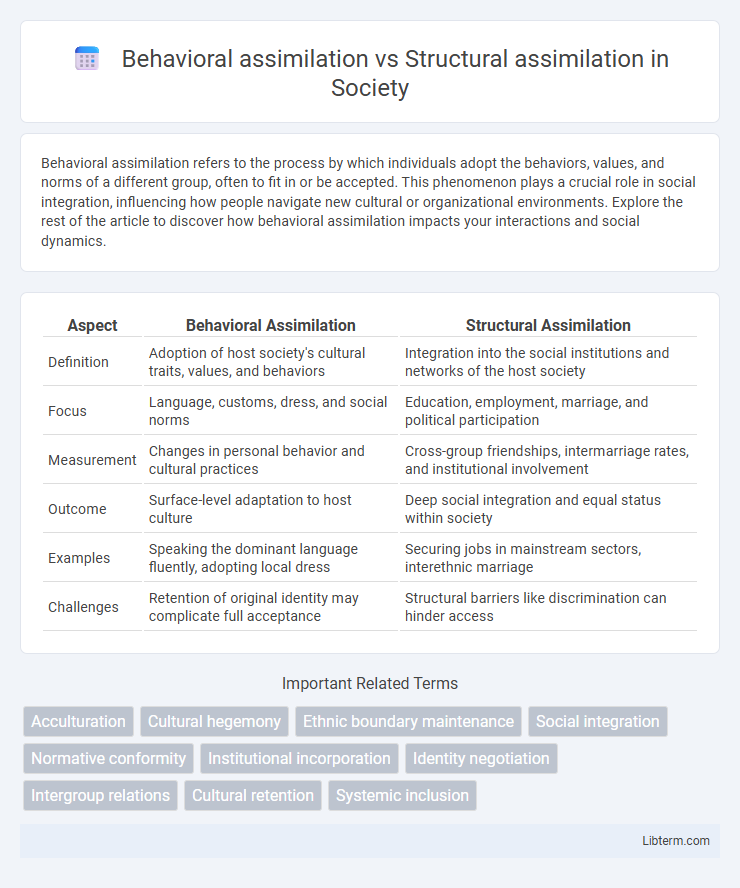
| Aspect | Behavioral Assimilation | Structural Assimilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adoption of host society's cultural traits, values, and behaviors | Integration into the social institutions and networks of the host society |
| Focus | Language, customs, dress, and social norms | Education, employment, marriage, and political participation |
| Measurement | Changes in personal behavior and cultural practices | Cross-group friendships, intermarriage rates, and institutional involvement |
| Outcome | Surface-level adaptation to host culture | Deep social integration and equal status within society |
| Examples | Speaking the dominant language fluently, adopting local dress | Securing jobs in mainstream sectors, interethnic marriage |
| Challenges | Retention of original identity may complicate full acceptance | Structural barriers like discrimination can hinder access |
Understanding Behavioral Assimilation
Behavioral assimilation involves the process by which individuals adopt the social behaviors, customs, and practices of a dominant culture, reflecting changes in daily interactions and lifestyle choices without necessarily altering institutional affiliations or economic status. This form of assimilation emphasizes cultural adaptation and social integration at the interpersonal level, often measured through language use, social networks, and participation in community activities. Understanding behavioral assimilation highlights the importance of social learning and cultural conformity in reducing intergroup differences while maintaining distinct structural positions within society.
Defining Structural Assimilation
Structural assimilation refers to the integration of minority group members into the social networks, institutions, and organizations of the dominant group, marked by equal participation in schools, workplaces, and political systems. It goes beyond behavioral assimilation, which involves adopting cultural patterns and social behaviors, by emphasizing the breaking down of barriers to entry within societal structures. Successful structural assimilation leads to full inclusion, eradication of segregation, and sustained equality in social, economic, and political spheres.
Key Differences Between Behavioral and Structural Assimilation
Behavioral assimilation refers to the process by which individuals adopt the cultural norms, values, language, and behaviors of the dominant group, enabling smoother social interactions and acceptance at an interpersonal level. Structural assimilation involves the integration of minority group members into the social, economic, and institutional frameworks of the dominant society, such as gaining access to education, employment, and political participation. The key difference lies in behavioral assimilation emphasizing cultural adaptation and social practices, whereas structural assimilation focuses on the establishment of equal status and participation within societal institutions.
Historical Contexts of Assimilation Theories
Behavioral assimilation refers to the process by which minority groups adopt the cultural norms, values, and behaviors of the dominant society, often studied within early 20th-century assimilation theories by sociologists like Robert Park. Structural assimilation involves the integration of minority groups into the social, economic, and institutional frameworks of the host society, emphasizing participation in key societal institutions such as education, employment, and political systems. Historical contexts show that early assimilation theories, developed during periods of mass immigration in the United States, differentiated between these two forms to explain both cultural adaptation and inclusion into societal structures.
The Role of Social Networks in Assimilation
Behavioral assimilation involves adopting the cultural norms and behaviors of the host society, while structural assimilation refers to integration into the social network and institutional frameworks of that society. Social networks play a crucial role in structural assimilation by providing access to employment, education, and social support, enabling immigrants to establish meaningful connections beyond their ethnic enclaves. The density and diversity of social ties directly influence the speed and extent of both behavioral and structural assimilation processes.
Cultural Practices and Behavioral Adaptation
Behavioral assimilation involves the adoption of cultural practices, values, and social norms of the dominant group, leading to changes in language, dress, and daily habits. Structural assimilation refers to the integration into social institutions such as education, employment, and intermarriage, reflecting deeper social inclusion beyond surface cultural adaptation. Both forms emphasize different dimensions of immigrant adaptation, with behavioral assimilation focusing on cultural practices and structural assimilation on social and institutional participation.
Institutional Integration and Structural Change
Behavioral assimilation involves individuals adopting the cultural norms, values, and behaviors of the dominant group, enhancing institutional integration through increased participation in social institutions like schools and workplaces. Structural assimilation refers to the broader process of minority groups gaining access to and representation in key societal structures, such as political offices and economic networks, driving significant structural change. Institutional integration under behavioral assimilation emphasizes cultural acceptance, while structural assimilation focuses on altering the power dynamics and composition of institutions to achieve long-term societal transformation.
Measuring Assimilation: Indicators and Metrics
Behavioral assimilation is measured through indicators such as language proficiency, social interactions, and cultural practices, reflecting an individual's adaptation to the host society's norms. Structural assimilation is assessed by metrics like occupational status, residential integration, and intermarriage rates, indicating the incorporation of individuals into the core institutions and social networks of the host society. Together, these variables provide a comprehensive evaluation of assimilation processes within immigrant populations.
Challenges and Critiques of Assimilation Models
Behavioral assimilation, emphasizing cultural adoption such as language and customs, faces challenges including the erasure of ethnic identity and the pressure to conform, often criticized for promoting cultural homogenization. Structural assimilation, involving integration into social institutions like education, employment, and politics, encounters obstacles like systemic discrimination and social exclusion perpetuating inequality despite superficial inclusion. Both models are critiqued for oversimplifying complex identity processes and ignoring multicultural coexistence, failing to address the persistence of racial and ethnic boundaries within societies.
Implications for Multicultural Societies
Behavioral assimilation emphasizes adopting the cultural norms, language, and social behaviors of the dominant group, which can lead to a loss of cultural identity and reduced diversity in multicultural societies. Structural assimilation involves integration into social institutions such as education, employment, and politics, promoting equal access and participation without necessarily erasing cultural differences. Multicultural societies benefit from balancing these assimilation types by encouraging structural assimilation to foster social cohesion while respecting behavioral diversity to preserve cultural richness.
Behavioral assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com