Your worldview shapes how you interpret experiences, make decisions, and interact with others, forming the foundation of your beliefs and values. Understanding different perspectives helps expand your mindset and fosters empathy in an increasingly diverse world. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your insight into how worldviews influence every aspect of life.
Table of Comparison
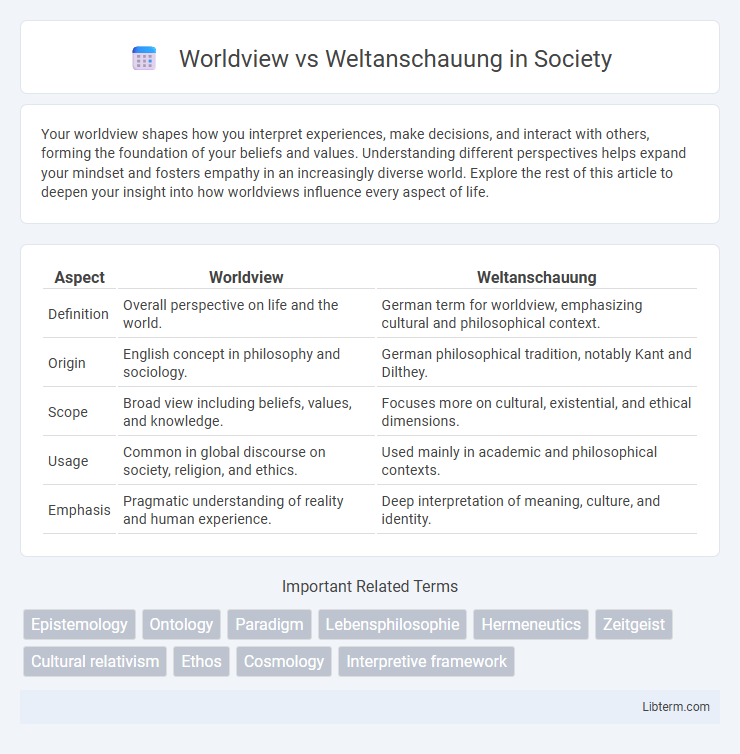
| Aspect | Worldview | Weltanschauung |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall perspective on life and the world. | German term for worldview, emphasizing cultural and philosophical context. |
| Origin | English concept in philosophy and sociology. | German philosophical tradition, notably Kant and Dilthey. |
| Scope | Broad view including beliefs, values, and knowledge. | Focuses more on cultural, existential, and ethical dimensions. |
| Usage | Common in global discourse on society, religion, and ethics. | Used mainly in academic and philosophical contexts. |
| Emphasis | Pragmatic understanding of reality and human experience. | Deep interpretation of meaning, culture, and identity. |
Introduction to Worldview and Weltanschauung
Worldview and Weltanschauung both represent frameworks through which individuals interpret reality, but Weltanschauung originates from German philosophy emphasizing a comprehensive, culturally rooted perception of existence. Worldview encompasses a broader, often cross-cultural analysis of beliefs, values, and experiences shaping an individual's understanding of the world. Understanding these concepts aids in exploring how different societies construct meaning and engage with life's fundamental questions.
Defining 'Worldview': Origins and Usage
Worldview, derived from the German term Weltanschauung, refers to an individual's comprehensive perspective on the world, encompassing beliefs, values, and interpretations of reality. Originating in philosophy and cultural studies, Weltanschauung was first popularized by German philosophers such as Immanuel Kant and Wilhelm Dilthey to describe the framework through which people perceive existence. In contemporary usage, worldview extends beyond philosophy to fields like psychology, anthropology, and theology, emphasizing its role in shaping cognition and behavior across diverse cultures.
Understanding 'Weltanschauung': A Deeper Dive
Weltanschauung, a German term meaning "worldview," encapsulates a comprehensive framework of beliefs, values, and experiences shaping an individual's perception of reality, surpassing the often narrower English interpretation of worldview. This concept integrates cultural, philosophical, and existential dimensions, influencing how one interprets existence, morality, and knowledge. Understanding Weltanschauung requires examining the underlying assumptions and cognitive structures that inform personal and collective perspectives, offering profound insights into human thought and behavior.
Historical Roots of Both Concepts
The historical roots of "Worldview" trace back to the English translation of the German term "Weltanschauung," first introduced in philosophy during the 18th century by Immanuel Kant, referring to a comprehensive perspective on the world. "Weltanschauung," rooted in German philosophical traditions, encompasses a deep cultural and existential framework shaping an individual's perception and interpretation of reality. Both concepts evolved through intellectual history, with Weltanschauung emphasizing a broader cultural and philosophical scope, influencing modern usages of worldview in anthropology, psychology, and sociology.
Linguistic Differences and Semantic Nuances
Worldview and Weltanschauung both describe an individual's comprehensive perspective on reality, but they differ in linguistic and semantic contexts. "Worldview," rooted in English, emphasizes a cognitive framework shaped by cultural, philosophical, and experiential factors, while "Weltanschauung," a German term, carries deeper connotations of an existential and ideological outlook on life. These nuances highlight that Weltanschauung often implies a more profound, implicit belief system embedded within language and culture compared to the broader, more flexible interpretation of worldview.
Philosophical Perspectives on Worldview vs Weltanschauung
Philosophical perspectives on worldview and Weltanschauung highlight nuanced distinctions where worldview refers to an individual's comprehensive cognitive framework for interpreting reality, while Weltanschauung encompasses the deeper, culturally embedded existential attitudes shaping one's understanding of life and the universe. The term Weltanschauung, rooted in German philosophy, particularly in Kant and Hegel, emphasizes a holistic, often communal interpretation of existence, integrating metaphysical and ethical dimensions beyond empirical observation. Contemporary philosophy examines how worldview operates cognitively and pragmatically in global contexts, whereas Weltanschauung retains its connotation of an intrinsic, historically situated philosophical orientation influencing ideology and identity formation.
Cultural Contexts and Global Interpretations
Worldview and Weltanschauung both describe frameworks through which individuals interpret reality, but Weltanschauung carries deeper philosophical and cultural connotations rooted in German intellectual history. In diverse cultural contexts, worldview encompasses broad perceptions influenced by religion, tradition, and societal norms, while Weltanschauung emphasizes an integrated, often existential perspective on human experience. Global interpretations reveal that worldview adapts to multicultural environments as flexible cognitive maps, whereas Weltanschauung persists as a more fixed ideological stance tied to historical and linguistic backgrounds.
Practical Implications in Modern Society
Worldview shapes everyday decisions and social interactions by providing individuals with a framework for interpreting reality, while Weltanschauung offers a deeper philosophical and cultural context influencing collective identity and values. In modern society, understanding the distinctions aids in cross-cultural communication, policymaking, and conflict resolution by addressing both surface-level perspectives and underlying ideological roots. Practical implications include enhanced empathy, improved negotiation strategies, and more effective integration of diverse belief systems within globalized communities.
Comparing and Contrasting Worldview and Weltanschauung
Worldview and Weltanschauung both refer to comprehensive frameworks shaping an individual's perception of reality, but worldview is a broader, more flexible concept often used in English to describe cultural and philosophical perspectives. Weltanschauung, a German term, carries deeper philosophical roots emphasizing an overarching life philosophy that integrates emotions, values, and existential meaning. While worldview can be more descriptive and analytical, Weltanschauung tends to capture a holistic, internalized experience of the world, reflecting a person's ingrained beliefs and attitudes.
Conclusion: Why the Distinction Matters
Understanding the distinction between "worldview" and "Weltanschauung" is crucial for accurately interpreting cultural and philosophical contexts. While "worldview" broadly refers to an individual's or group's comprehensive perspective on life and reality, "Weltanschauung" carries a deeper, more existential and philosophical connotation rooted in German philosophy. Recognizing this difference enhances clarity in cross-cultural communication, academic discourse, and the analysis of diverse belief systems.
Worldview Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com