Microservices architecture breaks down applications into small, independent services that communicate over well-defined APIs, enhancing scalability and flexibility. This approach allows Your development teams to deploy, update, and scale components individually, leading to faster innovation and more resilient systems. Discover how adopting microservices architecture can transform Your software development process by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
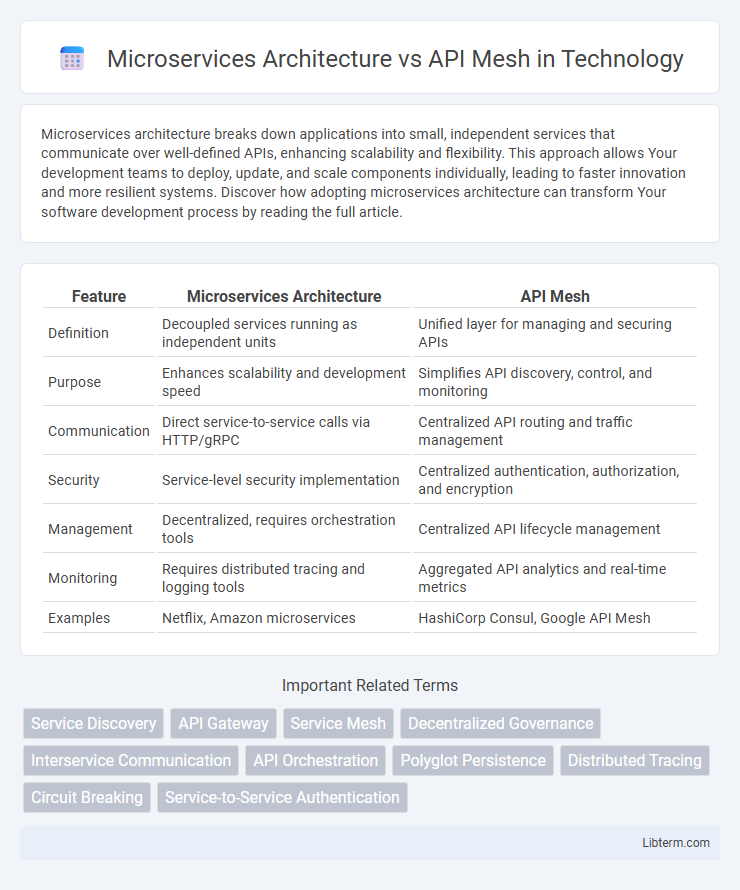
| Feature | Microservices Architecture | API Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decoupled services running as independent units | Unified layer for managing and securing APIs |
| Purpose | Enhances scalability and development speed | Simplifies API discovery, control, and monitoring |
| Communication | Direct service-to-service calls via HTTP/gRPC | Centralized API routing and traffic management |
| Security | Service-level security implementation | Centralized authentication, authorization, and encryption |
| Management | Decentralized, requires orchestration tools | Centralized API lifecycle management |
| Monitoring | Requires distributed tracing and logging tools | Aggregated API analytics and real-time metrics |
| Examples | Netflix, Amazon microservices | HashiCorp Consul, Google API Mesh |
Introduction to Microservices Architecture
Microservices Architecture is a design approach that structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled, independently deployable services, each focused on a specific business capability. This architecture enhances scalability, flexibility, and resilience by allowing teams to develop, deploy, and scale components autonomously. Microservices communicate through lightweight protocols such as HTTP/REST or messaging queues, enabling modular development and faster innovation cycles.
Defining API Mesh: An Overview
API Mesh is a distributed architectural layer that manages and governs APIs across microservices ecosystems, ensuring seamless connectivity, security, and observability. Unlike traditional Microservices Architecture, which focuses on decomposing applications into loosely coupled services, API Mesh centralizes API traffic control, enabling dynamic routing, policy enforcement, and service discovery. This approach enhances scalability and resilience by creating a unified network of APIs that simplifies complex interactions in microservices environments.
Core Principles of Microservices
Microservices architecture emphasizes decentralized services with single-responsibility, autonomous deployment, and independent data management, enabling scalability and fault isolation. Each microservice communicates via lightweight APIs, fostering modularity and continuous delivery. In contrast, API Mesh focuses on managing API communications across services but does not inherently address the core principles of bounded context and service autonomy fundamental to microservices design.
Key Features of API Mesh
API Mesh centralizes API management by providing dynamic routing, service discovery, and advanced security policies across microservices environments. It enhances observability through real-time monitoring and analytics, facilitating faster troubleshooting and performance optimization. Unlike traditional microservices architecture, API Mesh offers seamless scalability and resilience by abstracting API communication layers for consistent service interaction.
Architectural Differences: Microservices vs API Mesh
Microservices architecture decomposes applications into independent, loosely coupled services that communicate via APIs, focusing on modularity and scalability at the service level. API mesh operates as an overlay network managing API communications, providing centralized control, security, and observability without altering the underlying microservices. The architectural difference lies in microservices defining service boundaries and functionality, while API mesh governs the interaction and policy enforcement between these services.
Communication Patterns and Protocols
Microservices architecture relies on lightweight communication protocols like HTTP/REST and gRPC to enable synchronous and asynchronous interactions between independently deployable services, promoting scalability and fault isolation. API mesh, an evolution of service mesh, focuses on managing API-level communication with advanced routing, security, and observability features, often leveraging protocols such as HTTP/HTTPS, gRPC, and WebSockets for more granular control of API traffic. Both approaches emphasize decoupled service communication but differ as microservices architecture centers on service decomposition, while API mesh enhances API communication governance and policy enforcement.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Microservices architecture supports scalability by decomposing applications into independently deployable services, enabling targeted resource allocation and dynamic scaling per service. API mesh enhances performance through intelligent routing, load balancing, and fine-grained traffic management across microservices, optimizing communication latency and reliability. Combined, API mesh provides a robust infrastructure layer that maximizes microservices scalability and performance by ensuring efficient service-to-service interaction and operational observability.
Security Considerations in Both Models
Microservices architecture segments applications into independently deployable services, requiring robust security measures such as mutual TLS, fine-grained access control, and secure service-to-service authentication to protect communication pathways. API Mesh enhances this model by providing a centralized security layer that enforces consistent policies, handles threat detection, and offers end-to-end encryption across diverse APIs, improving visibility and control. Both models demand comprehensive monitoring and compliance strategies, but API Mesh delivers stronger centralized governance and faster incident response for complex ecosystems.
Use Cases and Real-World Implementations
Microservices architecture enables organizations to build scalable, independent services suited for complex applications like e-commerce platforms and financial systems, allowing teams to deploy and update components without affecting the entire system. API Mesh focuses on managing, securing, and monitoring API interactions across microservices, crucial in environments like large enterprises and fintech where API performance and governance are critical. Real-world implementations include Netflix using microservices for content delivery and Airbnb employing API Mesh to improve API observability and security across distributed services.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Microservices architecture emphasizes decomposing applications into independently deployable services to enhance scalability and maintainability, while API mesh focuses on managing and securing interactions between APIs through a dedicated infrastructure layer. Organizations prioritizing rapid development and fine-grained service ownership benefit from microservices, whereas teams needing centralized API governance, observability, and security may prefer an API mesh. Evaluating factors such as team structure, deployment complexity, and integration requirements ensures selecting the optimal approach aligned with organizational goals.
Microservices Architecture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com