Cloud storage offers scalable and secure solutions for storing your data remotely, accessible from any device with an internet connection. It reduces reliance on physical hardware, lowers costs, and ensures data is backed up and protected against loss. Discover how cloud storage can transform your data management by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
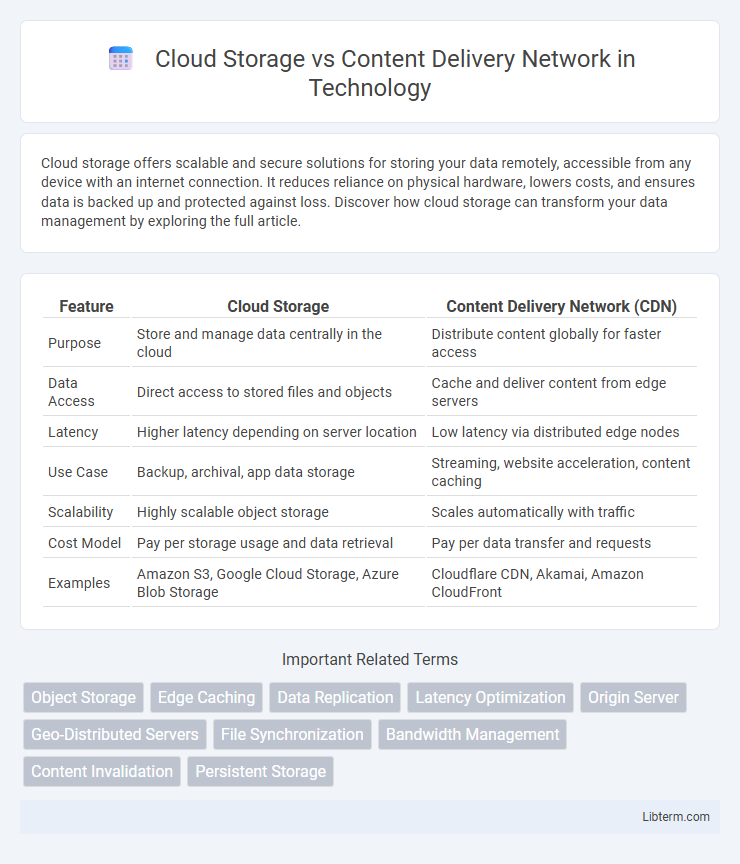
| Feature | Cloud Storage | Content Delivery Network (CDN) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Store and manage data centrally in the cloud | Distribute content globally for faster access |
| Data Access | Direct access to stored files and objects | Cache and deliver content from edge servers |
| Latency | Higher latency depending on server location | Low latency via distributed edge nodes |
| Use Case | Backup, archival, app data storage | Streaming, website acceleration, content caching |
| Scalability | Highly scalable object storage | Scales automatically with traffic |
| Cost Model | Pay per storage usage and data retrieval | Pay per data transfer and requests |
| Examples | Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, Azure Blob Storage | Cloudflare CDN, Akamai, Amazon CloudFront |
Introduction to Cloud Storage and CDN
Cloud Storage provides scalable and secure online storage solutions for data, enabling easy access, backup, and management across devices via cloud infrastructure. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) enhance web performance by distributing cached content through geographically dispersed servers, reducing latency and accelerating load times. Both technologies complement each other, with Cloud Storage holding original data and CDNs optimizing content delivery to end-users worldwide.
Key Differences Between Cloud Storage and CDN
Cloud storage primarily serves as a scalable repository for storing and managing data, enabling users to save files, back up information, and access content from anywhere over the internet. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) focus on delivering cached copies of data from cloud storage or other sources to end-users with high speed and low latency by distributing servers globally. The key differences lie in their functions: cloud storage emphasizes data persistence and centralized management, while CDNs optimize content delivery performance and reduce network load through geographic distribution.
How Cloud Storage Works
Cloud storage works by storing data on remote servers maintained by service providers, enabling users to access and manage files over the internet. Data is uploaded, encrypted, and distributed across multiple physical locations to ensure redundancy, durability, and low latency. This infrastructure supports scalable storage capacity and seamless file synchronization across devices and applications.
How Content Delivery Networks Operate
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) operate by distributing cached content across a globally dispersed network of edge servers, reducing latency by serving data from the server closest to the user's geographic location. They dynamically route requests to the optimal edge server while continuously synchronizing with the origin server to ensure up-to-date content delivery. This distributed system enhances load balancing, accelerates web performance, and improves reliability compared to centralized cloud storage solutions.
Use Cases for Cloud Storage
Cloud storage excels in use cases requiring scalable data archiving, secure backup solutions, and centralized file sharing for remote teams, providing durable and accessible repositories for diverse file types. It supports big data analytics by offering high-capacity storage for raw datasets, enabling efficient processing and retrieval. Enterprises leverage cloud storage for disaster recovery strategies, ensuring vital data remains intact and quickly restorable in case of system failures.
Use Cases for Content Delivery Networks
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) optimize content delivery by caching static and dynamic assets closer to end-users, reducing latency for websites, streaming services, and software downloads. CDNs are ideal for global distribution of high-traffic web content, live video streaming, and accelerating APIs for improved user experience. Compared to traditional cloud storage, CDNs enhance performance and scalability by minimizing server load and handling sudden spikes in traffic efficiently.
Performance Comparison: Cloud Storage vs CDN
Cloud Storage offers scalable and durable data storage optimized for long-term retention but can exhibit higher latency when serving content globally. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) enhance performance by distributing cached content across edge servers near end-users, significantly reducing load times and latency. For applications requiring rapid, geographically distributed content delivery, CDNs outperform Cloud Storage in speed and responsiveness.
Security Considerations: Cloud Storage vs CDN
Cloud storage offers robust security features such as encryption at rest and in transit, access control policies, and compliance certifications tailored for long-term data protection. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) enhance security by providing DDoS mitigation, web application firewalls, and token-based authentication to safeguard content during distribution. While cloud storage secures the data center environment and stored objects, CDNs focus on securing content delivery pathways and reducing attack surfaces closer to the end user.
Cost Comparison of Cloud Storage and CDN Solutions
Cloud storage generally offers lower costs for static data storage with pricing based on the volume of data stored and egress fees for data transfer, making it cost-effective for long-term storage needs. CDNs incur higher expenses due to their distributed network infrastructure, which optimizes content delivery speed by caching content closer to end-users but charges for requests, bandwidth, and geographic distribution. Evaluating usage patterns, such as frequency of data access and required delivery speed, is essential for accurately comparing the cost-efficiency of cloud storage versus CDN solutions.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Cloud storage offers scalable data storage with easy accessibility and cost-effective backup solutions, making it ideal for businesses requiring reliable data management and archival. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) enhance website performance by distributing content geographically, reducing latency, and improving load times for global audiences, which is crucial for businesses with high traffic or international reach. Selecting between cloud storage and CDN depends on whether your priority is secure data storage or fast content delivery to end-users, aligning with your business's operational needs and user experience goals.
Cloud Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com