Crafting effective messaging ensures your brand's voice resonates clearly with your target audience, driving engagement and building trust. Focus on simplicity, relevance, and emotional appeal to connect deeply and convey your core values. Explore the full article to discover strategies for creating impactful messaging that elevates your communication.
Table of Comparison
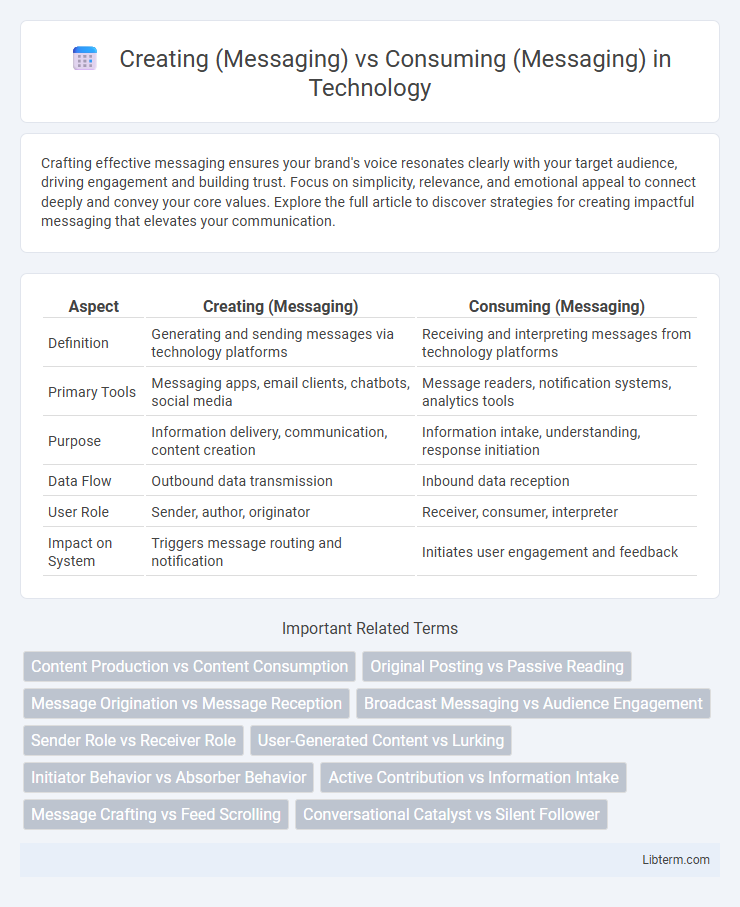
| Aspect | Creating (Messaging) | Consuming (Messaging) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Generating and sending messages via technology platforms | Receiving and interpreting messages from technology platforms |
| Primary Tools | Messaging apps, email clients, chatbots, social media | Message readers, notification systems, analytics tools |
| Purpose | Information delivery, communication, content creation | Information intake, understanding, response initiation |
| Data Flow | Outbound data transmission | Inbound data reception |
| User Role | Sender, author, originator | Receiver, consumer, interpreter |
| Impact on System | Triggers message routing and notification | Initiates user engagement and feedback |
Understanding Messaging: Creation vs Consumption
Messaging creation involves crafting clear, purposeful content that effectively conveys key information to targeted audiences, emphasizing message structure, tone, and relevance. Consuming messaging requires active interpretation, critical analysis, and contextual understanding to extract intended meaning and respond appropriately. Mastery of these processes enhances communication efficiency, ensuring messages are both impactful when created and accurately comprehended when received.
The Psychology Behind Crafting Messages
Crafting messages involves active cognitive engagement, where individuals organize thoughts and emotions to influence perceptions and behaviors, leveraging principles from cognitive psychology and communication theory. Consuming messages triggers interpretative processes shaped by prior knowledge, emotional states, and cognitive biases, affecting message reception and meaning-making. Understanding the psychology behind messaging enhances effectiveness in persuasion, emotional connection, and information retention.
Passive vs Active Engagement in Messaging
Creating messaging involves active engagement where users generate content, express ideas, and initiate conversations, fostering connectivity and personal expression. Consuming messaging reflects passive engagement, as users receive and interpret information without direct contribution, primarily acting as audience members. Balancing these roles enhances communication dynamics by promoting interactive dialogue and information dissemination.
Benefits of Creating Messages
Creating messaging allows for clear, targeted communication that builds brand identity and fosters customer engagement. It enables control over the narrative, ensuring consistent and persuasive messaging that resonates with the audience's needs and preferences. By producing original content, businesses can establish authority, boost SEO rankings, and drive higher conversion rates.
Impact of Consuming Messages on Communication Skills
Consuming messaging enhances communication skills by increasing exposure to diverse language patterns, vocabulary, and cultural contexts, which enriches comprehension and empathy. Regular engagement with varied messaging formats, such as texts, podcasts, and social media, sharpens critical listening and interpretive abilities essential for effective interpersonal communication. However, overconsumption without active reflection can lead to passive understanding, underscoring the importance of balanced interaction for skill development.
Strategies for Effective Message Creation
Effective message creation hinges on clarity, audience understanding, and purpose-driven content tailored to resonate with specific demographics. Employing targeted language, emotional triggers, and concise calls-to-action enhances engagement and message retention. Strategic message design considers platform nuances, ensuring adaptability across channels to maximize impact and foster meaningful consumer interaction.
Challenges in Message Consumption
Challenges in message consumption primarily involve efficiently processing large volumes of data while maintaining low latency and high reliability. Consumers must handle issues such as message duplication, ordering guarantees, and ensuring exactly-once processing semantics to prevent data inconsistencies. Scalability constraints and fault tolerance are critical obstacles that require robust stream processing frameworks like Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ to mitigate failures and maintain continuous data flow.
Balancing Creation and Consumption in Digital Communication
Balancing creation and consumption in digital communication requires understanding the impact of messaging patterns on productivity and mental well-being. Excessive messaging creation can lead to information overload, while overconsumption often causes distraction and reduced focus. Effective digital communication strategies emphasize moderated message generation paired with mindful consumption habits to maintain clarity and reduce cognitive fatigue.
Measuring the Success of Created vs Consumed Messages
Measuring the success of created messaging involves analyzing key performance indicators such as engagement rates, click-through rates, and conversion metrics that directly reflect how effectively messages prompt user actions. In contrast, success in consumed messaging is often evaluated through metrics like message reach, frequency, and audience retention, indicating how well the content is received and retained by the target audience. Employing comprehensive analytics tools enables businesses to compare both created and consumed messaging outcomes, optimizing communication strategies for maximum impact.
Future Trends in Messaging: From Consumers to Creators
Future trends in messaging emphasize a shift from passive consumption to active creation, empowering users to generate personalized content and interactive experiences. Advances in AI-driven messaging platforms enable seamless integration of multimedia, real-time collaboration, and context-aware responses, transforming traditional chat interfaces into dynamic communication ecosystems. This evolution fosters deeper engagement and creativity, positioning users not only as consumers but also as influential creators within digital conversations.
Creating (Messaging) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com