Network isolation enhances security by separating critical systems from less secure networks, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Implementing network segmentation techniques helps contain potential threats and improves traffic management within your infrastructure. Discover effective strategies to safeguard your network by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
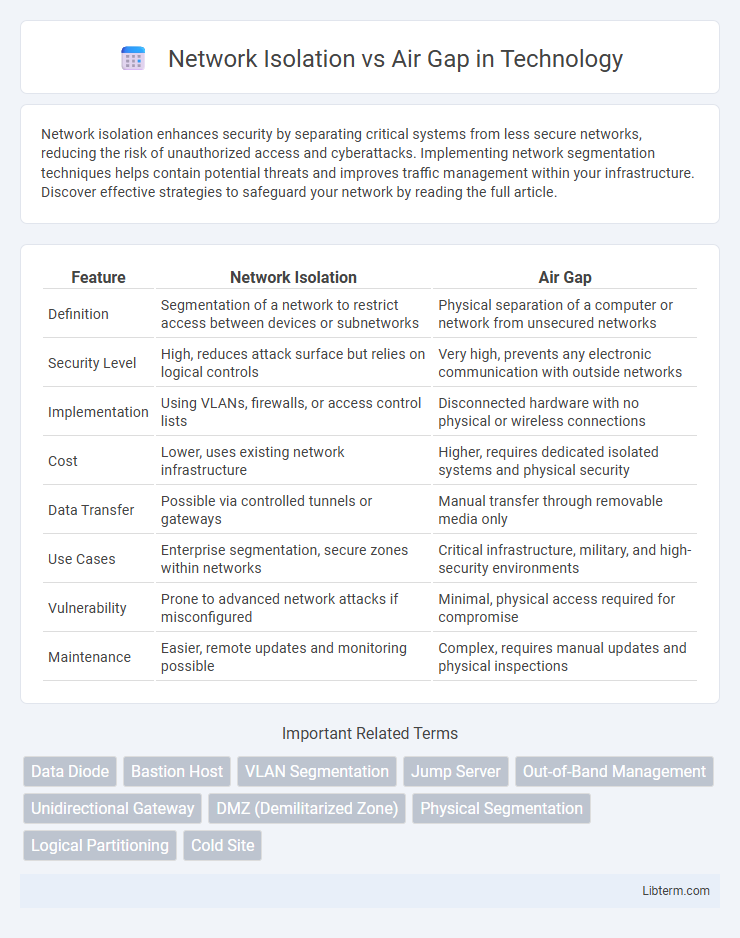
| Feature | Network Isolation | Air Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Segmentation of a network to restrict access between devices or subnetworks | Physical separation of a computer or network from unsecured networks |
| Security Level | High, reduces attack surface but relies on logical controls | Very high, prevents any electronic communication with outside networks |
| Implementation | Using VLANs, firewalls, or access control lists | Disconnected hardware with no physical or wireless connections |
| Cost | Lower, uses existing network infrastructure | Higher, requires dedicated isolated systems and physical security |
| Data Transfer | Possible via controlled tunnels or gateways | Manual transfer through removable media only |
| Use Cases | Enterprise segmentation, secure zones within networks | Critical infrastructure, military, and high-security environments |
| Vulnerability | Prone to advanced network attacks if misconfigured | Minimal, physical access required for compromise |
| Maintenance | Easier, remote updates and monitoring possible | Complex, requires manual updates and physical inspections |
Understanding Network Isolation
Network isolation involves segmenting a network into separate zones to control and restrict traffic flow, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and limiting potential attack surfaces. It uses firewalls, VLANs, and access controls to create boundaries within networks, enabling secure communication while minimizing exposure to threats. Understanding network isolation helps organizations implement effective security policies that balance connectivity needs with robust protection measures.
Defining Air Gap Security
Air gap security is a method of network isolation that physically separates a secure network from unsecured networks, ensuring no direct or wireless connections exist between them. This physical disconnection prevents unauthorized access, data leaks, and cyberattacks by eliminating network pathways that hackers could exploit. Unlike software-based network isolation, air gap security relies on hardware-level separation to create an impermeable barrier for sensitive data environments.
Key Differences Between Network Isolation and Air Gap
Network isolation restricts communications between devices or networks through controlled firewall rules and segmentation, allowing limited, secure data exchange. An air gap physically separates computer systems or networks, eliminating any direct or indirect connections to external networks to prevent unauthorized access. The key difference lies in network isolation permitting configurable connectivity under security policies, whereas an air gap enforces complete, physical disconnection for maximum security.
Use Cases for Network Isolation
Network isolation is commonly used in enterprise environments to segment sensitive systems from the general network, enhancing security by limiting access and reducing the attack surface. It is ideal for protecting critical assets like payment processing systems, internal databases, and development environments where controlled connectivity is necessary for productivity and security compliance. Unlike air gaps, which require complete physical separation, network isolation balances operational efficiency with robust protection by using firewalls, VLANs, and access control lists.
Typical Air Gap Implementation Scenarios
Typical air gap implementation scenarios include high-security environments such as military networks, industrial control systems, and critical infrastructure where sensitive data must be physically separated from unsecured networks to prevent cyber infiltration. Unlike network isolation, which may rely on segmented virtual networks or firewalls, air gaps enforce a physical disconnection between systems, eliminating external access paths. This method is commonly used in safeguarding classified information, preventing ransomware propagation, and securing operational technology (OT) environments from internet-based threats.
Security Advantages of Network Isolation
Network isolation enhances security by segmenting critical systems from general networks, minimizing exposure to cyber threats and unauthorized access. Unlike air gaps, which physically separate networks, network isolation uses controlled access points and firewalls to restrict communication, enabling monitored and managed data flow. This approach reduces the risk of lateral movement by attackers, ensuring sensitive information remains protected within isolated network segments.
Unique Benefits of Air Gap Solutions
Air gap solutions provide unmatched security by physically separating networks, eliminating risks from external cyber threats and unauthorized access. Unlike network isolation, air gaps ensure zero digital connectivity, significantly reducing the attack surface for malware, ransomware, and insider threats. This physical separation is critical for safeguarding highly sensitive environments such as military systems, critical infrastructure, and classified government data.
Challenges of Network Isolation Deployment
Network isolation deployment faces challenges including maintaining secure segmentation without disrupting critical communication between systems, managing complex configuration and ongoing monitoring to prevent unauthorized access, and ensuring scalability while balancing performance limitations caused by stringent network restrictions. Effective network isolation demands continuous policy updates and robust intrusion detection to counter evolving cyber threats. Organizations often struggle with integrating legacy systems that lack compatibility with modern isolation techniques, complicating deployment and increasing maintenance overhead.
Limitations and Risks of Air Gaps
Air gaps, while providing strong physical separation from external networks, suffer from significant limitations including the challenge of manual data transfers, which increase the risk of human error and insider threats. They do not fully eliminate security risks, as sophisticated malware can exploit infected removable media to breach isolated systems. Additionally, air gaps impede real-time monitoring and updates, leading to potential delays in detecting and responding to emerging cyber threats.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Choosing between network isolation and air gap depends on your organization's security needs and operational requirements. Network isolation segments critical systems within a controlled environment to limit exposure while maintaining necessary communication, making it suitable for businesses that require operational flexibility and moderate security. In contrast, an air gap physically disconnects systems from any network, offering the highest level of security ideal for organizations handling extremely sensitive data or mission-critical infrastructure where absolute protection from cyber threats is essential.
Network Isolation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com