Data mapping transforms diverse data sources into a unified format, ensuring accuracy and consistency across systems. This process is essential for seamless data integration, migration, and analytics, improving decision-making and operational efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to understand how effective data mapping can enhance your data management strategies.
Table of Comparison
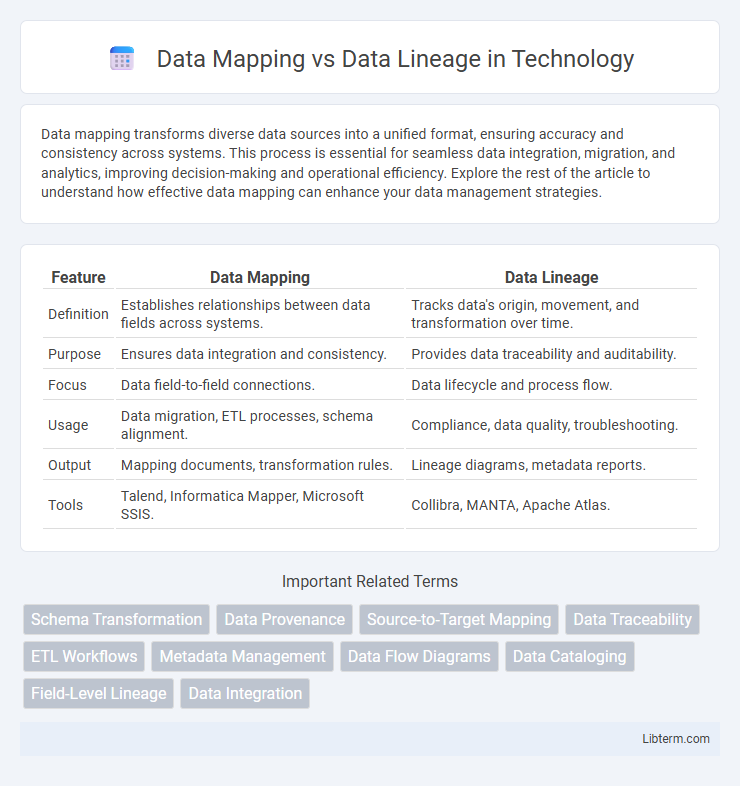
| Feature | Data Mapping | Data Lineage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Establishes relationships between data fields across systems. | Tracks data's origin, movement, and transformation over time. |
| Purpose | Ensures data integration and consistency. | Provides data traceability and auditability. |
| Focus | Data field-to-field connections. | Data lifecycle and process flow. |
| Usage | Data migration, ETL processes, schema alignment. | Compliance, data quality, troubleshooting. |
| Output | Mapping documents, transformation rules. | Lineage diagrams, metadata reports. |
| Tools | Talend, Informatica Mapper, Microsoft SSIS. | Collibra, MANTA, Apache Atlas. |
Introduction to Data Mapping and Data Lineage
Data mapping involves creating connections between data fields from different sources to facilitate integration, transformation, and migration processes. Data lineage provides a detailed visualization of data's origin, journey, and transformations across the entire data lifecycle, ensuring transparency and traceability. Understanding both concepts is essential for effective data governance, quality control, and compliance in enterprise data management.
Understanding Data Mapping
Data mapping involves the process of matching fields from one database to another to ensure accurate data integration, transformation, and migration. It is critical for maintaining data consistency, enabling efficient data warehousing, and supporting ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations. Understanding data mapping helps organizations streamline data workflows, improve data quality, and enhance interoperability between disparate data systems.
Understanding Data Lineage
Data lineage provides a comprehensive visualization of the data's journey from its origin through all transformations, enabling organizations to track data flow and ensure accuracy and compliance. Unlike data mapping, which defines relationships between data elements across systems, data lineage offers detailed insights into how data is processed, transformed, and utilized throughout its lifecycle. This granular tracking aids in impact analysis, debugging, and regulatory reporting, making data lineage critical for data governance and trust.
Key Differences Between Data Mapping and Data Lineage
Data mapping involves creating relationships between data fields from different sources to enable accurate data integration and transformation, while data lineage tracks the life cycle of data by documenting its origin, movement, and changes across systems. Key differences include their primary purposes: data mapping focuses on defining how data elements correspond across databases, whereas data lineage emphasizes transparency and traceability of data flow for governance and compliance. Data mapping is often a preliminary step facilitating integration processes, whereas data lineage provides ongoing visibility into data's journey, supporting impact analysis and troubleshooting.
Benefits of Data Mapping
Data mapping enhances data integration by translating disparate data formats into a unified structure, improving data consistency and accuracy across systems. It streamlines data migration and transformation processes, reducing errors and accelerating project timelines. This clarity enables better decision-making by providing a clear understanding of data sources and destination relationships.
Benefits of Data Lineage
Data Lineage provides a comprehensive view of data flow from its origin to consumption, enabling organizations to ensure data accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA. It enhances data governance by identifying data transformations, dependencies, and quality issues, facilitating faster impact analysis and error resolution. Clear visibility into data lineage supports better decision-making and trust in data assets across the enterprise.
Common Use Cases for Data Mapping
Data mapping is commonly used for data integration, migration, and transformation projects, enabling seamless data flow between disparate systems by establishing relationships between source and target data elements. It plays a critical role in data quality management by ensuring consistent data interpretation across platforms and facilitating compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Data lineage, while focused on tracking the data life cycle and its transformations, complements data mapping by providing visibility into data origin, movement, and modification within complex data environments.
Common Use Cases for Data Lineage
Data lineage is crucial for regulatory compliance, enabling organizations to trace data flow and transformations to meet standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. It supports impact analysis by helping data engineers and analysts understand how changes in data sources affect downstream systems and reports. Data lineage also enhances data governance through transparency, improving data quality and trust across business intelligence and analytics processes.
Tools and Technologies for Data Mapping and Lineage
Data mapping tools like Talend, Informatica PowerCenter, and Mulesoft facilitate the transformation and integration of data between disparate systems by defining source-to-target relationships. For data lineage, solutions such as Apache Atlas, Collibra, and Microsoft Purview provide comprehensive tracking and visualization of data flow and transformations across the data lifecycle. These technologies enhance data governance by ensuring accuracy, compliance, and transparency through automated metadata management and impact analysis.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Selecting between data mapping and data lineage depends on your organization's data governance goals and operational needs. Data mapping excels at defining data relationships and transformations for integration and migration projects, while data lineage provides comprehensive tracking of data flow and changes for compliance and auditability. Prioritize data lineage if regulatory transparency and impact analysis are critical, whereas data mapping suits scenarios prioritizing data structure alignment and system interconnectivity.
Data Mapping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com