DNS Round Robin is a load balancing technique that distributes client requests across multiple servers by rotating the order of IP addresses returned in DNS responses. This method helps improve redundancy and availability by spreading traffic evenly, but it does not account for server health or real-time load. Discover how implementing DNS Round Robin can optimize your network performance and ensure consistent service by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
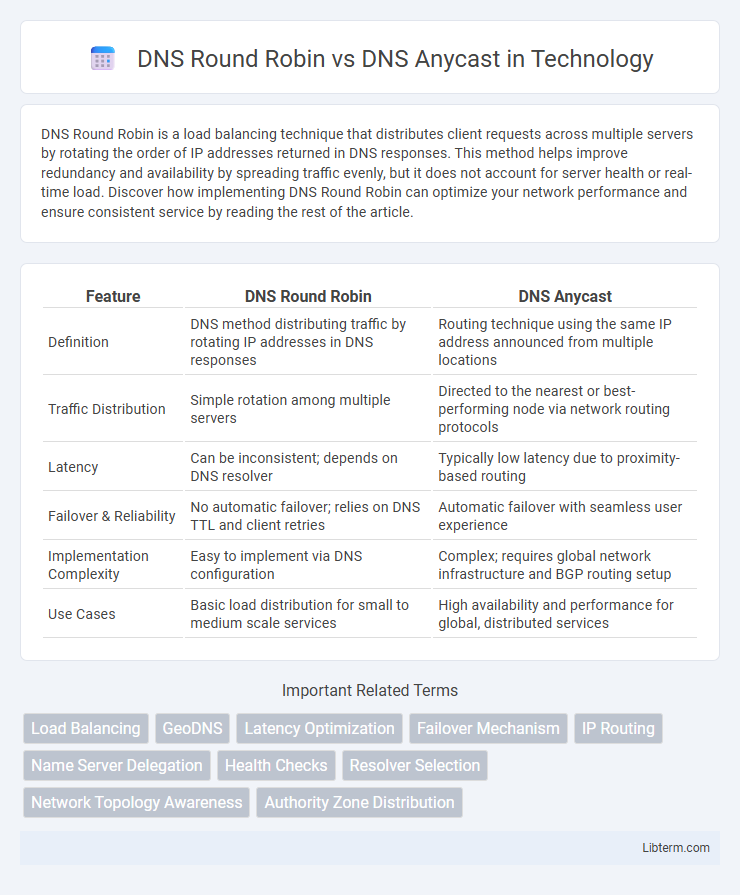
| Feature | DNS Round Robin | DNS Anycast |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | DNS method distributing traffic by rotating IP addresses in DNS responses | Routing technique using the same IP address announced from multiple locations |
| Traffic Distribution | Simple rotation among multiple servers | Directed to the nearest or best-performing node via network routing protocols |
| Latency | Can be inconsistent; depends on DNS resolver | Typically low latency due to proximity-based routing |
| Failover & Reliability | No automatic failover; relies on DNS TTL and client retries | Automatic failover with seamless user experience |
| Implementation Complexity | Easy to implement via DNS configuration | Complex; requires global network infrastructure and BGP routing setup |
| Use Cases | Basic load distribution for small to medium scale services | High availability and performance for global, distributed services |
Introduction to DNS Load Balancing
DNS load balancing improves website performance and reliability by distributing traffic across multiple servers. Round Robin DNS cycles through a list of IP addresses, assigning user requests in a rotating order, which is simple but can lead to uneven load distribution. DNS Anycast routes users to the nearest or best-performing server using identical IP addresses advertised from multiple locations, optimizing latency and fault tolerance.
What is DNS Round Robin?
DNS Round Robin is a load balancing technique that distributes client requests by cycling through a list of multiple IP addresses associated with a single domain name. It operates by returning different IP addresses in a sequential order for each DNS query, helping to evenly spread traffic across several servers. This method is simple to implement but lacks health checks, potentially directing traffic to non-responsive servers.
How DNS Anycast Works
DNS Anycast improves global site performance by routing user requests to the nearest available DNS server using identical IP addresses advertised from multiple locations across the internet. This routing relies on internet routing protocols like BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) to direct queries to the topologically closest server, minimizing latency and enhancing redundancy. Unlike DNS Round Robin, which cycles through a list of IPs in a fixed sequence, DNS Anycast dynamically manages traffic flow to optimize speed and reliability in real-time.
Key Differences Between Round Robin and Anycast
DNS Round Robin distributes incoming requests by rotating through a list of multiple IP addresses assigned to a single domain, providing simple load balancing without geographic awareness. DNS Anycast routes user queries to the nearest or most optimal server based on network topology, enhancing performance and redundancy through intelligent traffic direction. Unlike Round Robin, Anycast offers improved fault tolerance and lower latency by leveraging the global internet routing infrastructure.
Performance Comparison: Round Robin vs Anycast
DNS Round Robin distributes traffic evenly by rotating IP addresses in DNS responses, which can lead to inconsistent performance due to varying server loads and geographical latency. DNS Anycast routes user queries to the nearest or best-performing server through the network layer, significantly improving response times and reducing latency by leveraging multiple global locations. Performance-wise, Anycast offers superior reliability and faster connections compared to Round Robin by dynamically directing traffic based on real-time network conditions rather than static DNS responses.
Reliability and Failover Considerations
DNS Round Robin distributes traffic evenly across multiple servers by cycling through a list of IP addresses, improving load balancing but lacking automatic failover detection, which can result in requests being sent to unresponsive servers. DNS Anycast assigns the same IP address to multiple geographically dispersed servers, routing users to the nearest or best-performing node, enhancing reliability through automatic failover and reduced latency. For critical applications requiring seamless failover and high availability, DNS Anycast offers superior resilience compared to the simpler, less fail-safe Round Robin approach.
Security Implications of DNS Round Robin and Anycast
DNS Round Robin distributes traffic evenly across multiple servers by rotating IP addresses, but it lacks built-in security mechanisms, making it vulnerable to DNS spoofing and amplification attacks. DNS Anycast provides enhanced security by directing user requests to the nearest or healthiest server via shared IP addresses, reducing the attack surface and improving resilience against DDoS attacks. Anycast's ability to quickly reroute traffic during attacks offers superior protection compared to Round Robin's static, cyclical distribution method.
Use Cases for DNS Round Robin
DNS Round Robin is ideal for load balancing across multiple servers hosting identical services, ensuring even distribution of client requests in small to medium-sized networks with moderate traffic. It suits scenarios where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are priorities, such as basic web hosting environments or internal corporate networks. Round Robin provides resilience by cycling through a list of IP addresses, but lacks intelligent routing or proximity-based delivery, making it less suitable for global or geo-distributed applications compared to DNS Anycast.
When to Choose DNS Anycast
DNS Anycast is ideal for global services requiring low latency and high availability by routing user requests to the nearest or best-performing data center through identical IP addresses advertised from multiple locations. Choose DNS Anycast when effective DDoS mitigation, improved fault tolerance, and consistent user experience across widespread geographical areas are critical. Unlike DNS Round Robin, which distributes traffic in a simple, cyclical manner without geographic consideration, Anycast intelligently directs queries to optimize performance and reliability.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right DNS Strategy
Choosing between DNS Round Robin and DNS Anycast depends on specific performance and redundancy needs. DNS Round Robin offers straightforward load distribution across multiple servers, ideal for simple, regional setups, while DNS Anycast provides faster global resolution and enhanced fault tolerance by routing queries to the nearest data center. Evaluating traffic patterns, geographic spread, and reliability requirements ensures the optimal DNS architecture for scalable and efficient network performance.
DNS Round Robin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com