Mobile computing enables seamless access to information and applications anytime and anywhere, using portable devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops. It integrates wireless networks, cloud services, and real-time data processing to enhance productivity and communication on the go. Discover how mobile computing can transform your work and lifestyle by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
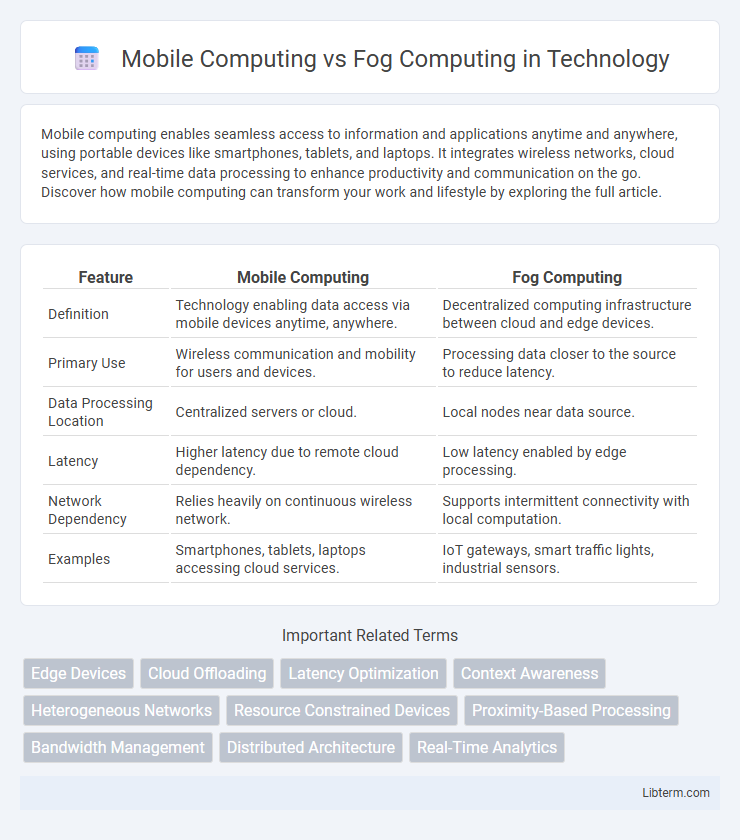
| Feature | Mobile Computing | Fog Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology enabling data access via mobile devices anytime, anywhere. | Decentralized computing infrastructure between cloud and edge devices. |
| Primary Use | Wireless communication and mobility for users and devices. | Processing data closer to the source to reduce latency. |
| Data Processing Location | Centralized servers or cloud. | Local nodes near data source. |
| Latency | Higher latency due to remote cloud dependency. | Low latency enabled by edge processing. |
| Network Dependency | Relies heavily on continuous wireless network. | Supports intermittent connectivity with local computation. |
| Examples | Smartphones, tablets, laptops accessing cloud services. | IoT gateways, smart traffic lights, industrial sensors. |
Introduction to Mobile Computing and Fog Computing
Mobile computing enables seamless access to data and applications through wireless devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, supporting real-time communication and remote work. Fog computing extends cloud capabilities by processing data closer to the source via edge nodes, reducing latency and bandwidth usage in IoT and mobile networks. Both technologies optimize connectivity and computing power, yet fog computing enhances mobile computing by offering localized data processing for improved efficiency and faster response times.
Core Principles of Mobile Computing
Mobile computing centers on enabling seamless access to computing resources and data through portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, emphasizing wireless communication and continuous connectivity. Core principles include mobility support, ubiquitous access, and real-time data processing, ensuring devices can operate effectively regardless of location. In contrast, fog computing extends cloud capabilities closer to the data source, focusing on low latency, local processing, and distributed network architecture to improve efficiency and responsiveness.
Core Principles of Fog Computing
Fog computing extends cloud capabilities by decentralizing data processing closer to the network edge, enabling reduced latency and enhanced real-time analytics compared to mobile computing. It operates on core principles such as geographical distribution, location awareness, and support for mobility, which collectively optimize resource utilization and improve response times for IoT applications. By integrating computing, storage, and networking functions into local nodes, fog computing provides scalable, low-latency services essential for time-sensitive and bandwidth-intensive tasks.
Architecture: Mobile vs Fog Computing
Mobile computing architecture centers on devices such as smartphones and tablets that rely on wireless networks to access cloud services, emphasizing real-time data processing at the endpoint. Fog computing architecture extends cloud capabilities by distributing computing, storage, and networking resources closer to data sources through fog nodes, reducing latency and improving efficiency. This decentralized structure enhances support for Internet of Things (IoT) applications by enabling localized analytics and faster decision-making compared to traditional mobile computing frameworks.
Data Processing and Storage Capabilities
Mobile computing relies on cloud servers for extensive data processing and storage, which can cause latency and dependence on network connectivity. Fog computing decentralizes data processing by distributing storage and computation closer to the data source, enabling real-time analytics and reducing bandwidth usage. This local processing capability enhances response times and supports IoT applications requiring immediate decision-making.
Latency and Real-Time Processing
Mobile computing often experiences higher latency due to reliance on centralized cloud data centers, which can delay real-time processing tasks. Fog computing reduces latency by distributing computing resources closer to the data source at the network edge, enabling faster decision-making and real-time analytics. This edge-centric approach enhances responsiveness for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities, where immediate data processing is critical.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Mobile computing relies on centralized cloud servers, which can expose data to risks during transmission and storage, making end-to-end encryption and secure authentication critical. Fog computing processes data closer to the network edge, reducing latency and minimizing exposure by limiting data sent to the cloud, thus enhancing privacy and enabling localized security controls. Both paradigms require robust access management and continuous monitoring to protect against evolving threats and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Use Cases and Practical Applications
Mobile computing enables real-time data access and processing on smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices, supporting use cases like remote healthcare, field workforce management, and location-based services. Fog computing extends cloud capabilities by processing data closer to the source with edge devices, enhancing applications such as smart traffic management, industrial IoT monitoring, and autonomous vehicle coordination. Both technologies optimize data handling in distributed environments but cater to different latency and bandwidth requirements across sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
Performance Comparison: Mobile vs Fog Computing
Mobile computing relies on wireless networks and limited device resources, often resulting in higher latency and lower processing power compared to fog computing. Fog computing extends cloud capabilities by processing data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time performance for latency-sensitive applications. This localized data handling significantly enhances response times and bandwidth efficiency compared to traditional mobile computing frameworks.
Future Trends in Mobile and Fog Computing
Future trends in mobile computing emphasize edge AI integration and enhanced 5G capabilities, enabling real-time data processing and augmented reality applications. Fog computing is evolving with advanced distributed architectures and stronger security protocols, fostering low-latency analytics and IoT scalability. Convergence of mobile and fog computing will drive smarter environments through seamless resource management and adaptive network infrastructures.
Mobile Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com