Serverless architecture allows you to build and run applications without managing servers, enabling automatic scaling and reduced operational costs. This approach enhances agility and accelerates deployment by focusing on code rather than infrastructure. Explore the rest of the article to understand how serverless architecture can transform your development process.
Table of Comparison
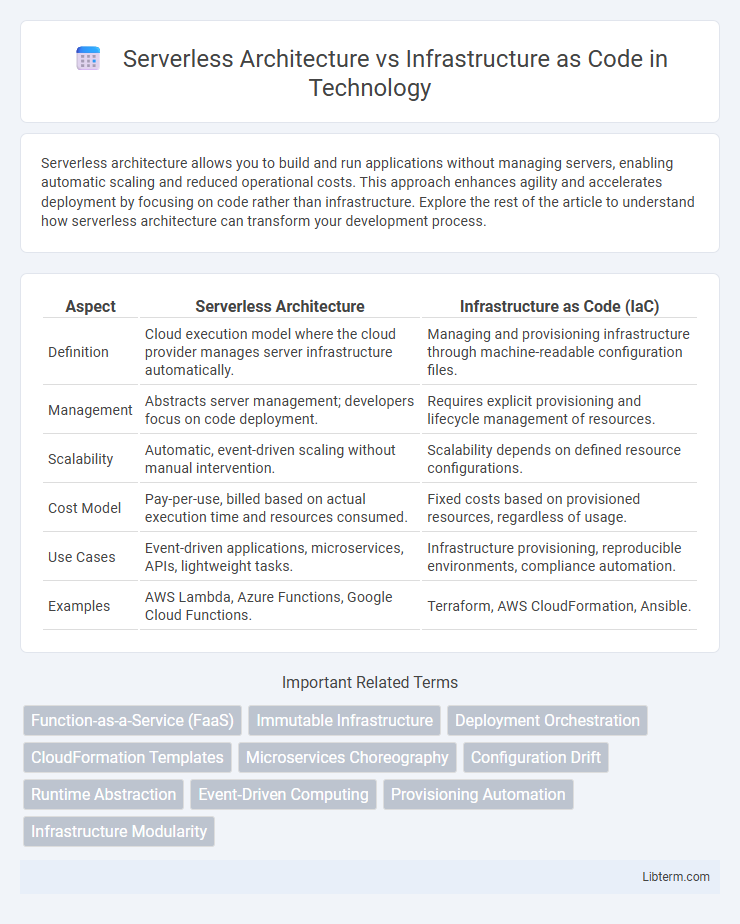
| Aspect | Serverless Architecture | Infrastructure as Code (IaC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud execution model where the cloud provider manages server infrastructure automatically. | Managing and provisioning infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files. |
| Management | Abstracts server management; developers focus on code deployment. | Requires explicit provisioning and lifecycle management of resources. |
| Scalability | Automatic, event-driven scaling without manual intervention. | Scalability depends on defined resource configurations. |
| Cost Model | Pay-per-use, billed based on actual execution time and resources consumed. | Fixed costs based on provisioned resources, regardless of usage. |
| Use Cases | Event-driven applications, microservices, APIs, lightweight tasks. | Infrastructure provisioning, reproducible environments, compliance automation. |
| Examples | AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions. | Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, Ansible. |
Understanding Serverless Architecture
Serverless architecture enables developers to build and deploy applications without managing underlying servers, relying on cloud providers like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions to handle infrastructure automatically. This model scales seamlessly based on demand, reduces operational overhead, and optimizes cost by charging only for actual usage. Understanding serverless architecture involves recognizing its event-driven nature, stateless compute functions, and decoupled services that simplify application development and accelerate deployment cycles.
What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is a practice that automates the provisioning and management of computing infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files, replacing manual setup processes. IaC enables consistent, repeatable deployments by defining infrastructure components such as servers, networks, and storage in code, often using tools like Terraform, AWS CloudFormation, or Ansible. Unlike serverless architecture, which abstracts infrastructure management entirely, IaC provides granular control over resources while promoting scalability and automation within cloud environments.
Key Differences Between Serverless and IaC
Serverless architecture abstracts server management by automatically handling infrastructure scaling, resource allocation, and maintenance, allowing developers to focus solely on code deployment. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) involves defining and provisioning physical or virtual infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files, enabling consistent and repeatable environment setups. The key difference lies in serverless providing a fully managed runtime environment, while IaC requires explicit infrastructure configuration and management to deploy applications.
Benefits of Serverless Architecture
Serverless architecture provides significant benefits such as automatic scaling, cost efficiency by charging only for actual usage, and reduced operational complexity by eliminating server management. It enables developers to focus on writing code without worrying about infrastructure provisioning or maintenance. The inherent event-driven model enhances responsiveness and accelerates deployment cycles compared to Infrastructure as Code (IaC), which primarily manages infrastructure automation but still requires resource provisioning and scaling.
Advantages of Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) offers significant advantages by automating the provisioning and management of cloud resources, ensuring consistency and reducing human error. It enables version control of infrastructure configurations, facilitating collaboration and rollback capabilities. IaC enhances scalability and reproducibility, making it easier to deploy complex environments across multiple stages and regions.
Scalability: Serverless vs IaC
Serverless architecture inherently provides automatic scalability by dynamically allocating resources based on demand without manual intervention, ensuring optimal performance during traffic spikes. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) facilitates scalability through automated provisioning and management of infrastructure resources, enabling consistent and repeatable scaling processes across environments. Serverless excels in abstracting infrastructure management for seamless scaling, while IaC offers granular control ideal for complex, customizable scaling strategies.
Cost Considerations for Serverless and IaC
Serverless Architecture significantly reduces operational costs by eliminating the need for server provisioning and maintenance, charging users based on actual usage and scaling automatically to meet demand. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) streamlines infrastructure deployment and management, enabling cost optimization through automation, version control, and repeatable environments, but requires upfront investment in configuration and ongoing maintenance. Cost considerations for Serverless focus on pay-per-execution pricing models, while IaC emphasizes reducing manual overhead and preventing configuration drift to avoid unexpected expenses.
Security Implications: Serverless vs IaC
Serverless architecture minimizes attack surfaces by abstracting server management and automatically handling patching, reducing risks associated with manual configurations. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enhances security through consistent, repeatable provisioning of environments, enabling version-controlled policies and automated compliance checks. Combining serverless with IaC allows teams to enforce security best practices programmatically, ensuring scalability while maintaining robust access controls and vulnerability management.
Use Cases: When to Choose Serverless or IaC
Serverless architecture excels in event-driven applications such as real-time data processing, chatbots, and microservices where automatic scaling and reduced operational overhead are critical. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is ideal for complex environments requiring consistent, repeatable deployments, version control, and detailed infrastructure management in multi-cloud or hybrid cloud scenarios. Organizations should choose serverless for rapid development and reduced maintenance, while IaC suits projects needing precise control over resources, compliance, and extensive customization.
Future Trends in Cloud Deployment Approaches
Serverless architecture offers dynamic scaling and cost-efficiency by abstracting server management, while Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enhances automation and consistency in provisioning cloud resources. Future trends indicate growing integration of serverless frameworks with IaC tools like Terraform and AWS CloudFormation to streamline deployment pipelines and enhance operational agility. Advances in AI-driven optimization and hybrid cloud strategies will further drive adoption, enabling more intelligent resource allocation and seamless multi-cloud management.
Serverless Architecture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com