Polyrepo is a strategy for managing multiple repositories in a single development environment, allowing teams to streamline collaboration and maintain codebases independently. This approach enhances scalability, improves version control, and reduces the complexity of dependencies across projects. Discover how incorporating polyrepo can transform your development workflow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
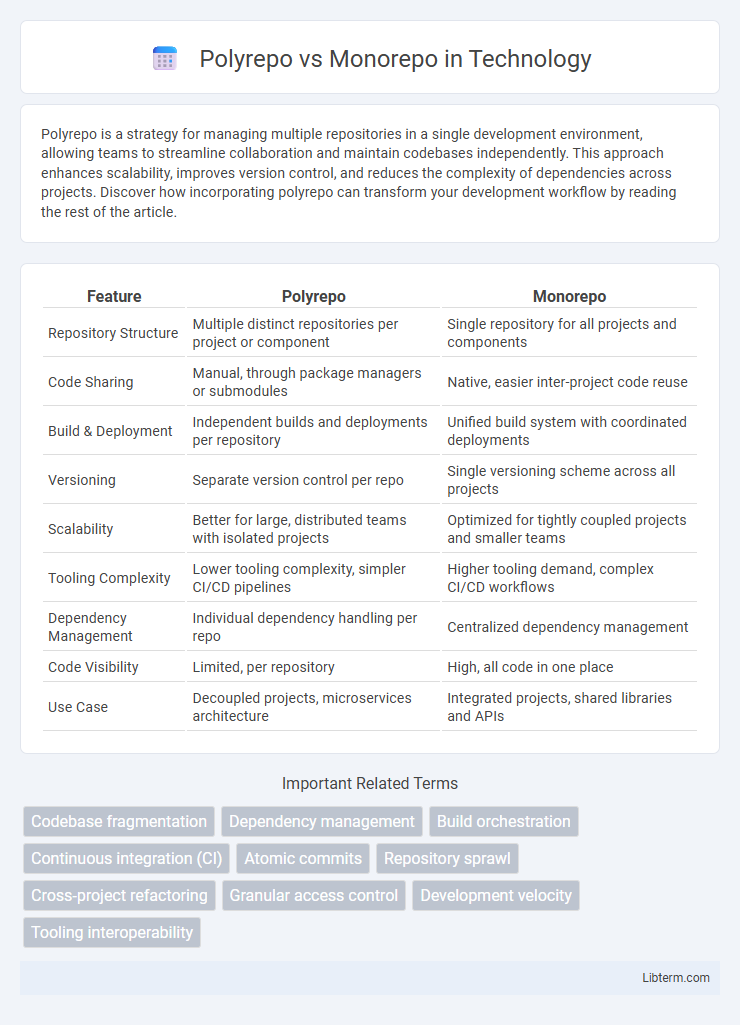
| Feature | Polyrepo | Monorepo |
|---|---|---|
| Repository Structure | Multiple distinct repositories per project or component | Single repository for all projects and components |
| Code Sharing | Manual, through package managers or submodules | Native, easier inter-project code reuse |
| Build & Deployment | Independent builds and deployments per repository | Unified build system with coordinated deployments |
| Versioning | Separate version control per repo | Single versioning scheme across all projects |
| Scalability | Better for large, distributed teams with isolated projects | Optimized for tightly coupled projects and smaller teams |
| Tooling Complexity | Lower tooling complexity, simpler CI/CD pipelines | Higher tooling demand, complex CI/CD workflows |
| Dependency Management | Individual dependency handling per repo | Centralized dependency management |
| Code Visibility | Limited, per repository | High, all code in one place |
| Use Case | Decoupled projects, microservices architecture | Integrated projects, shared libraries and APIs |
Introduction to Polyrepo and Monorepo
Polyrepo architecture organizes source code into multiple distinct repositories, allowing teams to manage projects independently with clear boundaries and tailored versioning. Monorepo consolidates all codebases into a single repository, enabling streamlined dependency management and unified version control but potentially increasing complexity in large-scale environments. Choosing between polyrepo and monorepo depends on factors like team size, project dependencies, and deployment workflows for optimized development efficiency.
Understanding the Polyrepo Model
The polyrepo model organizes codebases into multiple independent repositories, each dedicated to a specific project or component. This structure enhances modularity by isolating development workflows, allowing teams to work autonomously without the overhead of unrelated code. Polyrepo setups simplify version control and reduce build times by limiting the scope to single repositories, improving scalability for large organizations with diverse projects.
Exploring the Monorepo Architecture
Monorepo architecture consolidates multiple projects into a single repository, enabling streamlined dependency management and code sharing across teams. This approach improves refactoring efficiency and simplifies integration testing by maintaining a unified version history. Large organizations like Google and Facebook leverage monorepos to enhance collaboration and maintain consistency in their complex codebases.
Key Differences Between Polyrepo and Monorepo
Polyrepo organizes codebases into multiple independent repositories, enabling isolated development, versioning, and deployment cycles per project, which enhances modularity and simplifies access control. Monorepo consolidates all projects into a single repository, facilitating code sharing, unified dependency management, and streamlined refactoring across teams. Key differences include repository structure, scalability, build complexity, and the impact on collaboration workflows and continuous integration pipelines.
Benefits of Using Polyrepo
Polyrepo architecture offers enhanced modularity, enabling teams to work independently on separate repositories, which reduces codebase complexity and minimizes merge conflicts. This approach improves security by isolating projects, limiting the potential impact of vulnerabilities to individual repositories. Polyrepo also facilitates targeted version control and deployment strategies, allowing faster updates and easier rollback for specific components without affecting the entire system.
Advantages of Adopting Monorepo
Monorepo offers streamlined dependency management by centralizing all codebases into a single repository, simplifying versioning and integration. It enhances collaboration across teams through unified code visibility and consistent development practices, reducing duplication and conflicts. Centralized tooling in monorepos enables efficient code refactoring, testing, and deployment, accelerating release cycles and improving overall productivity.
Common Challenges with Polyrepo
Polyrepo setups often face challenges such as maintaining consistency across multiple repositories, which can lead to fragmented codebases and duplicated dependencies. Managing version control and coordinating updates becomes complex, increasing the risk of integration errors and inefficient collaboration. These issues can slow down development workflows compared to unified environments like monorepos.
Typical Issues Faced in Monorepo Setups
Monorepo setups often encounter challenges such as complex dependency management, slower build and test cycles due to the vast codebase, and difficulty in scaling version control systems for large teams. Conflicts from simultaneous changes by multiple developers can lead to integration bottlenecks and increased merge conflicts. Additionally, maintaining clear boundaries between projects within a monorepo requires strict governance and tooling to avoid code entanglement and technical debt.
Decision Criteria: Choosing Polyrepo or Monorepo
Choosing between polyrepo and monorepo depends primarily on team size, project complexity, and deployment frequency. Monorepos excel in environments with tightly integrated services, enabling consistent dependency management and atomic commits across projects. Polyrepos suit decentralized teams needing autonomy, supporting distinct versioning and isolated deployments for independent services or modules.
Best Practices for Repository Management
Effective repository management in polyrepo setups involves clear modularization, maintaining strict version control per repository, and using automated CI/CD pipelines tailored to individual components. In monorepo environments, best practices include enforcing consistent coding standards across all projects, implementing robust dependency management, and leveraging build tools that optimize incremental builds to reduce integration times. Both approaches benefit from thorough documentation, regular code reviews, and synchronized release processes to ensure code quality and streamline collaboration among diverse teams.
Polyrepo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com