Data federation integrates data from multiple sources into a unified view without moving the data physically, enabling real-time access and analysis. This approach simplifies data management and enhances decision-making by providing a single point of query for distributed information. Explore the rest of the article to discover how data federation can optimize your data strategy.
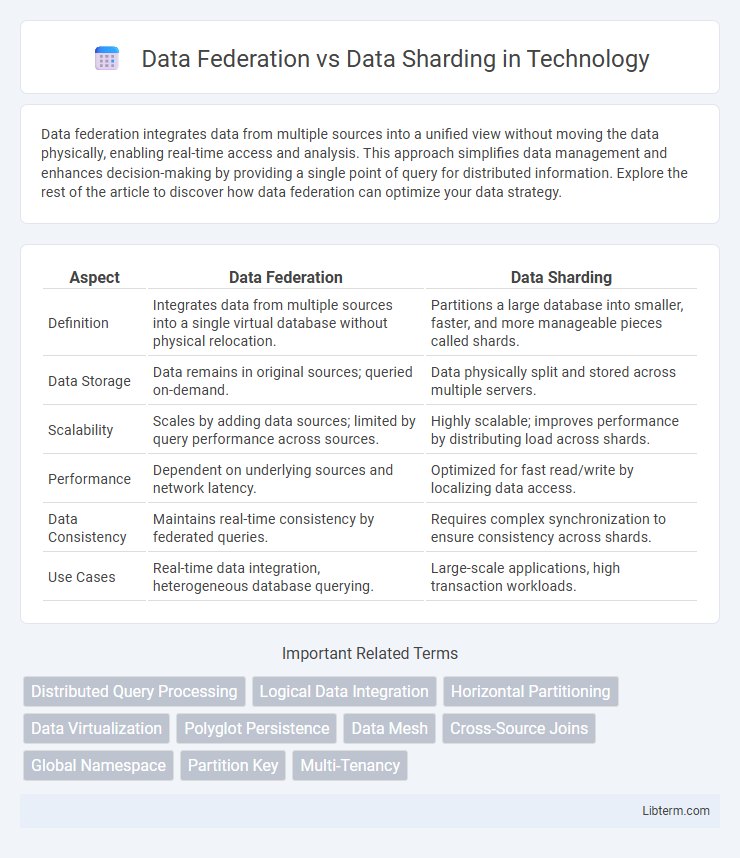
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Data Federation | Data Sharding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates data from multiple sources into a single virtual database without physical relocation. | Partitions a large database into smaller, faster, and more manageable pieces called shards. |
| Data Storage | Data remains in original sources; queried on-demand. | Data physically split and stored across multiple servers. |
| Scalability | Scales by adding data sources; limited by query performance across sources. | Highly scalable; improves performance by distributing load across shards. |
| Performance | Dependent on underlying sources and network latency. | Optimized for fast read/write by localizing data access. |
| Data Consistency | Maintains real-time consistency by federated queries. | Requires complex synchronization to ensure consistency across shards. |
| Use Cases | Real-time data integration, heterogeneous database querying. | Large-scale applications, high transaction workloads. |
Understanding Data Federation: An Overview
Data federation enables real-time access to data distributed across multiple heterogeneous sources without physically moving or replicating it, enhancing data integration and reducing latency. It creates a unified virtual view that allows users to query multiple databases as if they were a single repository, streamlining analytics and reporting processes. This approach contrasts with data sharding, which partitions data into smaller segments stored across separate databases, focusing on horizontal scalability and performance optimization.
What Is Data Sharding? Key Concepts
Data sharding is a database partitioning technique that divides large datasets into smaller, manageable pieces called shards, each stored on separate servers to improve performance and scalability. Key concepts include horizontal partitioning, where each shard holds a subset of rows from a table, distributed data management to balance load, and shard key selection that determines data distribution across shards. Data sharding enhances query efficiency and fault tolerance by isolating data segments, minimizing contention in distributed systems.
Core Differences Between Data Federation and Data Sharding
Data federation integrates data from multiple sources into a unified view without physically consolidating it, enabling real-time access and querying across diverse databases. Data sharding partitions a large database into smaller, more manageable pieces called shards, each hosted on separate servers to improve scalability and performance. The core difference lies in federation's virtual data aggregation versus sharding's physical data distribution to enhance system efficiency.
Use Cases: When to Choose Data Federation
Data federation is ideal for environments requiring real-time access to distributed data sources without centralized storage, enabling integrated views across heterogeneous databases such as CRM, ERP, and cloud services. It suits scenarios demanding quick data retrieval and unified analytics across multiple departments or organizations without extensive data migration. Use cases include business intelligence platforms, regulatory compliance reporting, and data virtualization where data consistency and agility are critical.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Data Sharding
Data sharding is ideal for applications requiring horizontal scaling to manage massive datasets with high transaction throughput, such as large-scale e-commerce platforms or social media networks. It optimizes performance by distributing data across multiple shards, reducing latency and preventing bottlenecks during peak loads. Enterprises with geographically dispersed user bases benefit from sharding by localizing data access, which enhances speed and fault tolerance.
Benefits of Data Federation in Modern Architectures
Data federation enables unified access to disparate data sources without physical data movement, improving real-time analytics and reducing latency. It enhances data governance and security by maintaining data at the source, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. This approach supports scalable and flexible architectures, allowing organizations to integrate diverse systems and streamline decision-making processes efficiently.
Advantages and Challenges of Data Sharding
Data sharding enhances database scalability by partitioning large datasets into smaller, manageable segments distributed across multiple servers, enabling faster query processing and improved performance for high-traffic applications. However, challenges include increased complexity in data management, potential data consistency issues, and difficulties in implementing cross-shard queries and transactions. Effective shard key selection and robust infrastructure are essential to mitigate latency, balance loads, and maintain fault tolerance in sharded environments.
Performance Impact: Federation vs Sharding
Data federation improves query performance by enabling access to multiple data sources without data duplication, reducing latency through real-time data retrieval. Data sharding enhances performance by partitioning large datasets horizontally, allowing parallel processing and reducing query load on individual nodes. Sharding offers better scalability and faster write operations, while federation excels in unifying diverse data but may introduce overhead in query aggregation.
Security Considerations for Both Approaches
Data federation centralizes data access across multiple sources, enhancing security through unified authentication and fine-grained access controls but introduces risks of a single point of failure and increased attack surface. Data sharding distributes data across multiple nodes, reducing the impact of breaches by isolating data fragments, yet complicates security management with the need for consistent encryption and access policies across shards. Both approaches require robust encryption, secure communication protocols, and vigilant monitoring to mitigate risks inherent to their architectures.
Choosing the Right Data Strategy for Your Business
Data federation integrates data from multiple sources into a unified view without physical consolidation, ideal for real-time analytics and maintaining data sovereignty. Data sharding partitions a database horizontally to distribute load and improve scalability, suitable for high-transaction environments requiring rapid data access. Choosing the right strategy depends on your business's need for centralized data visibility versus performance optimization and scalability in distributed systems.
Data Federation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com