API Gateway serves as a crucial intermediary that manages and routes client requests to appropriate backend services, ensuring security, scalability, and performance optimization. By handling authentication, rate limiting, and protocol translation, it simplifies the complexity of microservices architecture for Your applications. Explore the rest of the article to understand how implementing an API Gateway can transform your system's efficiency and security.
Table of Comparison
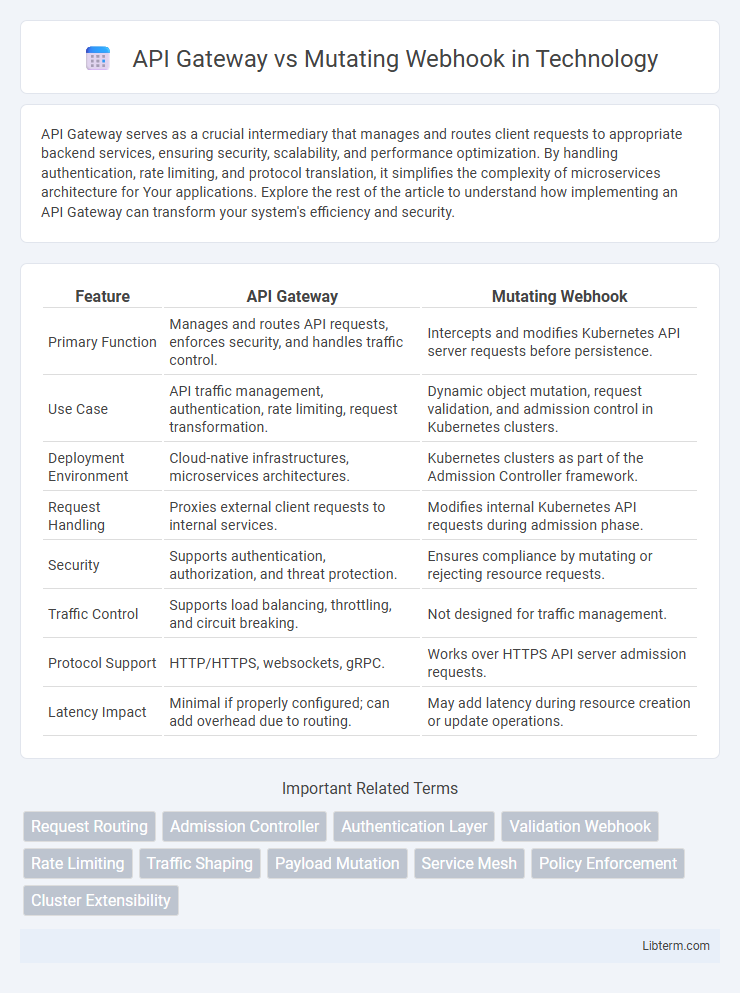
| Feature | API Gateway | Mutating Webhook |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages and routes API requests, enforces security, and handles traffic control. | Intercepts and modifies Kubernetes API server requests before persistence. |
| Use Case | API traffic management, authentication, rate limiting, request transformation. | Dynamic object mutation, request validation, and admission control in Kubernetes clusters. |
| Deployment Environment | Cloud-native infrastructures, microservices architectures. | Kubernetes clusters as part of the Admission Controller framework. |
| Request Handling | Proxies external client requests to internal services. | Modifies internal Kubernetes API requests during admission phase. |
| Security | Supports authentication, authorization, and threat protection. | Ensures compliance by mutating or rejecting resource requests. |
| Traffic Control | Supports load balancing, throttling, and circuit breaking. | Not designed for traffic management. |
| Protocol Support | HTTP/HTTPS, websockets, gRPC. | Works over HTTPS API server admission requests. |
| Latency Impact | Minimal if properly configured; can add overhead due to routing. | May add latency during resource creation or update operations. |
Introduction to API Gateway and Mutating Webhook
API Gateway serves as a centralized entry point that manages, authenticates, and routes API requests between clients and backend services, enhancing security and scalability. Mutating Webhook in Kubernetes intercepts API server requests to modify or validate resource configurations dynamically before they are persisted. Both play crucial roles in application architecture, with API Gateways optimizing external API management and Mutating Webhooks providing customizable control over cluster resource operations.
Core Concepts: API Gateway Explained
An API Gateway acts as a centralized entry point that manages, authenticates, and routes client requests to multiple backend services, enhancing security and scalability. It provides essential features such as request transformation, rate limiting, and load balancing to optimize API management. Unlike mutating webhooks, which dynamically modify Kubernetes objects during admission, API Gateways focus on controlling traffic flow and enforcing policies at the API layer.
Understanding Mutating Webhook Architecture
Mutating Webhook architecture in Kubernetes intercepts API server requests to modify or validate resources before they persist, enhancing cluster customization and security. Unlike API Gateway, which manages external traffic routing and load balancing, Mutating Webhook operates at the Kubernetes control plane level for real-time resource mutation. It leverages Admission Controller framework, running as HTTPS endpoints, ensuring dynamic and programmable API request transformation within the Kubernetes environment.
Key Differences: API Gateway vs Mutating Webhook
API Gateway primarily manages external API traffic by routing, throttling, and securing requests, while a Mutating Webhook modifies Kubernetes API server requests at runtime to enforce policies or inject configurations. API Gateways operate at the edge of a microservices architecture, handling authentication, load balancing, and protocol translation, whereas Mutating Webhooks function internally within Kubernetes clusters to dynamically mutate or validate resource objects during creation or update. The API Gateway focuses on external client interactions, offering centralized API management, while Mutating Webhooks provide cluster-internal request customization and policy enforcement.
Use Cases for API Gateways in Modern Applications
API Gateways serve as a centralized entry point managing, routing, and securing API traffic, ideal for microservices architectures, load balancing, and API analytics in modern applications. They handle tasks like authentication, rate limiting, request transformation, and monitoring, enabling seamless integration and scalability across distributed systems. Unlike Mutating Webhooks, which modify Kubernetes resource requests during admission control, API Gateways focus on external client-to-service communication and API management.
Typical Scenarios for Mutating Webhooks in Kubernetes
Mutating Webhooks in Kubernetes are typically used for request modification during admission control, such as injecting sidecar containers, adding or modifying resource labels, or enforcing security policies dynamically. These webhooks intercept API server requests to alter pod specifications, enhancing automation and consistency without requiring changes in the client side. Unlike API Gateways that manage external traffic routing and load balancing, Mutating Webhooks operate within the Kubernetes control plane to ensure resource configuration compliance and seamless operational workflows.
Performance Considerations and Scalability
API Gateway optimizes performance by efficiently routing requests and enabling caching, rate limiting, and load balancing, which enhances scalability in distributed systems. Mutating Webhooks introduce latency as they intercept and modify Kubernetes API requests, potentially becoming bottlenecks under high request volumes. Scalability challenges arise with Mutating Webhooks due to synchronous processing requirements and cluster-wide impact, whereas API Gateways scale horizontally with stateless proxy architectures.
Security Implications: API Gateway vs Mutating Webhook
API Gateways provide a centralized security layer by enforcing authentication, authorization, and traffic filtering, significantly reducing the attack surface for microservices architectures. Mutating Webhooks operate at the Kubernetes API server level, allowing dynamic request modifications but potentially introducing security risks if webhook endpoints are compromised or misconfigured. Properly securing API Gateways involves strong TLS enforcement and token validation, while Mutating Webhooks require rigorous access control and audit logging to prevent unauthorized object mutations.
Integration and Implementation Best Practices
API Gateway streamlines integration by centralizing request routing, authentication, and rate limiting, enabling seamless access to microservices through consistent APIs. Mutating Webhooks operate within Kubernetes, intercepting and modifying API server requests in real-time to enforce policies and inject configurations during pod creation. For best practices, implement API Gateways with clear schema contracts and throttling mechanisms, while designing Mutating Webhooks for idempotency, minimal latency, and robust validation to prevent cluster disruptions.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Workflow
API Gateway offers centralized request routing, authentication, and rate limiting, ideal for managing external API traffic with scalability and security. Mutating Webhook enables dynamic modification of Kubernetes resource configurations during admission, suitable for enforcing policies and injecting sidecar containers within cluster workflows. Choosing between API Gateway and Mutating Webhook depends on whether the primary need is external API management or internal Kubernetes resource mutation to optimize deployment automation and compliance.
API Gateway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com