System testing thoroughly evaluates the complete and integrated software to ensure it meets specified requirements and functions correctly in the intended environment. This phase identifies defects and verifies that all components work together seamlessly, improving overall system quality and reliability. Discover how system testing can secure your software's performance and dependability by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
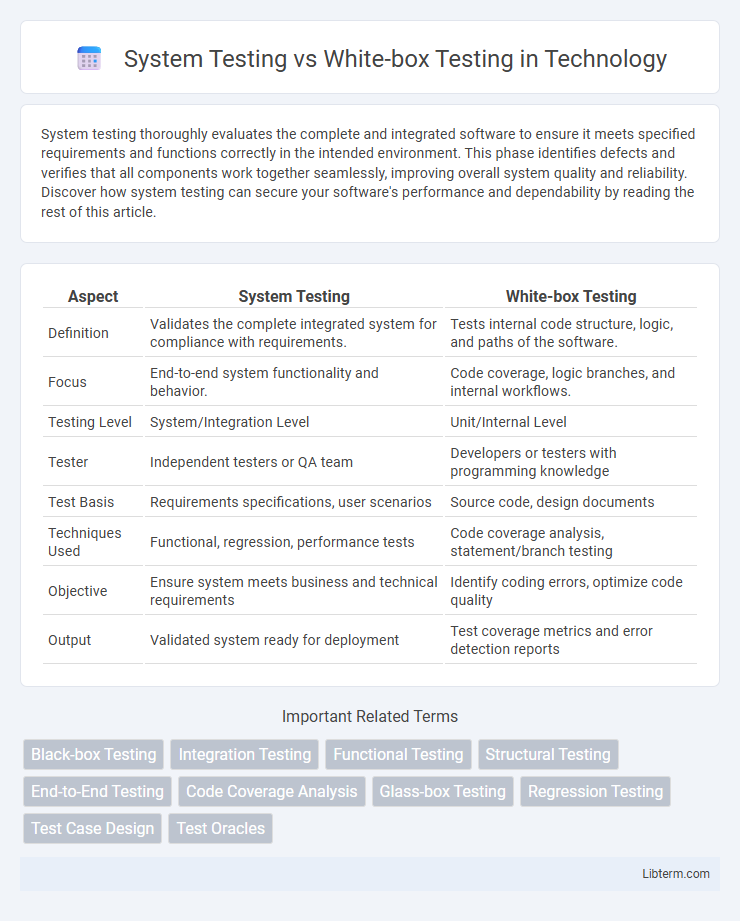
| Aspect | System Testing | White-box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Validates the complete integrated system for compliance with requirements. | Tests internal code structure, logic, and paths of the software. |
| Focus | End-to-end system functionality and behavior. | Code coverage, logic branches, and internal workflows. |
| Testing Level | System/Integration Level | Unit/Internal Level |
| Tester | Independent testers or QA team | Developers or testers with programming knowledge |
| Test Basis | Requirements specifications, user scenarios | Source code, design documents |
| Techniques Used | Functional, regression, performance tests | Code coverage analysis, statement/branch testing |
| Objective | Ensure system meets business and technical requirements | Identify coding errors, optimize code quality |
| Output | Validated system ready for deployment | Test coverage metrics and error detection reports |
Introduction to Software Testing
System testing evaluates the entire software application's functionality against requirements in a black-box manner, without focusing on internal code structures. White-box testing involves examining the internal logic and structure of the code to ensure path coverage, branch coverage, and statement execution. Both testing types are essential within the software testing lifecycle to identify defects at different levels, improving overall software quality and reliability.
Defining System Testing
System testing verifies the complete and integrated software product to ensure it meets specified requirements and functions correctly in its intended environment. It encompasses all system components, assessing system behavior, performance, and compliance with functional and non-functional requirements. This phase is critical for validating the entire application before deployment, contrasting with white-box testing, which focuses on internal code structure and logic.
What is White-box Testing?
White-box testing is a software testing method that examines the internal structures or workings of an application, requiring knowledge of the source code. This approach involves testing specific code paths, conditions, loops, and branches to ensure the software functions as intended under various scenarios. Unlike system testing, which evaluates the complete application from an external perspective, white-box testing targets the internal logic and code coverage to detect errors early in the development cycle.
Key Differences Between System and White-box Testing
System testing evaluates the complete and integrated software to verify compliance with specified requirements, focusing on external behavior and overall functionality. White-box testing examines the internal code structure, logic, and paths to ensure code quality and correctness through techniques like branch coverage and path testing. Unlike system testing, white-box testing requires detailed knowledge of the source code and is typically performed at the unit or integration testing levels.
Objectives of System Testing
System Testing aims to validate the complete and integrated software product to ensure it meets specified requirements and performs correctly in all intended environments. The primary objectives include verifying end-to-end functionality, detecting system-level defects, and confirming compliance with business and technical specifications. This contrasts with White-box Testing, which focuses on internal code structure and logic rather than overall system behavior.
Objectives of White-box Testing
White-box testing aims to verify the internal logic, code structure, and flow of an application to ensure all paths and conditions function correctly. It focuses on code coverage techniques such as statement, branch, and path coverage to identify hidden errors and vulnerabilities within the software. This approach helps improve code quality by validating algorithms, control structures, and data flow inside the program.
Techniques Used in System Testing
System testing employs techniques such as functional testing, usability testing, performance testing, and security testing to validate the complete integrated system against specified requirements. It involves black-box testing methods, focusing on inputs and expected outputs without knowledge of internal code structures. These techniques ensure the system operates correctly in real-world scenarios and meets user expectations.
Techniques Used in White-box Testing
White-box testing techniques involve code coverage analysis, including statement, branch, and path coverage to ensure thorough examination of internal logic. Test case design methods such as control flow testing, data flow testing, and loop testing enable identification of coding errors and vulnerabilities. These techniques provide detailed inspection of program structure, enhancing the detection of security flaws and functional defects compared to system testing, which evaluates the entire application from an external perspective.
Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
System Testing evaluates the complete integrated software to ensure it meets specified requirements, offering advantages such as validating end-to-end system functionality and detecting environment-related issues, but it can be time-consuming and may miss internal code errors. White-box Testing examines internal structures or workings of an application, providing advantages like thorough code coverage and early defect detection, though it requires detailed programming knowledge and can be complex to maintain. Choosing between the two depends on project needs; system testing excels in behavioral validation, while white-box testing is crucial for code-level accuracy and optimization.
When to Use System Testing vs White-box Testing
System testing is best used when validating the complete and integrated software product to ensure it meets specified requirements and functions correctly in the target environment. White-box testing is ideal during the development phase to verify internal code structures, logic paths, and control flows for detecting hidden errors and optimizing code quality. Use system testing for end-to-end validation and white-box testing for in-depth code analysis and unit-level defect identification.
System Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com