Colocation offers businesses a secure and reliable option to house their servers in professionally managed data centers with controlled environments and robust network connectivity. This approach reduces operational costs and enhances scalability while maintaining full control over your hardware. Explore the rest of the article to learn how colocation can optimize your IT infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
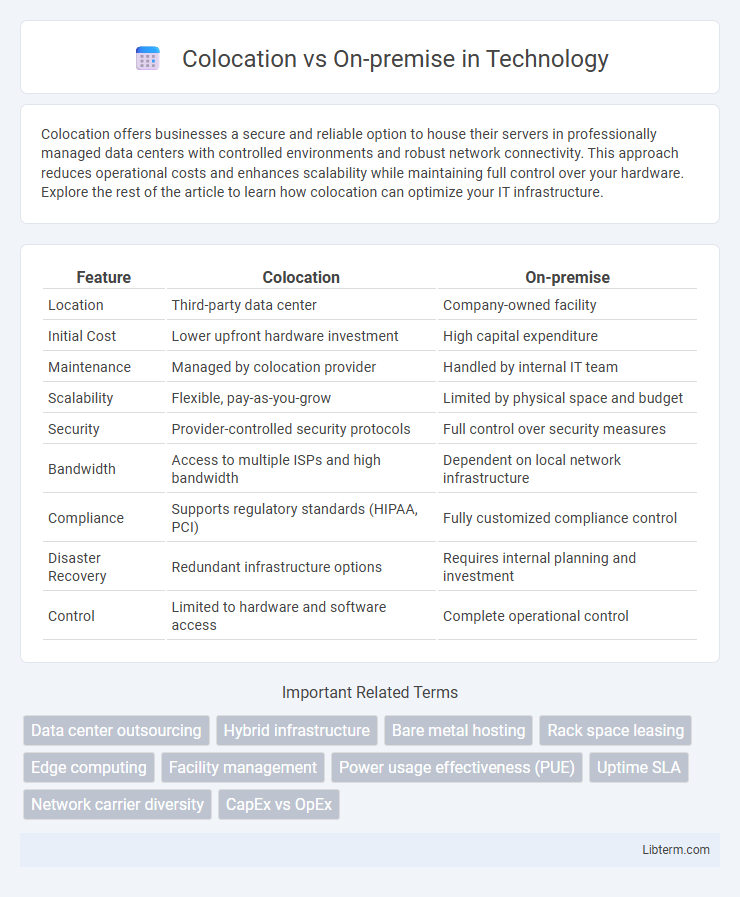
| Feature | Colocation | On-premise |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Third-party data center | Company-owned facility |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront hardware investment | High capital expenditure |
| Maintenance | Managed by colocation provider | Handled by internal IT team |
| Scalability | Flexible, pay-as-you-grow | Limited by physical space and budget |
| Security | Provider-controlled security protocols | Full control over security measures |
| Bandwidth | Access to multiple ISPs and high bandwidth | Dependent on local network infrastructure |
| Compliance | Supports regulatory standards (HIPAA, PCI) | Fully customized compliance control |
| Disaster Recovery | Redundant infrastructure options | Requires internal planning and investment |
| Control | Limited to hardware and software access | Complete operational control |
Introduction to Colocation and On-Premise Solutions
Colocation involves housing company-owned servers in a third-party data center, offering benefits like enhanced physical security, reliable power supply, and robust network connectivity compared to on-premise setups. In contrast, on-premise solutions require managing and maintaining servers within the organization's own facilities, demanding significant investment in infrastructure, cooling, and IT personnel. Choosing between colocation and on-premise depends on factors such as control requirements, scalability needs, and budget constraints.
Key Differences Between Colocation and On-Premise
Colocation involves housing servers and IT infrastructure in a third-party data center, offering benefits such as reduced capital expenditure, improved scalability, and enhanced physical security managed by the provider. On-premise deployment requires organizations to build and maintain their own data centers, leading to higher upfront costs, greater control over hardware, and direct management of security protocols. The key differences lie in cost structure, control, maintenance responsibilities, and scalability options, with colocation enabling businesses to leverage established facilities and on-premise providing complete ownership of infrastructure.
Cost Comparison: Colocation vs On-Premise
Colocation offers predictable, lower upfront capital expenses by sharing data center infrastructure, whereas on-premise requires significant investment in physical hardware, facilities, and maintenance. Operational costs for colocation are generally reduced due to economies of scale, while on-premise expenses include continuous utility bills, staffing, and equipment upgrades. Over time, colocation can deliver better cost efficiency with scalable solutions, whereas on-premise may become cost-prohibitive as infrastructure grows.
Security Considerations for Colocation and On-Premise
Colocation offers robust physical security measures such as biometric access controls, 24/7 surveillance, and staffed security personnel, reducing the risk of unauthorized entry. On-premise data centers allow organizations to implement customized security protocols tailored to specific compliance requirements but require dedicated resources for monitoring and maintenance. Network security in colocation relies on shared infrastructure protections, while on-premise solutions enable greater control over firewall configurations and intrusion detection systems.
Scalability and Flexibility: Which Is Better?
Colocation offers superior scalability by allowing businesses to easily expand their infrastructure without the constraints of physical space or hardware limitations found in on-premise setups. Flexibility in colocation enables rapid deployment of new servers and technologies tailored to evolving needs, unlike on-premise solutions that require significant capital expenditure and lead time for upgrades. Enterprises seeking dynamic growth and adaptable IT environments typically benefit more from colocation's scalable and flexible infrastructure compared to traditional on-premise configurations.
Performance and Reliability Factors
Colocation offers enhanced performance through access to high-quality, redundant network infrastructure and advanced cooling systems designed for optimal server operation. On-premise solutions rely heavily on the organization's internal resources, which can limit scalability and introduce risks related to hardware failures and power outages. Reliability in colocation centers is bolstered by multiple power feeds, backup generators, and professional monitoring, whereas on-premise setups require significant investment in maintenance and disaster recovery to achieve comparable uptime.
Maintenance and Management Requirements
Colocation facilities shift hardware maintenance responsibilities to the client, requiring internal IT teams to manage server upkeep, software updates, and troubleshooting remotely, while reducing physical infrastructure management burdens such as power and cooling. On-premise data centers demand comprehensive in-house maintenance and management, including hardware repairs, environmental control, and security oversight, leading to higher direct operational costs and dedicated staff. Choosing colocation optimizes resource allocation by leveraging provider-managed infrastructure, whereas on-premise setups require full ownership of maintenance protocols and facility management.
Compliance and Regulatory Implications
Colocation facilities often provide enhanced compliance with industry standards such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR by offering certified infrastructure, robust physical security, and regular audits, which can be challenging to replicate on-premise. On-premise solutions require direct responsibility for meeting regulatory requirements, including data sovereignty and audit readiness, demanding substantial investment in compliance management and security controls. Businesses managing sensitive data may prefer colocation to leverage expert compliance support while maintaining control over hardware, minimizing risks associated with regulatory penalties.
Use Cases: When to Choose Colocation or On-Premise
Colocation is ideal for businesses seeking scalable infrastructure without the capital expenses of building a data center, supporting use cases like rapid expansion, disaster recovery, and high-bandwidth applications. On-premise solutions are preferred when companies require full control over hardware, stringent data security, and compliance needs, especially in industries like finance and healthcare. Hybrid approaches combine both, enabling organizations to optimize workloads by balancing cost, control, and compliance requirements.
Future Trends in Data Center Strategies
Future trends in data center strategies indicate a rising preference for colocation due to its scalability, cost efficiency, and enhanced security features supported by advancements in AI-driven management and edge computing integration. On-premise data centers continue to evolve with increased automation, hybrid cloud adoption, and energy-efficient technologies aimed at reducing operational costs and carbon footprints. Enterprises are increasingly leveraging multi-cloud strategies combined with colocation to ensure agility, compliance, and high availability in their IT infrastructure.
Colocation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com