Effective log management is crucial for monitoring system performance, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring security compliance. Collecting, analyzing, and storing log data enables you to detect anomalies and respond swiftly to potential threats. Explore the full article to discover best practices and tools for optimizing your log management strategy.
Table of Comparison
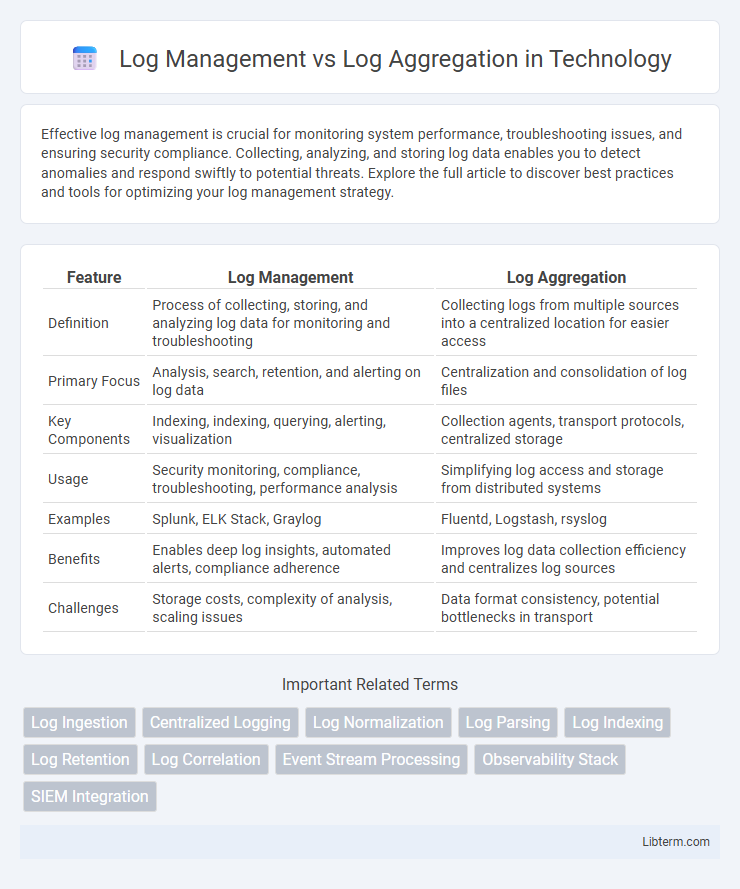
| Feature | Log Management | Log Aggregation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of collecting, storing, and analyzing log data for monitoring and troubleshooting | Collecting logs from multiple sources into a centralized location for easier access |
| Primary Focus | Analysis, search, retention, and alerting on log data | Centralization and consolidation of log files |
| Key Components | Indexing, indexing, querying, alerting, visualization | Collection agents, transport protocols, centralized storage |
| Usage | Security monitoring, compliance, troubleshooting, performance analysis | Simplifying log access and storage from distributed systems |
| Examples | Splunk, ELK Stack, Graylog | Fluentd, Logstash, rsyslog |
| Benefits | Enables deep log insights, automated alerts, compliance adherence | Improves log data collection efficiency and centralizes log sources |
| Challenges | Storage costs, complexity of analysis, scaling issues | Data format consistency, potential bottlenecks in transport |
Understanding Log Management
Log management encompasses the entire process of collecting, storing, analyzing, and monitoring log data from various IT systems to ensure operational visibility and security compliance. It involves not only aggregating logs but also parsing, indexing, and applying retention policies to enable efficient search and incident response. Effective log management platforms integrate with SIEM tools and support real-time alerting to detect anomalies and facilitate root cause analysis.
What is Log Aggregation?
Log aggregation is the process of collecting and centralizing log data from multiple sources into a single repository for easier analysis and monitoring. It enables organizations to consolidate logs from diverse systems, applications, and devices, facilitating real-time troubleshooting and security auditing. Log aggregation tools improve operational efficiency by providing a unified view of distributed log data, enhancing incident response and compliance management.
Key Differences Between Log Management and Log Aggregation
Log management involves the collection, storage, analysis, and monitoring of log data to enable troubleshooting, security, and compliance, whereas log aggregation focuses on the centralized gathering of logs from multiple sources into a single repository. Log management provides advanced querying, alerting, and long-term retention capabilities, while log aggregation primarily ensures efficient data collection and consolidation for easier access. Effective log management platforms typically incorporate aggregation as a subset of broader functionalities including indexing and correlation.
Core Features of Log Management
Log Management centers on the systematic collection, storage, and analysis of log data to ensure security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Core features include log collection from diverse sources, real-time monitoring, centralized storage with retention policies, comprehensive search and query capabilities, and alerting based on specific log events or anomalies. In contrast, Log Aggregation primarily focuses on consolidating log data from multiple systems into a single repository but lacks advanced analysis and alerting functionalities inherent in Log Management platforms.
Benefits of Log Aggregation
Log aggregation centralizes log data from diverse sources into a unified platform, enabling faster and more efficient analysis compared to traditional log management methods. It enhances real-time monitoring, simplifies troubleshooting, and improves system reliability by providing comprehensive visibility across distributed environments. This consolidation also supports advanced analytics and alerting capabilities, leading to proactive issue detection and optimized operational performance.
Use Cases for Log Management
Log management is crucial for monitoring system performance, troubleshooting errors, and ensuring security compliance by collecting, storing, and analyzing log data from various sources. It enables real-time alerting, forensic analysis of incidents, and maintaining audit trails for regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA. Unlike log aggregation, which primarily focuses on consolidating logs from multiple systems, log management provides structured analytics and actionable insights to optimize IT operations and enhance cybersecurity posture.
Use Cases for Log Aggregation
Log aggregation consolidates log data from multiple sources into a centralized repository, enabling real-time monitoring, troubleshooting, and security analysis across distributed systems. Use cases for log aggregation include detecting anomalies in application behavior, facilitating compliance audits by maintaining comprehensive log records, and improving incident response times by providing a unified view of system performance. This centralized approach contrasts with log management, which broadly covers the collection, storage, and analysis of logs but may lack the real-time, cross-source integration critical for complex environments.
Challenges in Log Data Handling
Log management involves the collection, storage, and analysis of log data, facing challenges such as handling large data volumes, ensuring data integrity, and enabling real-time monitoring. Log aggregation consolidates logs from multiple sources into a centralized platform, but struggles with normalization, dealing with diverse log formats, and maintaining system performance under high ingestion rates. Both processes demand robust infrastructure to manage scalability, security, and compliance while minimizing data loss and latency in log processing.
Choosing the Right Log Solution for Your Organization
Log management involves collecting, storing, and analyzing extensive log data for compliance, security, and troubleshooting, while log aggregation centralizes logs from multiple sources for easier access and correlation. Choosing the right log solution depends on your organization's scale, compliance requirements, and real-time analysis needs, with advanced platforms offering integrated search, alerting, and visualization features. Prioritizing scalability, security, and ease of integration ensures optimal log handling, improving operational visibility and incident response efficiency.
Future Trends in Log Management and Aggregation
Future trends in log management and log aggregation emphasize advanced machine learning algorithms to automatically detect anomalies and predict system failures, enhancing proactive monitoring capabilities. Cloud-native architectures and serverless computing drive the adoption of scalable, real-time log aggregation platforms capable of handling massive data streams with minimal latency. Integration with AI-powered analytics and automated incident response systems is becoming standard, improving operational efficiency and reducing mean time to resolution (MTTR) in complex IT environments.
Log Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com