Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are critical for detecting and blocking malicious activities in real-time to safeguard your network infrastructure. These systems analyze traffic patterns and immediately respond to threats, minimizing potential breaches and data loss. Explore the rest of the article to understand how IPS can enhance your cybersecurity strategy effectively.
Table of Comparison
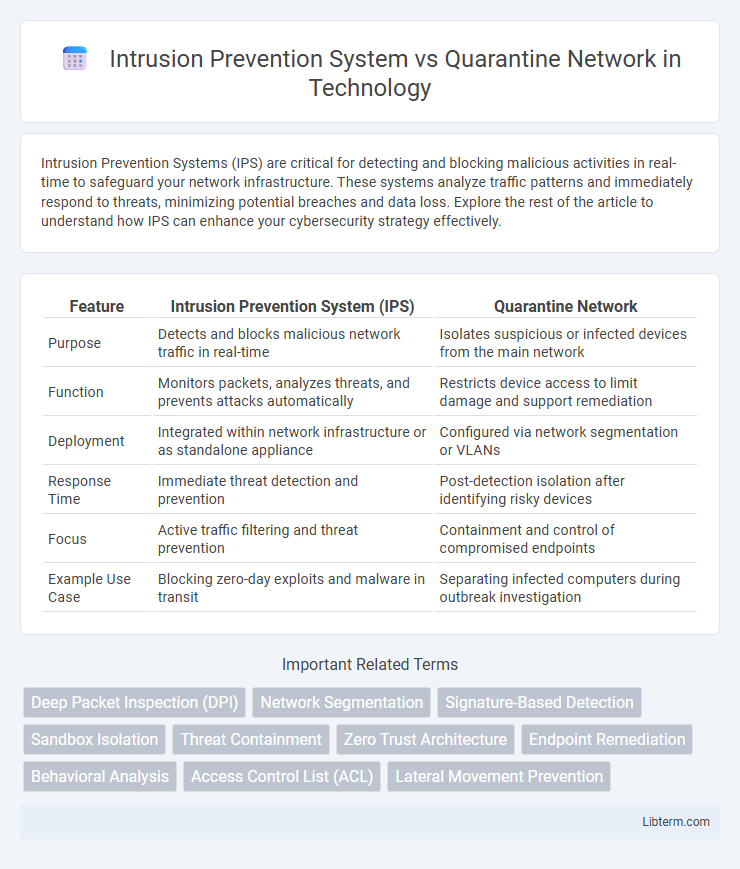
| Feature | Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) | Quarantine Network |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects and blocks malicious network traffic in real-time | Isolates suspicious or infected devices from the main network |
| Function | Monitors packets, analyzes threats, and prevents attacks automatically | Restricts device access to limit damage and support remediation |
| Deployment | Integrated within network infrastructure or as standalone appliance | Configured via network segmentation or VLANs |
| Response Time | Immediate threat detection and prevention | Post-detection isolation after identifying risky devices |
| Focus | Active traffic filtering and threat prevention | Containment and control of compromised endpoints |
| Example Use Case | Blocking zero-day exploits and malware in transit | Separating infected computers during outbreak investigation |
Introduction to Network Security Measures
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) monitor and analyze network traffic to detect and block malicious activities in real-time, enhancing proactive defense against cyber threats. Quarantine Networks isolate compromised devices or suspicious traffic segments to prevent widespread infection and contain threats within a controlled environment. Both measures are critical components of comprehensive network security strategies, ensuring robust protection and minimizing the risk of data breaches.
What is an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)?
An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is a network security technology designed to detect and block malicious activities in real-time by analyzing network traffic for suspicious patterns or known threats. It operates inline within the network, automatically preventing attacks such as malware, exploits, and unauthorized access before they reach critical systems. Unlike a quarantine network, which isolates compromised devices for remediation, an IPS actively stops threats to maintain network integrity and reduce the risk of security breaches.
Understanding the Quarantine Network Approach
The Quarantine Network approach isolates suspicious devices from the main network to prevent potential threats from spreading, allowing for thorough analysis and remediation without compromising overall security. Unlike traditional Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) that actively block malicious traffic in real-time, quarantine networks create a contained environment where infected or non-compliant devices are restricted until they meet predefined security policies. This method enhances network resilience by minimizing the risk of lateral movement by attackers and facilitates controlled recovery processes.
Key Features of Intrusion Prevention Systems
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively monitor network traffic to detect and block suspicious activities in real-time, ensuring proactive threat mitigation. Key features include deep packet inspection, automated response capabilities, signature-based and anomaly-based detection, and integration with firewall technologies for comprehensive network security. Unlike Quarantine Networks that isolate compromised devices, IPS prevents attacks before they reach critical systems, maintaining continuous network integrity.
Core Functions of Quarantine Networks
Quarantine networks isolate compromised or suspicious devices to prevent the spread of malware and unauthorized access within an enterprise network, ensuring containment before remediation. They enforce strict access controls, allowing only limited communication necessary for threat identification and system updates. By segmenting affected devices from critical network resources, quarantine networks play a vital role in minimizing security risks and maintaining overall network integrity.
IPS vs Quarantine Network: Detection & Response
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) proactively detect and block malicious network traffic in real-time using signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods, minimizing threats before they infiltrate the network. Quarantine networks isolate suspicious devices or traffic by redirecting them into a restricted environment where further analysis or remediation occurs without impacting the main network. While IPS focuses on immediate threat prevention through automated responses, quarantine networks emphasize containment and controlled investigation to mitigate risks during incident response.
Deployment Architecture: IPS and Quarantine Network
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are typically deployed inline within the network architecture, enabling real-time traffic analysis and automatic blocking of malicious activities before they reach critical assets. Quarantine networks, also known as remediation or sandbox environments, are isolated segments designed to contain and analyze potentially compromised devices or traffic without risking the main network integrity. The deployment architecture for IPS emphasizes active blocking and prevention through inline inspection, while quarantine networks focus on segregation and controlled containment for threat remediation and forensics.
Advantages and Limitations of IPS
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) offer real-time threat detection and automatic blocking of malicious activities, enhancing network security by preventing attacks before they cause damage. Their advantages include deep packet inspection, low false-positive rates, and seamless integration with firewalls, but limitations involve potential performance bottlenecks and the challenge of evolving threat patterns requiring frequent updates. Compared to Quarantine Networks, which isolate infected devices to contain threats, IPS provides proactive defense but may struggle against advanced evasion techniques and insider threats.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Quarantine Network
Quarantine networks isolate suspicious devices to prevent potential threats from spreading, enhancing overall security by containing risks early. Benefits include reducing exposure to critical systems and minimizing disruption to normal network operations, while drawbacks involve potential delays in device functionality restoration and complexities in managing quarantined assets. Effective quarantine networks require robust policies and constant monitoring to balance security with operational efficiency.
Choosing The Right Solution: Use Cases & Recommendations
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) actively monitor network traffic to detect and block malicious activities in real-time, ideal for environments requiring immediate threat mitigation such as enterprise networks and data centers. Quarantine networks isolate compromised devices to prevent lateral movement, making them suitable for organizations prioritizing containment and remediation in segmented infrastructures. Selecting the right solution depends on operational needs: IPS offers proactive defense with low latency, while quarantine networks provide controlled isolation for managing infected endpoints safely.
Intrusion Prevention System Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com