Session consistency ensures that your interactions with a system remain reliable and coherent throughout a user session by maintaining the same state across multiple requests. This consistency is crucial for applications like online banking, shopping carts, and personalized services where uninterrupted data flow enhances user experience. Explore the rest of this article to understand how session consistency improves system performance and user satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
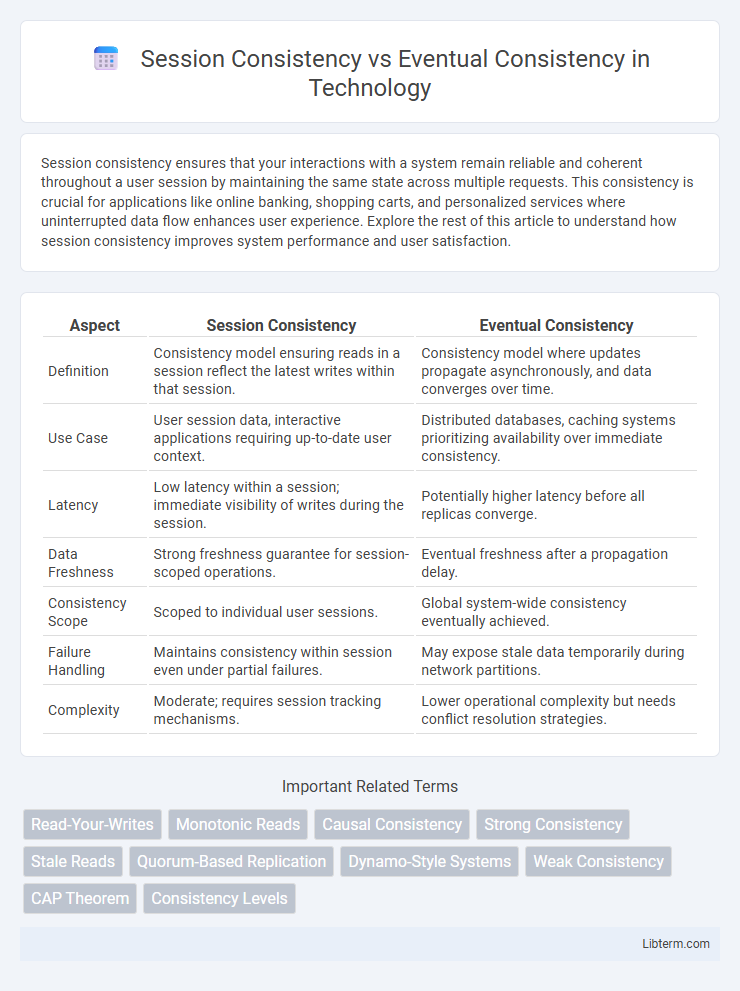
| Aspect | Session Consistency | Eventual Consistency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistency model ensuring reads in a session reflect the latest writes within that session. | Consistency model where updates propagate asynchronously, and data converges over time. |
| Use Case | User session data, interactive applications requiring up-to-date user context. | Distributed databases, caching systems prioritizing availability over immediate consistency. |
| Latency | Low latency within a session; immediate visibility of writes during the session. | Potentially higher latency before all replicas converge. |
| Data Freshness | Strong freshness guarantee for session-scoped operations. | Eventual freshness after a propagation delay. |
| Consistency Scope | Scoped to individual user sessions. | Global system-wide consistency eventually achieved. |
| Failure Handling | Maintains consistency within session even under partial failures. | May expose stale data temporarily during network partitions. |
| Complexity | Moderate; requires session tracking mechanisms. | Lower operational complexity but needs conflict resolution strategies. |
Introduction to Data Consistency Models
Session consistency ensures that within a single user session, read operations reflect the most recent write operations, providing a coherent view of data. Eventual consistency allows for temporary inconsistencies across distributed systems but guarantees that all replicas will converge to the same state over time. These data consistency models address the trade-off between data accuracy and system availability in distributed database architectures.
What is Session Consistency?
Session consistency guarantees that within a single session, all read operations reflect the most recent write, ensuring users see a consistent and up-to-date view of the data during their interaction. This model is commonly implemented in distributed databases and caching systems to provide a balance between performance and data accuracy. Session consistency helps prevent stale data reads while allowing for some latency and replication delays across different sessions or users.
Understanding Eventual Consistency
Eventual consistency ensures that all replicas of a distributed system will converge to the same state over time, even if updates are not immediately visible across all nodes. This model prioritizes availability and partition tolerance by allowing temporary data inconsistencies during network delays or failures. Systems like Amazon Dynamo and Cassandra implement eventual consistency to maximize responsiveness in large-scale environments.
Key Differences Between Session and Eventual Consistency
Session consistency ensures that a user sees a consistent view of data within a single session, maintaining read-your-writes guarantees and providing stronger consistency for individual clients. Eventual consistency allows updates to propagate asynchronously across replicas, meaning data may temporarily diverge before converging to a consistent state across the entire system. The key difference lies in session consistency's affinity to a single client's interaction scope versus eventual consistency's broader system-wide eventual convergence without immediate guarantees.
Use Cases for Session Consistency
Session consistency is ideal for applications where users expect to see their own recent updates immediately, such as online shopping carts, social media feeds, and collaborative document editing. It ensures that within a single session, all read operations reflect the latest writes, providing a seamless and responsive user experience. This consistency model balances performance and accuracy, making it suitable for interactive applications that do not require global immediate synchronization.
When to Choose Eventual Consistency
Eventual consistency is ideal for distributed systems requiring high availability and partition tolerance, such as large-scale e-commerce platforms or social media applications where immediate data synchronization is not critical. Systems prioritizing low latency and scalability over strict accuracy, like caching servers or content delivery networks, benefit from eventual consistency models. Choosing eventual consistency improves performance by allowing write operations to complete without waiting for all replicas to synchronize, ensuring user experience remains responsive under high load.
Impact on Application Performance and Scalability
Session consistency ensures read-your-writes guarantees within a user session, leading to predictable application behavior but potentially increased latency due to synchronous coordination. Eventual consistency improves scalability by allowing asynchronous updates across distributed nodes, reducing write latency and enabling higher throughput at the cost of temporary data staleness. Applications requiring immediate consistency for user interactions benefit from session consistency, while large-scale, distributed systems favor eventual consistency to optimize performance under heavy loads.
Real-World Examples: Session vs Eventual Consistency
Session consistency ensures users experience a consistent view of their data within a single session, ideal for applications like online shopping carts where users expect immediate reflection of changes. Eventual consistency suits distributed systems like social media feeds, where updates propagate over time and users tolerate slight delays in seeing the latest posts. Companies like Amazon DynamoDB implement eventual consistency for scalability, while applications requiring strict consistency, such as banking transactions, rely on session consistency models.
Best Practices for Implementing Consistency Models
Implementing session consistency involves maintaining a user's read and write order within a session to ensure they see their most recent operations, which is essential for user-centric applications requiring immediate feedback. Eventual consistency best practices include designing systems that tolerate temporary data divergence by implementing conflict resolution strategies and monitoring replication delays to achieve high availability and scalability. Choosing the right consistency model depends on application requirements for latency, data accuracy, and fault tolerance, often requiring trade-offs between user experience and system performance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Consistency Model
Selecting the right consistency model depends on the application's requirements for data accuracy and responsiveness. Session consistency ensures that users experience up-to-date information during their session, making it ideal for applications needing immediate consistency without sacrificing performance. Eventual consistency suits systems prioritizing high availability and partition tolerance, where temporary data staleness is acceptable in exchange for scalability and fault tolerance.
Session Consistency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com