Resource reservation ensures guaranteed availability of critical assets by allocating them in advance to meet specific needs. This process optimizes operational efficiency and prevents resource conflict or downtime during peak demand. Explore the full article to discover how your organization can benefit from effective resource reservation strategies.
Table of Comparison
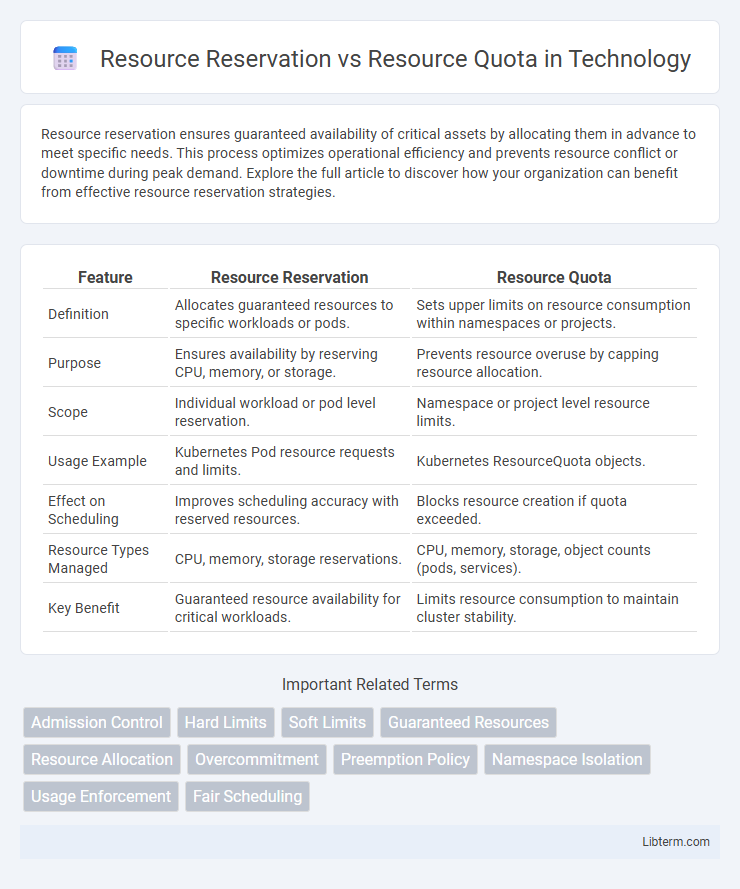
| Feature | Resource Reservation | Resource Quota |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates guaranteed resources to specific workloads or pods. | Sets upper limits on resource consumption within namespaces or projects. |
| Purpose | Ensures availability by reserving CPU, memory, or storage. | Prevents resource overuse by capping resource allocation. |
| Scope | Individual workload or pod level reservation. | Namespace or project level resource limits. |
| Usage Example | Kubernetes Pod resource requests and limits. | Kubernetes ResourceQuota objects. |
| Effect on Scheduling | Improves scheduling accuracy with reserved resources. | Blocks resource creation if quota exceeded. |
| Resource Types Managed | CPU, memory, storage reservations. | CPU, memory, storage, object counts (pods, services). |
| Key Benefit | Guaranteed resource availability for critical workloads. | Limits resource consumption to maintain cluster stability. |
Introduction to Resource Management
Resource Reservation ensures guaranteed resources by allocating specific CPU and memory to containers, preventing resource contention in Kubernetes clusters. Resource Quota limits the total resource consumption across namespaces, controlling the overall usage and preventing resource exhaustion. Effective resource management balances Reservation for stability and Quota for governance to optimize cluster performance and availability.
Defining Resource Reservation
Resource Reservation refers to the guaranteed allocation of specific amounts of CPU, memory, or other resources to a container or workload within a Kubernetes cluster, ensuring performance stability and preventing resource contention. It is configured through resource requests in pod specifications, indicating the minimum resources a pod requires to run effectively. This built-in mechanism enables precise capacity planning and helps maintain quality of service by reserving resources before workload scheduling.
Understanding Resource Quota
Resource Quota in Kubernetes is a mechanism to limit the overall resource consumption across namespaces, controlling CPU, memory, and storage usage to ensure fair distribution and prevent resource exhaustion. Unlike Resource Reservation, which assigns minimum resource guarantees to individual pods or containers, Resource Quota enforces maximum usage thresholds, helping administrators manage cluster capacity effectively. Understanding Resource Quota is essential for maintaining cluster stability by preventing any single team or application from consuming disproportionate resources.
Key Differences Between Reservation and Quota
Resource Reservation guarantees a specific amount of resources, such as CPU or memory, for a workload to ensure consistent performance and availability. Resource Quota limits the total resource consumption within a namespace or project, preventing overallocation and controlling resource usage across multiple workloads. While reservations prioritize guaranteed resources for individual tasks, quotas focus on enforcing usage boundaries at an aggregate level.
Advantages of Resource Reservation
Resource Reservation ensures guaranteed allocation of resources such as CPU and memory for critical applications, preventing resource contention and improving workload reliability. By reserving specific amounts of resources, systems can maintain consistent performance under high demand, reducing latency and avoiding application crashes. This proactive allocation supports effective capacity planning and enhances overall system stability in multi-tenant environments.
Benefits of Implementing Resource Quota
Implementing Resource Quota in Kubernetes ensures efficient resource allocation by limiting CPU and memory usage per namespace, preventing resource exhaustion and promoting cluster stability. Resource Quota enforces fair resource distribution among teams, enhancing multi-tenant environment management and avoiding noisy neighbor issues. This governance mechanism improves overall cluster performance by maintaining predictable resource consumption and enabling capacity planning.
Use Cases for Resource Reservation
Resource Reservation ensures guaranteed access to specific compute or storage resources for high-priority workloads, preventing resource contention in multi-tenant environments, ideal for real-time applications or critical batch processing that require predictable performance. Resource Quota limits the overall amount of resources a user or team can consume, promoting fair usage and preventing over-allocation but does not guarantee resource availability. Use cases for Resource Reservation include dedicated CPU allocation for latency-sensitive microservices, reserved memory for in-memory databases, and exclusive GPU time for machine learning model training jobs.
Use Cases for Resource Quota
Resource Quota is essential for managing resource consumption in multi-tenant Kubernetes clusters by limiting CPU, memory, and storage usage per namespace, preventing resource exhaustion and ensuring fair distribution. Use cases include controlling resource allocation in development, testing, and production environments to avoid noisy neighbor issues and enforce organizational policies. Unlike Resource Reservation, which guarantees resources for specific pods, Resource Quota enforces constraints at the namespace level to maintain cluster stability and cost management.
Choosing Between Reservation and Quota
Choosing between resource reservation and resource quota depends on workload predictability and criticality; reservations guarantee resource availability by reserving CPU and memory ahead of time, ensuring performance for critical applications with consistent demand. Resource quotas limit the total amount of resources a namespace or user can consume, preventing resource exhaustion and promoting fair distribution in multi-tenant environments without guaranteeing immediate availability. Organizations with variable workloads benefit from quotas to avoid resource hogging, while those with strict performance requirements prefer reservations to secure dedicated resources.
Best Practices for Effective Resource Allocation
Resource Reservation ensures dedicated CPU and memory resources for critical Kubernetes pods to guarantee performance under high load, while Resource Quota limits overall resource consumption within namespaces to enforce fair distribution and prevent resource exhaustion. Best practices include setting realistic Reservation values based on actual workload requirements and configuring Quotas to balance cluster efficiency and user demands, avoiding overcommitment that can lead to resource contention. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of these parameters help maintain optimal resource allocation and cluster stability in dynamic environments.
Resource Reservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com