PaaS (Platform as a Service) offers a cloud-based environment that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This service simplifies coding and accelerates development by providing ready-to-use tools, frameworks, and runtime environments. Discover how PaaS can transform your software projects by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
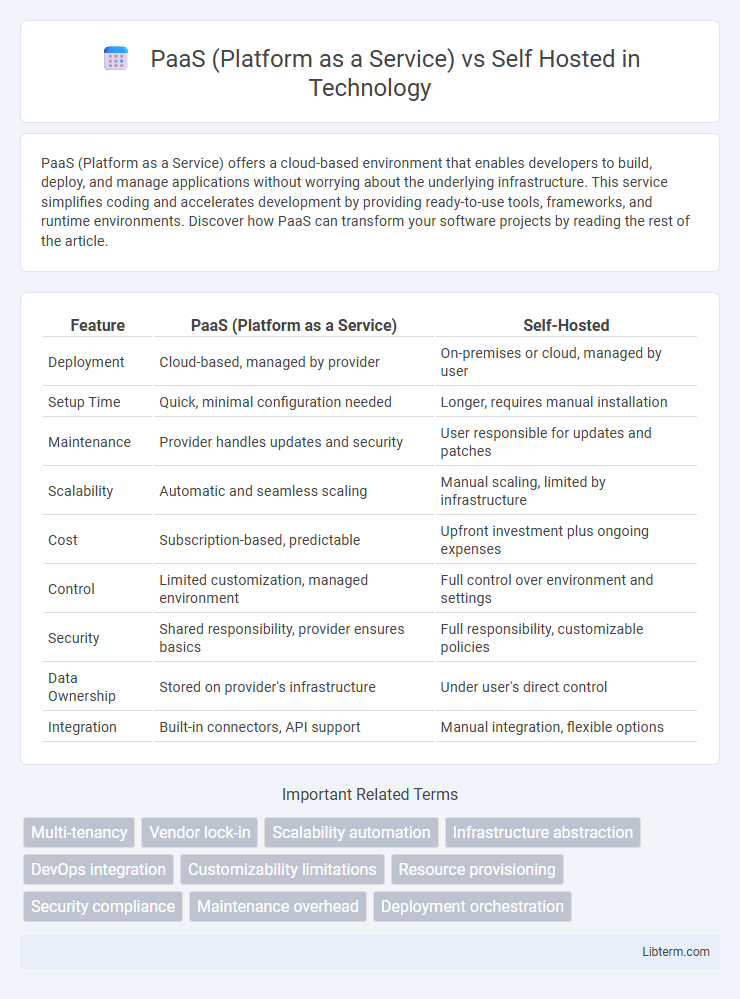
| Feature | PaaS (Platform as a Service) | Self-Hosted |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud-based, managed by provider | On-premises or cloud, managed by user |
| Setup Time | Quick, minimal configuration needed | Longer, requires manual installation |
| Maintenance | Provider handles updates and security | User responsible for updates and patches |
| Scalability | Automatic and seamless scaling | Manual scaling, limited by infrastructure |
| Cost | Subscription-based, predictable | Upfront investment plus ongoing expenses |
| Control | Limited customization, managed environment | Full control over environment and settings |
| Security | Shared responsibility, provider ensures basics | Full responsibility, customizable policies |
| Data Ownership | Stored on provider's infrastructure | Under user's direct control |
| Integration | Built-in connectors, API support | Manual integration, flexible options |
Introduction to PaaS and Self-Hosted Solutions
PaaS (Platform as a Service) offers cloud-based environments that streamline application development by providing pre-configured infrastructure, middleware, and development tools. Self-hosted solutions require on-premises infrastructure management, giving organizations full control over hardware, software, and security but demanding greater IT resources and maintenance efforts. Choosing between PaaS and self-hosted platforms hinges on factors like scalability needs, customization requirements, and available technical expertise.
Core Features: PaaS vs Self-Hosted Platforms
PaaS platforms offer streamlined deployment, automatic scaling, and built-in infrastructure management, enabling developers to focus on application development without worrying about server maintenance. Self-hosted platforms provide complete control over configurations, data security, and customization, but require in-house expertise for hardware management, updates, and troubleshooting. Core features comparison highlights PaaS's ease of use and operational efficiency against self-hosted solutions' flexibility and control.
Deployment and Scalability Differences
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers streamlined deployment through pre-configured environments, enabling developers to launch applications quickly without managing underlying infrastructure. In contrast, self-hosted solutions require manual setup and ongoing maintenance of servers, which can complicate deployment and slow down scalability efforts. PaaS automatically scales resources based on demand, providing elastic scalability, whereas self-hosted systems often need manual hardware upgrades or complex configurations to scale efficiently.
Cost Comparison: PaaS vs Self-Hosting
PaaS (Platform as a Service) typically involves predictable subscription fees based on resource usage, reducing upfront hardware and maintenance costs compared to self-hosted solutions. Self-hosting demands significant capital investment for servers, infrastructure, and ongoing IT management, potentially increasing total cost of ownership over time. Cost efficiency of PaaS versus self-hosting varies depending on scalability needs, administrative overhead, and long-term operational expenses.
Security Considerations for Each Approach
PaaS offers integrated security features managed by cloud providers, including automated updates, threat detection, and compliance certifications, reducing the burden on developers but limiting customization. Self-hosted platforms require organizations to implement and maintain security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular patching, demanding deeper expertise and resources. Evaluating risk tolerance, regulatory requirements, and internal security capabilities is crucial when choosing between PaaS and self-hosted solutions.
Customization and Flexibility
PaaS offers streamlined customization through pre-configured environments but may limit deep flexibility due to fixed platform constraints, ideal for rapid development with standardized tools. Self-hosted solutions provide extensive customization and full control over hardware, software, and configurations, enabling tailored environments to meet specific performance and security needs. Organizations prioritizing unique workflows and extensive integration often prefer self-hosted for maximum adaptability, while those seeking ease of management lean toward PaaS.
Maintenance and Support Responsibilities
PaaS (Platform as a Service) providers manage maintenance tasks such as software updates, security patches, and infrastructure monitoring, significantly reducing the operational burden on users. In contrast, self-hosted solutions require organizations to assume full responsibility for system upkeep, including hardware management, software updates, and troubleshooting. This shift often demands dedicated IT staff and resources to ensure continuous system availability and security compliance.
Performance and Reliability Analysis
PaaS (Platform as a Service) offers optimized performance through managed infrastructure, automatic scaling, and built-in redundancy, ensuring high reliability with minimal downtime. Self-hosted solutions provide full control over hardware and software configurations, which can lead to customized performance tuning but require significant expertise to maintain consistent reliability and handle failover scenarios. Performance in self-hosted environments depends heavily on resource allocation and in-house management capabilities, whereas PaaS leverages cloud provider SLAs and global data centers to deliver scalable, resilient services.
Use Cases: When to Choose PaaS or Self-Hosted
PaaS is ideal for startups and agile development teams seeking rapid deployment, scalability, and minimal infrastructure management, particularly for web applications, APIs, and microservices. Self-hosted solutions suit enterprises requiring full control over customization, data privacy, and compliance, especially in regulated industries like finance and healthcare. Evaluating factors such as cost predictability, maintenance resources, and integration complexity determines whether PaaS or self-hosted platforms best align with specific business needs.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Platform for Your Needs
Choosing between PaaS and self-hosted solutions depends on factors such as scalability, control, and maintenance preferences. PaaS offers streamlined deployment, automatic updates, and reduced infrastructure management, ideal for businesses seeking agility and lower operational overhead. In contrast, self-hosted platforms provide greater customization, data control, and security but require dedicated resources for setup and ongoing administration.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com