Watercolor painting captures the delicate interplay of light and color through translucent layers and fluid brushstrokes, offering a unique blend of control and spontaneity. This medium's versatility allows artists to create everything from vivid landscapes to subtle portraits with a softness that is hard to replicate. Explore the rest of the article to discover techniques and tips that will enhance your watercolor skills.
Table of Comparison
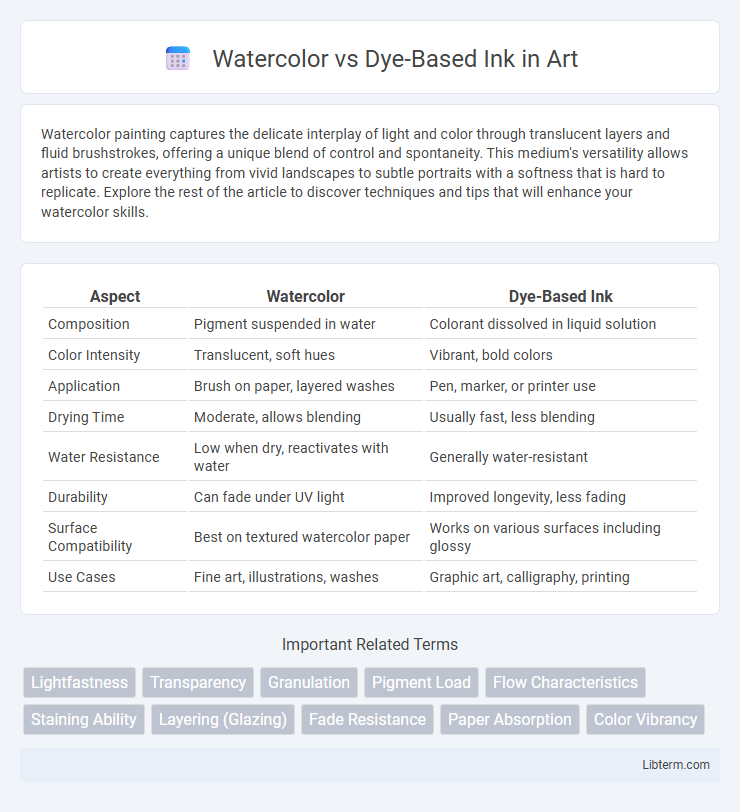
| Aspect | Watercolor | Dye-Based Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pigment suspended in water | Colorant dissolved in liquid solution |
| Color Intensity | Translucent, soft hues | Vibrant, bold colors |
| Application | Brush on paper, layered washes | Pen, marker, or printer use |
| Drying Time | Moderate, allows blending | Usually fast, less blending |
| Water Resistance | Low when dry, reactivates with water | Generally water-resistant |
| Durability | Can fade under UV light | Improved longevity, less fading |
| Surface Compatibility | Best on textured watercolor paper | Works on various surfaces including glossy |
| Use Cases | Fine art, illustrations, washes | Graphic art, calligraphy, printing |
Understanding Watercolor and Dye-Based Ink
Watercolor uses pigment particles suspended in water, creating translucent layers that blend smoothly on paper and offer rich, archival quality. Dye-based ink contains soluble dyes that produce vibrant colors and quick drying times but may fade faster due to lower lightfastness. Understanding the distinct compositions and applications helps artists choose between long-lasting vibrancy of watercolor pigments and the fluidity and brightness of dye-based inks.
Composition and Properties Comparison
Watercolor paints consist primarily of pigments suspended in a water-soluble binder such as gum arabic, offering transparency and smooth blending properties ideal for layering and washes. Dye-based inks are composed of soluble colorants dissolved in a liquid vehicle, providing intense, vibrant hues with faster drying times but less lightfastness and potential bleed on porous surfaces. The choice between watercolor and dye-based ink depends on desired effects, permanence, and substrate compatibility, with watercolors favored for artistic depth and dye inks preferred for crisp, vivid lines.
Color Vibrancy and Pigmentation
Watercolor exhibits softer, more translucent hues due to its pigment particles suspended in a water medium, resulting in a delicate, layered vibrancy that changes with water dilution. Dye-based ink offers intense, saturated colors with high pigmentation that penetrates paper fibers, producing sharp, bright results ideal for bold illustrations and calligraphy. The choice between watercolor and dye-based ink depends on desired color depth and vibrancy, with watercolors excelling in subtle tonal variations and dye-based inks delivering consistent, vivid pigmentation.
Application Techniques and Tools
Watercolor and dye-based ink differ significantly in application techniques and tools, with watercolor typically applied using brushes that hold and control water for blending and layering effects, while dye-based inks often utilize pens, markers, or dip tools that provide fine lines and vibrant, uniform color saturation. Watercolors require techniques like wet-on-wet, wet-on-dry, and glazing to achieve transparency and gradient effects, whereas dye-based inks excel in precision work, calligraphy, and rapid drying properties that support detailed illustrations and graphic designs. Tools such as synthetic or sable brushes are preferred for watercolors to manipulate pigment flow, while technical pens, brush pens, and airbrushes are favored for dye-based inks to maximize color intensity and crisp line work.
Drying Time and Layering Effects
Watercolor paints typically have a slower drying time, allowing for smoother blending and gradient effects, while dye-based inks dry much faster, enabling quicker layering without extensive waiting. The slower evaporation rate of watercolors facilitates more subtle transitions and softer edges, ideal for wet-on-wet techniques. In contrast, dye-based inks offer sharp, vivid layers with less bleeding, making them suitable for precise layering and fine detail work.
Water Resistance and Longevity
Watercolor paints generally lack water resistance, as their pigments are designed to rehydrate and blend with water, leading to potential smudging or color fading when exposed to moisture. Dye-based inks, often used in fountain pens and markers, tend to be less water-resistant compared to pigment-based inks, making them prone to running and fading over time when wet. For projects requiring durability and longevity, pigment inks or waterproof markers are typically preferred over dye-based inks and traditional watercolors.
Paper Compatibility and Surface Behavior
Watercolor exhibits excellent compatibility with textured and heavyweight papers, allowing pigments to settle evenly and blend seamlessly due to its granulating properties. Dye-based ink performs best on smooth, coated surfaces where vibrant colors achieve high saturation and sharp detail, but it may cause bleeding and feathering on absorbent papers. While watercolor creates depth through layering and pigment interaction on rough fibers, dye-based ink relies on rapid absorption and drying, affecting its surface behavior and color intensity across different paper types.
Artistic Styles and Suitable Projects
Watercolor offers translucent layers and subtle blending ideal for landscapes, portraits, and impressionistic styles, enhancing depth and texture in artworks. Dye-based ink provides vibrant, intense colors with rapid drying suitable for detailed illustrations, calligraphy, and graphic design projects requiring precision and bold lines. Artists often choose watercolor for fluid, expressive effects, while dye-based ink excels in sharp, defined visuals and mixed media compositions.
Cost and Accessibility
Watercolor paints typically cost more upfront than dye-based inks but offer a greater range of pigments and blending possibilities, making them a preferred choice for artists seeking versatility. Dye-based inks are generally more affordable and widely accessible, easily found in pens, markers, and refill bottles at varying price points suitable for hobbyists and professionals. While dyes dry quickly and provide vibrant colors, watercolors require more careful handling but allow for unique effects, influencing their cost-effectiveness depending on the project scope.
Choosing the Right Medium for Your Art
Watercolor offers a transparent, blendable medium ideal for creating delicate washes and subtle gradients, making it perfect for landscapes and soft, atmospheric effects. Dye-based ink provides vibrant, fast-drying colors with sharp lines and high saturation, preferred for detailed illustrations and graphic work. Selecting between watercolor and dye-based ink depends on your desired visual outcome, whether you prioritize fluid softness or crisp precision in your artwork.
Watercolor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com