Atmospheric perspective enhances depth in landscapes by simulating how air particles affect color and clarity over distance, resulting in muted tones and less detail farther away. This technique mimics natural atmospheric conditions, making scenes appear more realistic and immersive. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering atmospheric perspective can elevate your artwork's spatial depth.
Table of Comparison
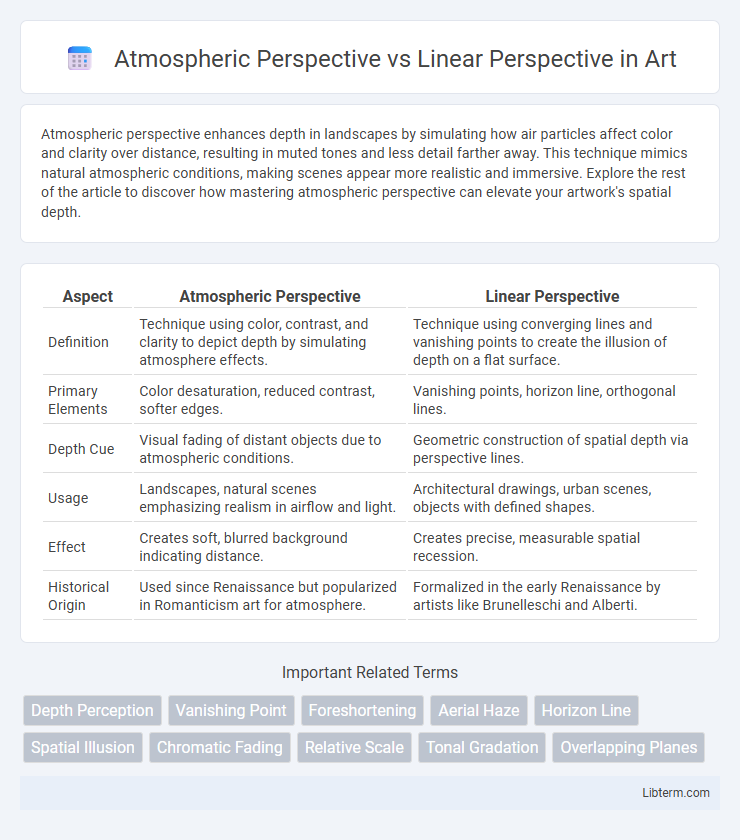
| Aspect | Atmospheric Perspective | Linear Perspective |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique using color, contrast, and clarity to depict depth by simulating atmosphere effects. | Technique using converging lines and vanishing points to create the illusion of depth on a flat surface. |
| Primary Elements | Color desaturation, reduced contrast, softer edges. | Vanishing points, horizon line, orthogonal lines. |
| Depth Cue | Visual fading of distant objects due to atmospheric conditions. | Geometric construction of spatial depth via perspective lines. |
| Usage | Landscapes, natural scenes emphasizing realism in airflow and light. | Architectural drawings, urban scenes, objects with defined shapes. |
| Effect | Creates soft, blurred background indicating distance. | Creates precise, measurable spatial recession. |
| Historical Origin | Used since Renaissance but popularized in Romanticism art for atmosphere. | Formalized in the early Renaissance by artists like Brunelleschi and Alberti. |
Introduction to Visual Depth in Art
Atmospheric perspective enhances visual depth by simulating the effect of the atmosphere on distant objects, using softer contrasts, decreased saturation, and bluish hues to create a sense of depth. Linear perspective relies on geometric principles, such as converging parallel lines and vanishing points, to depict spatial depth and three-dimensionality on a flat surface. Combining these techniques allows artists to achieve realistic spatial relationships and a convincing illusion of depth in their compositions.
Defining Atmospheric Perspective
Atmospheric perspective refers to the technique in visual art where depth and distance are conveyed by simulating the effect of the atmosphere on objects viewed from afar, resulting in color desaturation, reduced contrast, and haziness as objects recede into the background. This method emphasizes the gradation of tones, cooler hues, and diminished detail to create a sense of space and depth that mimics real-world viewing conditions. Unlike linear perspective, which relies on geometric lines converging at vanishing points to structure spatial relationships, atmospheric perspective manipulates color and clarity to evoke a realistic impression of distance.
Defining Linear Perspective
Linear perspective is a geometric technique that creates the illusion of depth and volume on a flat surface by converging parallel lines toward one or more vanishing points on the horizon. It relies on mathematical principles to depict spatial relationships and scale objects accurately as they recede into the distance. This method contrasts with atmospheric perspective, which uses color and clarity variations to suggest depth.
Historical Development of Perspective Techniques
The historical development of perspective techniques reveals distinct evolutions in atmospheric and linear perspectives, with atmospheric perspective emerging in the Renaissance to depict depth through color and clarity changes, while linear perspective was mathematically formalized by Filippo Brunelleschi in the early 15th century to create accurate spatial representation using vanishing points. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci advanced atmospheric perspective by studying natural light and haze effects, complementing the precise geometric rules of linear perspective that dominated Western art. These perspectives combined to revolutionize realism in painting, influencing artistic methods and visual perception from the Renaissance onward.
Key Principles of Atmospheric Perspective
Atmospheric perspective relies on the key principle that objects appear lighter, less detailed, and bluer as their distance from the viewer increases due to the scattering of light by particles in the air. This effect creates a sense of depth by simulating the natural haze and color shifts observed in the atmosphere. Unlike linear perspective, which uses geometric convergence and vanishing points, atmospheric perspective depends on tonal and color changes to convey spatial relationships.
Key Principles of Linear Perspective
Linear perspective is based on the principle that parallel lines converge at a single vanishing point on the horizon, creating a sense of depth and spatial accuracy. Objects appear smaller as they recede into the distance, following consistent scale reductions relative to their position along the converging lines. This technique relies on geometric precision to simulate three-dimensional space on a two-dimensional surface, distinguishing it from atmospheric perspective, which uses color and clarity changes to convey depth.
Comparing Visual Effects: Atmosphere vs Geometry
Atmospheric perspective enhances depth perception by simulating the scattering of light through air, causing distant objects to appear lighter, blurrier, and less saturated, which mimics natural atmospheric conditions. Linear perspective relies on geometric principles with converging lines toward vanishing points, creating precise spatial relationships and scale accuracy on flat surfaces. The visual effect of atmospheric perspective emphasizes mood and spatial distance through color and clarity shifts, while linear perspective delivers exact structural realism and dimensional order.
Application in Painting and Illustration
Atmospheric perspective enhances depth in painting by using color shifts, value contrasts, and reduced detail to simulate how the atmosphere affects distant objects, creating a natural sense of spatial recession. Linear perspective relies on geometric rules, such as vanishing points and converging lines, to construct accurate spatial relationships and proportions in illustrations. Combining both techniques allows artists to achieve realistic depth effects, with atmospheric perspective adding mood and softness while linear perspective ensures structural accuracy.
Choosing the Right Perspective Technique
Choosing the right perspective technique depends on the visual goals and environmental context of the artwork. Atmospheric perspective enhances depth by simulating color desaturation and reduced contrast over distance, ideal for outdoor scenes with expansive landscapes. Linear perspective relies on converging lines to create precise spatial relationships, making it essential for architectural or interior compositions requiring accurate proportions.
Atmospheric Perspective vs Linear Perspective: Summary and Final Thoughts
Atmospheric perspective enhances depth perception by simulating the effect of air and light scattering, causing distant objects to appear lighter, less saturated, and blurrier, whereas linear perspective relies on geometric principles like vanishing points and converging lines to create spatial depth. Mastery of atmospheric perspective involves understanding color shifts and contrast reduction over distance, complementing the precise spatial framework established by linear perspective. Both techniques are essential in art and design for creating realistic and immersive environments by balancing optical phenomena with structural accuracy.
Atmospheric Perspective Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com