Screenprinting offers a versatile and cost-effective method for producing high-quality designs on various materials such as fabric, paper, and plastic. This technique uses a mesh screen, ink, and a squeegee to transfer images with vivid colors and long-lasting durability. Discover how screenprinting can elevate your creative projects by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
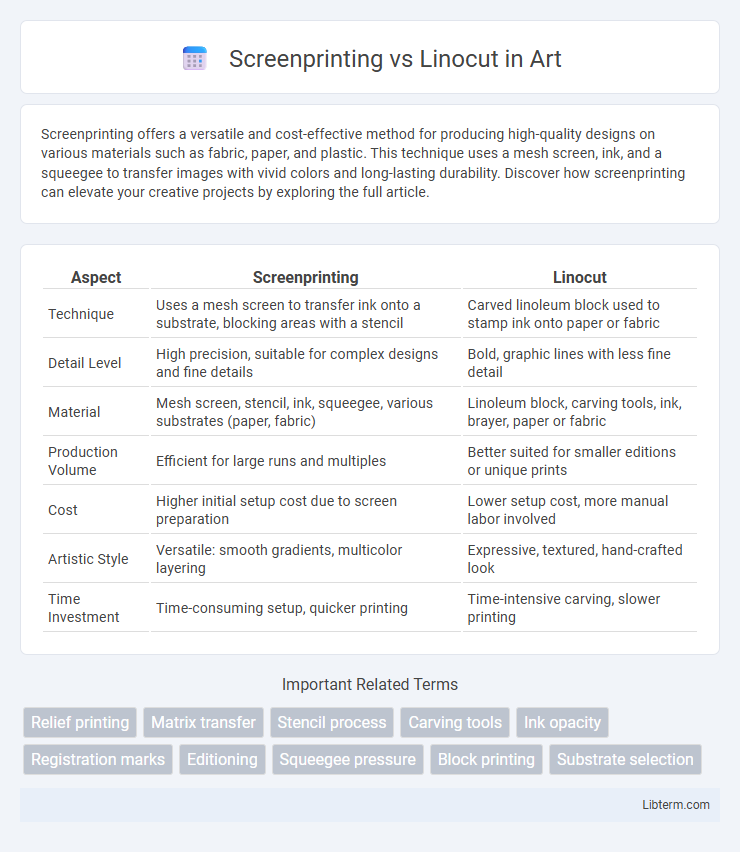
| Aspect | Screenprinting | Linocut |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Uses a mesh screen to transfer ink onto a substrate, blocking areas with a stencil | Carved linoleum block used to stamp ink onto paper or fabric |
| Detail Level | High precision, suitable for complex designs and fine details | Bold, graphic lines with less fine detail |
| Material | Mesh screen, stencil, ink, squeegee, various substrates (paper, fabric) | Linoleum block, carving tools, ink, brayer, paper or fabric |
| Production Volume | Efficient for large runs and multiples | Better suited for smaller editions or unique prints |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost due to screen preparation | Lower setup cost, more manual labor involved |
| Artistic Style | Versatile: smooth gradients, multicolor layering | Expressive, textured, hand-crafted look |
| Time Investment | Time-consuming setup, quicker printing | Time-intensive carving, slower printing |
Introduction to Screenprinting and Linocut
Screenprinting involves pushing ink through a mesh stencil to create bold, vibrant images with precise color layering, making it ideal for mass production and detailed graphic designs. Linocut is a relief printing technique where artists carve designs into linoleum blocks, producing textured prints with strong contrasts and organic, hand-crafted qualities. Both methods offer unique artistic expressions, with screenprinting emphasizing sharp detail and reproducibility, while linocut highlights manual craftsmanship and tactile depth.
Historical Background of Screenprinting and Linocut
Screenprinting traces its origins to ancient China during the Song Dynasty, evolving significantly in the early 20th century with advancements in stenciling techniques. Linocut, emerging in the early 20th century as well, gained prominence through artists like Pablo Picasso who popularized the use of linoleum blocks for printmaking. Both methods reflect distinct historical trajectories: screenprinting rooted in fabric decoration and commercial use, while linocut developed primarily as an artistic medium within the modernist movement.
Core Principles: How Screenprinting Works
Screenprinting operates by forcing ink through a fine mesh screen that has been selectively blocked to create a stencil, allowing ink to pass only where the design is intended. The screen is stretched tightly over a frame, and a squeegee pushes the ink across the surface, transferring the image onto the printing substrate. This technique enables the production of vibrant, consistent prints on a variety of materials, including textiles, paper, and plastics.
Core Principles: How Linocut Works
Linocut involves carving a design into a linoleum block, removing the negative spaces to create raised areas that hold ink. The ink is then applied to the raised surface, and paper or fabric is pressed onto the block to transfer the image. This relief printing technique emphasizes manual craftsmanship and allows for bold, textured prints with distinctive carving marks.
Materials and Tools Required for Each Technique
Screenprinting utilizes a mesh screen, squeegee, emulsion, and specialized inks that require precise preparation and exposure for stencil creation. Linocut demands a linoleum block, carving tools with various blade shapes, and block printing ink, emphasizing manual carving skills and direct contact printing. Both methods require paper or fabric as substrates but differ significantly in texture, detail potential, and material handling.
Visual Styles and Artistic Effects Compared
Screenprinting offers vibrant, consistent color application and sharp lines ideal for bold, graphic designs with smooth gradients, while linocut produces textured, organic marks with visible carving patterns that create a raw, tactile quality. The layering capability in screenprinting enables complex color separations and precise overlays, contrasting with linocut's characteristic high-contrast imagery and limited color palette derived from manual ink application. Artists choose screenprinting for crisp, commercial aesthetics, whereas linocut appeals for expressive, handcrafted visuals emphasizing texture and depth.
Advantages of Screenprinting
Screenprinting offers superior versatility with the ability to print on various materials such as fabric, paper, glass, and plastic, making it ideal for diverse projects. This technique allows for vibrant, high-opacity colors and precise detail reproduction, which enhances the overall quality of prints. The process is also highly scalable for large production runs, ensuring consistency and efficiency in commercial and artistic applications.
Advantages of Linocut
Linocut offers distinct advantages such as greater ease in carving due to its softer, more pliable material compared to wood or screenprinting stencils, allowing for more detailed and precise designs. The technique is cost-effective, requiring minimal tools and materials, making it accessible for beginners and small-scale printmakers. Linocut prints boast a unique tactile quality and bold, high-contrast lines that provide an expressive and handcrafted aesthetic unmatched by screenprinting's smoother, more uniform results.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Screenprinting and linocut both face challenges such as inconsistent ink application and image clarity issues. Common troubleshooting methods include adjusting ink viscosity, maintaining proper pressure, and ensuring accurate registration to prevent misalignment. Proper cleaning of screens and carving tools also helps avoid clogging and unwanted marks, enhancing print quality.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Screenprinting offers vibrant color layering and durability, making it ideal for mass production and detailed designs on fabrics or posters. Linocut provides a tactile, handcrafted aesthetic with bold contrasts, suited for small editions and artistic expressions on paper or textiles. Consider project scale, desired texture, and color complexity to select the technique that best matches your creative goals and production needs.
Screenprinting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com