Photomontage is a creative technique that combines multiple photographs into a single seamless image to convey a new, often surreal or conceptual narrative. This method is widely used in advertising, art, and digital media to enhance visual storytelling and capture the viewer's attention. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective photomontage techniques and tools that can elevate your visual projects.
Table of Comparison
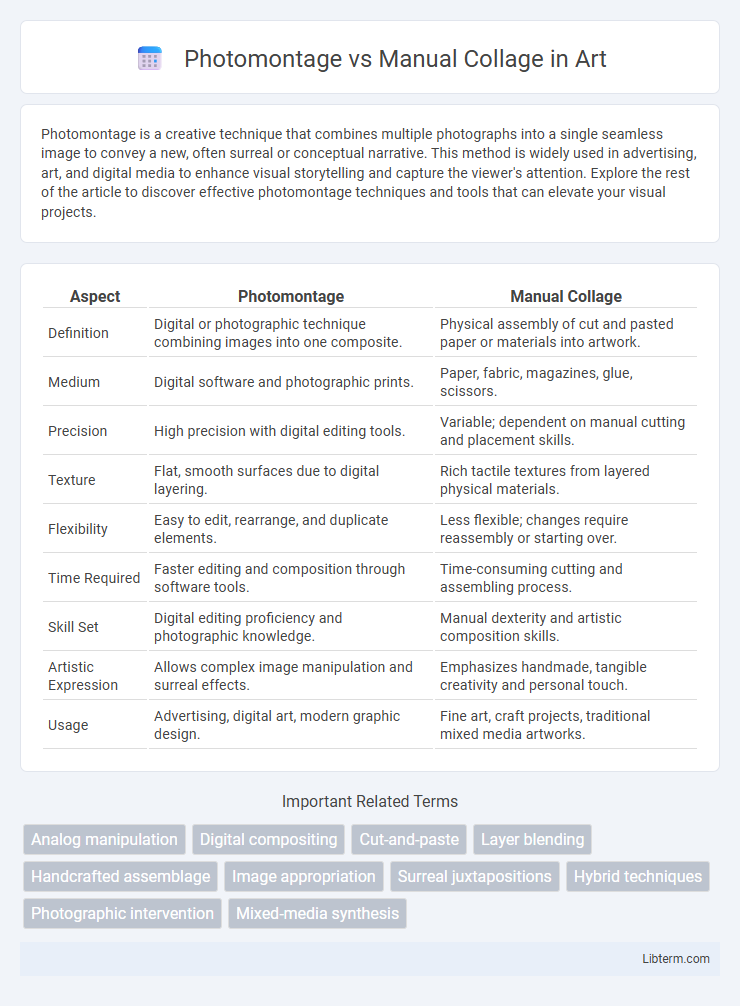
| Aspect | Photomontage | Manual Collage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital or photographic technique combining images into one composite. | Physical assembly of cut and pasted paper or materials into artwork. |
| Medium | Digital software and photographic prints. | Paper, fabric, magazines, glue, scissors. |
| Precision | High precision with digital editing tools. | Variable; dependent on manual cutting and placement skills. |
| Texture | Flat, smooth surfaces due to digital layering. | Rich tactile textures from layered physical materials. |
| Flexibility | Easy to edit, rearrange, and duplicate elements. | Less flexible; changes require reassembly or starting over. |
| Time Required | Faster editing and composition through software tools. | Time-consuming cutting and assembling process. |
| Skill Set | Digital editing proficiency and photographic knowledge. | Manual dexterity and artistic composition skills. |
| Artistic Expression | Allows complex image manipulation and surreal effects. | Emphasizes handmade, tangible creativity and personal touch. |
| Usage | Advertising, digital art, modern graphic design. | Fine art, craft projects, traditional mixed media artworks. |
Introduction to Photomontage and Manual Collage
Photomontage is a digital technique that seamlessly blends multiple photographs into a single composition, leveraging software tools to create intricate and precise visual narratives. Manual collage involves physically assembling various materials--such as paper, fabric, and photographs--onto a surface, emphasizing tactile creativity and texture manipulation. Both methods serve as powerful artistic practices for combining disparate images, yet photomontage relies on digital technology while manual collage centers on hands-on craftsmanship.
Defining Photomontage: Techniques and Tools
Photomontage involves digitally combining multiple photographs using software like Adobe Photoshop, enabling precise layering, blending, and manipulation of images to create seamless compositions. Techniques include masking, layering, color correction, and digital retouching, which enhance realism and allow complex visual narratives. Unlike manual collage, photomontage leverages digital tools for accuracy, flexibility, and the ability to easily edit or experiment with different elements.
Understanding Manual Collage: Traditional Artistry
Manual collage emphasizes hands-on craftsmanship by assembling physical materials such as paper, fabric, and photographs to create textured, layered compositions. This traditional artistry requires meticulous cutting, arranging, and gluing, allowing for tactile interaction and unique, one-of-a-kind artworks. Unlike digital photomontage, manual collage preserves the tangible quality and unpredictability inherent in handcrafted pieces.
Historical Evolution: From Scissors to Software
Photomontage originated in the early 20th century as artists cut and pasted photographic images with scissors to create new compositions, reflecting avant-garde movements like Dada and Surrealism. Manual collage evolved through tactile techniques involving paper, fabric, and mixed media, emphasizing texture and physical layering. The digital age introduced software tools like Adobe Photoshop, transforming photomontage into a versatile art form with limitless manipulation possibilities, blending historical craftsmanship with modern technology.
Key Differences: Digital Precision vs. Hands-on Creation
Photomontage utilizes digital tools to seamlessly combine multiple images with precise alignment, layering, and editing capabilities, offering unmatched accuracy and flexibility in composition. Manual collage relies on physical materials such as paper, fabric, and photographs, emphasizing tactile creativity and the unique textures and imperfections that result from hands-on assembly. The key difference lies in photomontage's digital precision and ease of modification versus manual collage's organic, handcrafted aesthetic and tangible interaction.
Artistic Expression: Unique Features of Each Medium
Photomontage leverages digital tools and photographic elements to create surreal, layered compositions that blend reality and imagination, offering precise control over image manipulation and seamless integration. Manual collage, crafted with tactile materials like paper, fabric, and found objects, conveys raw texture and physicality, emphasizing spontaneity and the artist's hand. Each medium uniquely shapes artistic expression through the interplay of technology and materiality, allowing distinct narrative and aesthetic possibilities.
Accessibility: Materials, Skills, and Learning Curves
Photomontage requires digital tools like image editing software, offering quick adjustments but demanding computer literacy and higher initial investment. Manual collage uses tangible materials such as paper, scissors, and glue, making it more accessible for beginners and those without digital access. The learning curve for manual collage centers on hands-on techniques, while photomontage involves mastering software features and digital workflow.
Creative Possibilities: Limitations and Freedoms
Photomontage enables precise manipulation of images using digital tools, allowing seamless blending and infinite layering, which expands creative possibilities beyond physical constraints. Manual collage offers tactile experimentation with texture and material diversity but is limited by the physical space and permanence of glue or tape. Both methods balance creative freedoms and limitations, with photomontage excelling in flexibility and correction, while manual collage provides unique sensory and analog experiences.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Photomontage, pioneered by artists like Hannah Hoch and John Heartfield, utilizes photographic images combined digitally or through mechanical means to create surreal or politically charged compositions, exemplified by Hoch's "Cut with the Kitchen Knife." Manual collage, popularized by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, involves physically assembling paper, fabric, and found objects to produce tactile artworks such as Picasso's "Still Life with Chair Caning." Both techniques have significantly influenced modern art, with photomontage emphasizing digital manipulation and manual collage focusing on material texture and layering.
Choosing Your Medium: Factors to Consider
Choosing between photomontage and manual collage hinges on factors such as desired precision, texture, and artistic expression. Photomontage offers digital manipulation for seamless blending and intricate detail, ideal for project revisions and reproducibility. Manual collage provides tactile depth and unique material interactions, appealing to artists seeking authentic, hands-on creativity and textural variety.
Photomontage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com