Bauhaus revolutionized modern design by integrating art, craft, and technology into a cohesive philosophy emphasizing functionality and simplicity. Its influence spans architecture, graphic design, interior decor, and typography, shaping visual culture throughout the 20th century and beyond. Discover how Bauhaus principles can inspire your creative projects by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
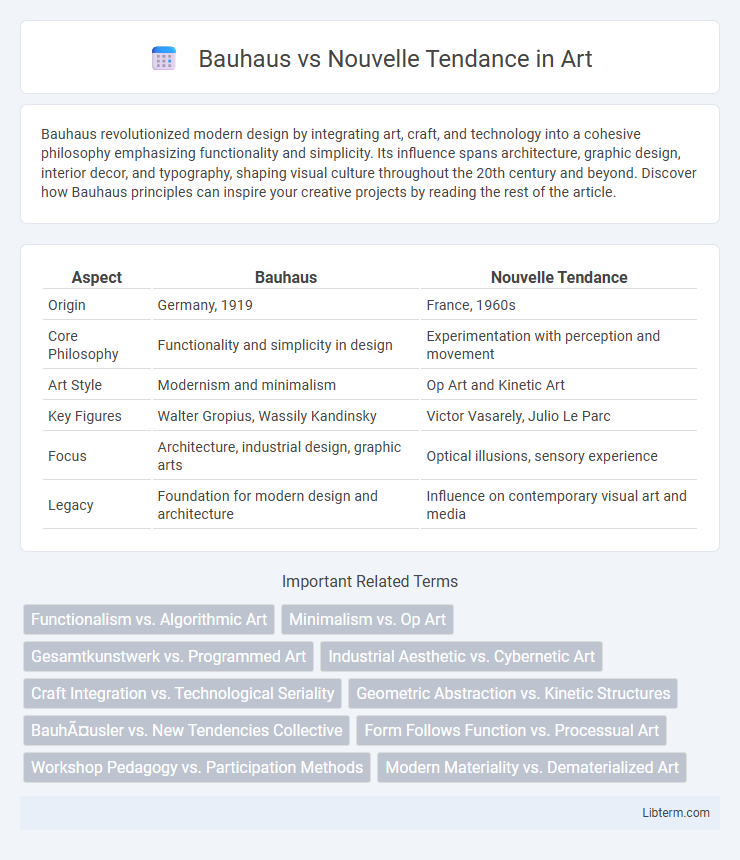
| Aspect | Bauhaus | Nouvelle Tendance |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Germany, 1919 | France, 1960s |
| Core Philosophy | Functionality and simplicity in design | Experimentation with perception and movement |
| Art Style | Modernism and minimalism | Op Art and Kinetic Art |
| Key Figures | Walter Gropius, Wassily Kandinsky | Victor Vasarely, Julio Le Parc |
| Focus | Architecture, industrial design, graphic arts | Optical illusions, sensory experience |
| Legacy | Foundation for modern design and architecture | Influence on contemporary visual art and media |
Introduction to Bauhaus and Nouvelle Tendance
Bauhaus emerged in 1919 as a revolutionary German design school emphasizing functionality, simplicity, and the integration of art, craft, and technology. Nouvelle Tendance, founded in the 1960s, focused on kinetic and optical art, exploring perception and interactivity through innovative materials and dynamic forms. Both movements significantly influenced modern art and design, with Bauhaus shaping architecture and industrial design, while Nouvelle Tendance pushed the boundaries of visual experience and experimentation.
Historical Contexts and Origins
Bauhaus emerged in Germany in 1919, influenced by the aftermath of World War I and the desire to unify art, craft, and technology into functional design. Nouvelle Tendance originated in the early 1960s in Europe, rooted in the post-war avant-garde movement and experimental visual art focused on perception and optical illusions. Both movements reflect their distinct historical contexts: Bauhaus responds to industrialization and social reform, while Nouvelle Tendance explores new media and viewer interaction in the context of mid-20th-century artistic innovation.
Core Philosophies and Artistic Aims
Bauhaus emphasized functionality and simplicity, integrating art, craft, and technology to create practical designs that serve everyday life. Nouvelle Tendance prioritized viewer interaction and experimental forms, using optical illusions and kinetic art to challenge perception and engage audiences dynamically. Both movements sought to break traditional boundaries, but Bauhaus focused on uniting art with industrial production while Nouvelle Tendance explored sensory experience and participatory art.
Key Artists and Influencers
Key artists of the Bauhaus movement include Walter Gropius, Paul Klee, Wassily Kandinsky, and Marcel Breuer, whose works emphasized functional design and the integration of art, craft, and technology. Nouvelle Tendance featured influential figures like Yves Klein, Getulio Alviani, and Francois Morellet, who explored kinetic and optical art through experimental use of light, movement, and perception. Both movements significantly shaped modern art and design by challenging traditional aesthetics and focusing on innovation.
Design Principles: Bauhaus vs Nouvelle Tendance
Bauhaus design principles emphasize functionalism, simplicity, and the integration of art, craft, and technology, with a focus on geometric forms and minimal ornamentation. Nouvelle Tendance prioritizes perceptual experimentation, optical effects, and kinetic interaction, using dynamic shapes and vibrant colors to challenge viewers' visual experiences. Bauhaus centers on rational construction, while Nouvelle Tendance explores sensory engagement through movement and illusion.
Approaches to Functionality and Aesthetic
Bauhaus emphasized a seamless integration of functionality and aesthetic through minimalism, geometric forms, and practical materials, prioritizing usability and mass production. Nouvelle Tendance challenged traditional forms by exploring kinetic and perceptual art, focusing on dynamic interaction and sensory experience rather than strict functional utility. Both movements shaped modern design but diverged in Bauhaus's focus on utilitarian simplicity versus Nouvelle Tendance's emphasis on experimental, perceptual aesthetics.
Influence on Architecture and Visual Arts
Bauhaus revolutionized architecture and visual arts through its functional design principles, emphasizing simplicity, geometric forms, and integration of craft with industrial techniques, profoundly shaping modernist architecture worldwide. Nouvelle Tendance, emerging in the 1960s, introduced kinetic and op art elements, focusing on perception, movement, and optical illusions, influencing interactive visual arts and experimental architectural facades. Both movements redefined aesthetic approaches by merging artistic innovation with technological advancements, impacting urban design, interior spaces, and graphic design.
Impact on Modern Design Movements
Bauhaus revolutionized modern design by introducing functionalism and simplicity, emphasizing clean lines and mass production techniques that influenced architecture, furniture, and graphic design globally. Nouvelle Tendance expanded on this legacy by prioritizing kinetic art and perceptual experiences, integrating movement and viewer interaction, which significantly impacted the development of Op Art and interactive installations. Both movements collectively shaped modern design's evolution by merging practicality with innovative visual experimentation, setting foundations for contemporary artistic expression.
Criticisms and Controversies
Bauhaus faced criticism for its perceived rigidity and functionalism, often seen as neglecting emotional expression and cultural diversity in design. Nouvelle Tendance sparked controversy due to its experimental approach, challenging traditional aesthetics and provoking debates over the role of art in society. Both movements questioned established norms but diverged significantly in methodology and ideological emphasis, leading to polarized receptions within the art and design communities.
Legacy and Contemporary Relevance
Bauhaus profoundly influenced modern design, emphasizing functionalism and simplicity that continue to inspire architecture, graphic design, and industrial products globally. Nouvelle Tendance introduced experimental, participatory art forms, shaping contemporary interactive installations and kinetic art movements. Both legacies underscore enduring principles--Bauhaus in streamlined aesthetics and Nouvelle Tendance in dynamic viewer engagement--vital to contemporary creative practices.
Bauhaus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com