Pastiche is an artistic work that imitates the style or character of one or more other artists, often blending various elements to create a new piece that pays homage to its sources. This technique is common in literature, film, and visual arts as a celebration or critique of the original works. Explore the rest of the article to discover how pastiche influences creativity and how you can recognize it in different mediums.
Table of Comparison
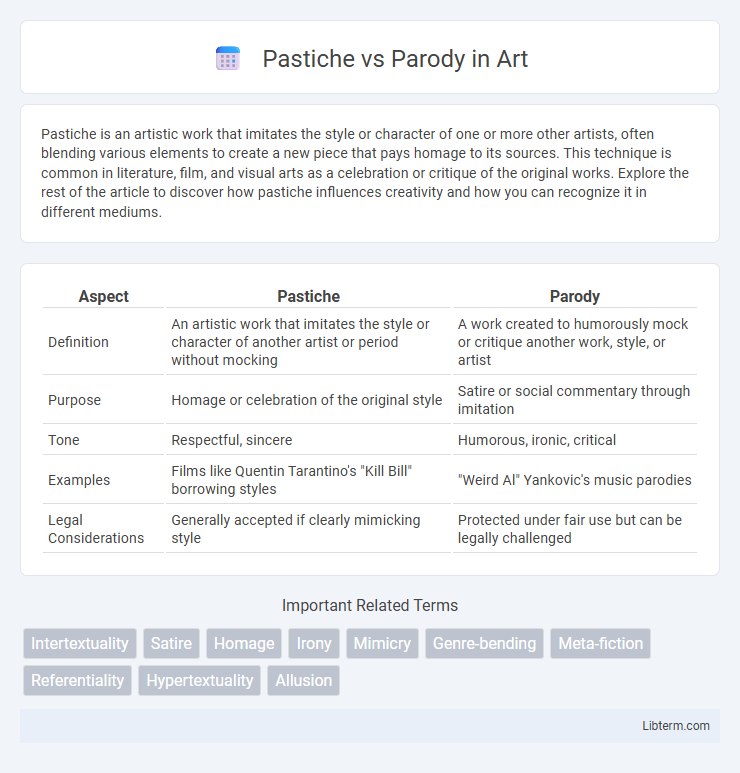
| Aspect | Pastiche | Parody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An artistic work that imitates the style or character of another artist or period without mocking | A work created to humorously mock or critique another work, style, or artist |
| Purpose | Homage or celebration of the original style | Satire or social commentary through imitation |
| Tone | Respectful, sincere | Humorous, ironic, critical |
| Examples | Films like Quentin Tarantino's "Kill Bill" borrowing styles | "Weird Al" Yankovic's music parodies |
| Legal Considerations | Generally accepted if clearly mimicking style | Protected under fair use but can be legally challenged |
Understanding Pastiche and Parody
Pastiche involves imitating the style or character of a work or artist in a respectful and celebratory manner, often blending multiple influences to create a new composition. Parody, by contrast, exaggerates or mocks the original work's style or content to produce humor or critique. Both techniques rely on recognizable elements of the source material, but pastiche honors the original, while parody aims to entertain or expose flaws through satire.
Defining the Art of Pastiche
Pastiche is an artistic technique that involves imitating the style, tone, or character of another work in a respectful and celebratory manner, often blending multiple influences without mocking the source material. Unlike parody, which exaggerates and distorts to create humor or criticism, pastiche serves as homage, preserving the original work's aesthetic and thematic elements. This form of art allows creators to explore and honor diverse genres or periods, enriching cultural dialogues through stylistic replication.
Breaking Down the Concept of Parody
Parody involves the imitation of a particular work, style, or genre with deliberate exaggeration for comedic or satirical effect, emphasizing critique or humor. It often relies on recognizable elements from the original to create a humorous contrast that highlights flaws or absurdities. Breaking down the concept of parody reveals its role in cultural commentary, using exaggeration and mimicry to engage audiences through familiar references and social critique.
Key Differences: Pastiche vs Parody
Pastiche imitates the style or character of another work or artist as a form of homage, often blending multiple influences without mocking the original, while parody exaggerates or distorts distinctive features to create humor or satire. Pastiche emphasizes respectful replication and celebration of source material, contrasting parody's intent to critique or entertain through ridicule. The key difference lies in pastiche's earnest imitation versus parody's playful or critical subversion of the original work.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Pastiche originated in the Italian Renaissance, where artists and writers imitated classical styles to pay homage and demonstrate mastery, evolving as a respectful blend of various influences across literature and visual arts. Parody dates back to ancient Greek literature, notably Aristophanes' comedic plays, where it functioned as satire by exaggerating and mocking original works to critique social and political issues. Over time, pastiche retained its celebratory tone, while parody increasingly emphasized humor and irony in cultural commentary.
Techniques Used in Pastiche
Pastiche employs imitation techniques that honor and replicate the style, motifs, and themes of the original work without mockery, often blending multiple influences to create a respectful homage. It utilizes stylistic mimicry, tone replication, and structural emulation to evoke the essence of the source material while adding a unique artistic touch. Key techniques include layering intertextual references, maintaining genre-specific conventions, and incorporating characteristic visual or narrative elements to produce a coherent and appreciative re-creation.
How Parody Functions in Culture
Parody functions in culture by using imitation to critique or satirize existing works, highlighting societal norms and exposing underlying absurdities. It operates as a form of cultural commentary that both entertains and provokes critical thinking, often subverting established narratives. Through exaggeration and humor, parody encourages audiences to question original texts and the cultural values they represent.
Notable Examples of Pastiche in Media
Pastiche in media often celebrates original works by blending styles and genres without satire, as seen in Quentin Tarantino's "Kill Bill," which fuses martial arts cinema with spaghetti western elements. Another notable example is Wes Anderson's "The Grand Budapest Hotel," which mimics the aesthetics of early 20th-century European storytelling and design. These pastiches honor their source materials through respectful imitation rather than comedic distortion.
Famous Parodies and Their Impact
Famous parodies such as Mel Brooks' "Young Frankenstein" and Weird Al Yankovic's musical spoofs have significantly impacted pop culture by humorously critiquing original works while entertaining audiences. These parodies often highlight the quirks and conventions of their source material, fostering a deeper appreciation and critical perspective among fans. Their success demonstrates how parody serves as both homage and satire, influencing media and inspiring new creative expressions.
Choosing Between Pastiche and Parody in Creative Work
Choosing between pastiche and parody depends on the creator's intent and the desired audience reaction; pastiche respectfully imitates a style to celebrate or honor, while parody employs exaggeration to critique or humorously comment on the original work. Understanding the nuances of these techniques allows artists to evoke nostalgia or provoke thought effectively without alienating the audience. An informed choice enhances creative impact by aligning the work's tone and purpose with the expectations and cultural context of its viewers.
Pastiche Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com