Credit risk evaluates the potential for a borrower to default on loan obligations, affecting lenders and investors through financial losses. Accurate assessment of credit risk involves analyzing credit scores, financial history, and market conditions to minimize exposure. Explore the rest of this article to understand how managing credit risk can protect your financial interests and optimize lending decisions.
Table of Comparison
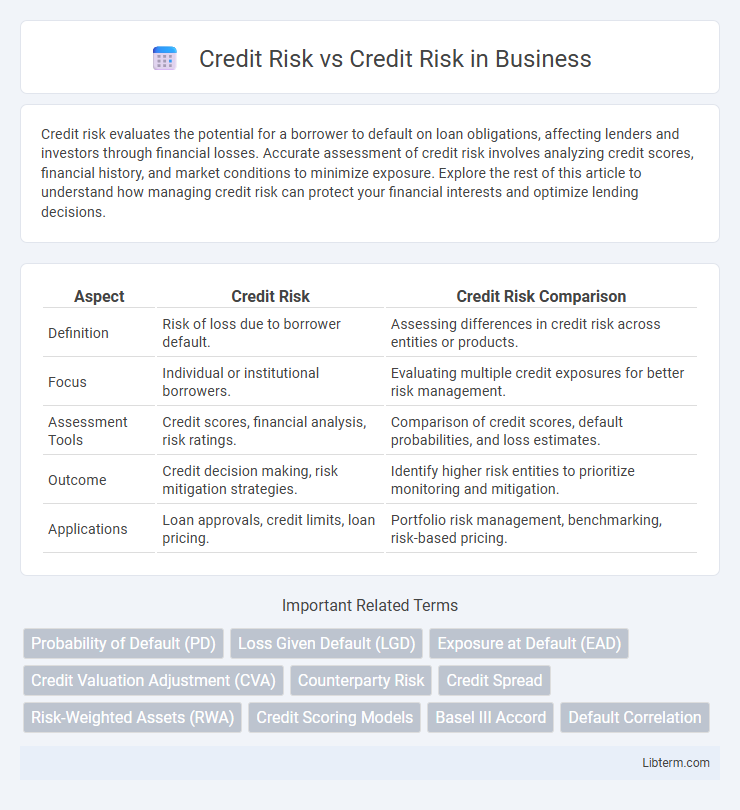
| Aspect | Credit Risk | Credit Risk Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Risk of loss due to borrower default. | Assessing differences in credit risk across entities or products. |
| Focus | Individual or institutional borrowers. | Evaluating multiple credit exposures for better risk management. |
| Assessment Tools | Credit scores, financial analysis, risk ratings. | Comparison of credit scores, default probabilities, and loss estimates. |
| Outcome | Credit decision making, risk mitigation strategies. | Identify higher risk entities to prioritize monitoring and mitigation. |
| Applications | Loan approvals, credit limits, loan pricing. | Portfolio risk management, benchmarking, risk-based pricing. |
Understanding Credit Risk: A Definition
Credit risk refers to the potential loss a lender faces when a borrower fails to meet their debt obligations, impacting financial stability and lending decisions. Understanding credit risk involves assessing the borrower's creditworthiness through factors such as credit history, income, and outstanding debts to predict the likelihood of default. Effective credit risk management employs quantitative models and risk scoring to minimize potential losses and ensure sound credit allocation.
Types of Credit Risk in Financial Systems
Types of credit risk in financial systems primarily include default risk, where borrowers fail to meet debt obligations, and counterparty risk, involving the possibility that the other party in a financial transaction may not fulfill contractual obligations. Concentration risk arises when exposure is heavily skewed towards a single borrower or sector, increasing vulnerability to specific economic downturns. Migration risk refers to the deterioration in credit quality leading to lower credit ratings and higher loss provisions.
Credit Risk Assessment: Methods and Approaches
Credit risk assessment involves evaluating the likelihood that a borrower will default on their debt obligations using quantitative methods such as credit scoring models, logistic regression, and machine learning algorithms. Approaches also include qualitative analysis of factors like borrower's financial health, industry conditions, and macroeconomic trends to enhance predictive accuracy. Advanced techniques like stress testing and scenario analysis provide deeper insights into potential credit losses under adverse conditions.
Credit Risk vs Counterparty Risk: Key Differences
Credit risk refers to the possibility of a borrower failing to meet debt obligations, impacting lenders or investors directly. Counterparty risk specifically involves the risk that the other party in a financial transaction, such as derivatives or trading contracts, will default before settlement. Understanding the distinction is crucial for financial institutions managing loan portfolios versus transactional exposures.
Factors Influencing Credit Risk Exposure
Credit risk exposure is primarily influenced by borrower creditworthiness, economic conditions, and loan characteristics such as amount and duration. Industry stability and geographic location also impact the likelihood of default, as sectors facing downturns increase risk levels. Effective credit risk management relies on analyzing credit scores, debt-to-income ratios, and macroeconomic indicators to minimize potential losses.
Evaluating Credit Risk: Tools and Metrics
Evaluating credit risk involves assessing the likelihood of a borrower defaulting on debt obligations using tools such as credit scoring models, probability of default (PD), loss given default (LGD), and exposure at default (EAD). Advanced metrics like credit value at risk (Credit VaR) and credit migration analysis provide quantitative measures for potential losses and changes in credit quality. Incorporating these tools enables financial institutions to make data-driven lending decisions and manage portfolio risk effectively.
Managing Credit Risk: Best Practices
Effective management of credit risk involves rigorous credit assessment, continuous monitoring of borrower financial health, and the implementation of robust credit policies tailored to specific industry risks. Leveraging advanced data analytics and credit scoring models enhances the accuracy of risk evaluation and early identification of potential defaults. Establishing diversified credit portfolios and maintaining clear communication with clients further mitigates exposure and supports long-term financial stability.
Impact of Credit Risk on Lending Institutions
Credit risk directly affects lending institutions by increasing the likelihood of loan defaults, which can lead to significant financial losses and reduced profitability. Higher credit risk necessitates stricter lending criteria and elevated interest rates to compensate for potential losses, impacting loan growth and customer acquisition. Effective credit risk management is crucial for maintaining capital adequacy, regulatory compliance, and overall financial stability within lending institutions.
Credit Risk Mitigation Strategies
Credit risk mitigation strategies involve techniques such as collateralization, credit derivatives, and diversification to reduce potential losses from borrower default. Financial institutions implement credit scoring models and perform rigorous credit analysis to assess borrower creditworthiness and set appropriate lending terms. Effective risk mitigation enhances portfolio quality by minimizing exposure and improving recovery rates in adverse credit events.
Future Trends in Credit Risk Management
Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence are transforming credit risk management by enabling more accurate risk prediction and real-time monitoring. The integration of machine learning algorithms with big data sources allows lenders to assess borrower creditworthiness beyond traditional credit scores. Future trends indicate a shift towards automated decision-making processes and enhanced regulatory compliance through blockchain technology and enhanced transparency.
Credit Risk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com