A joint venture is a strategic business alliance where two or more parties collaborate to achieve a specific goal while sharing resources, risks, and rewards. This partnership allows companies to combine expertise, enter new markets, and enhance competitiveness without merging entirely. Discover how forming a joint venture can transform Your business opportunities by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
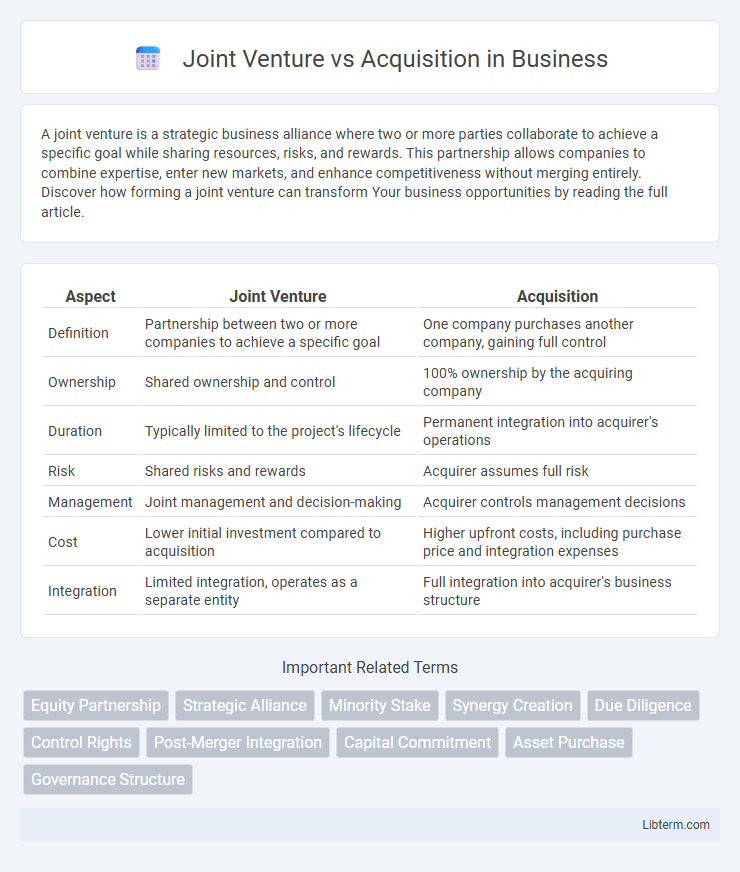
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Acquisition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between two or more companies to achieve a specific goal | One company purchases another company, gaining full control |
| Ownership | Shared ownership and control | 100% ownership by the acquiring company |
| Duration | Typically limited to the project's lifecycle | Permanent integration into acquirer's operations |
| Risk | Shared risks and rewards | Acquirer assumes full risk |
| Management | Joint management and decision-making | Acquirer controls management decisions |
| Cost | Lower initial investment compared to acquisition | Higher upfront costs, including purchase price and integration expenses |
| Integration | Limited integration, operates as a separate entity | Full integration into acquirer's business structure |
Introduction to Joint Venture and Acquisition
A joint venture involves two or more companies collaborating to create a new business entity while sharing resources, risks, and profits, allowing access to new markets and technologies without full ownership transfer. An acquisition occurs when one company purchases another, gaining complete control and integrating the acquired business into its operations to enhance market share, capabilities, or product offerings. Both strategies are essential for growth but differ in structure, control, and financial commitment.
Definition of Joint Venture
A Joint Venture (JV) is a strategic alliance where two or more parties create a new business entity, sharing ownership, risks, and profits. Unlike acquisitions, JVs maintain the independence of the participating companies while collaborating on specific projects or markets. This structure enables resource pooling and expertise exchange without transferring full control or ownership.
Definition of Acquisition
An acquisition occurs when one company purchases another company's shares or assets to assume control and ownership, integrating it into its existing operations. This strategic move allows the acquiring firm to quickly expand market share, diversify product lines, or gain access to new technologies and customers. Unlike joint ventures, acquisitions result in a complete transfer of ownership and responsibility from the target company to the acquiring entity.
Key Differences Between Joint Venture and Acquisition
A joint venture involves two or more companies creating a new, shared entity to pursue specific business objectives while maintaining their separate identities, whereas an acquisition results in one company purchasing and fully integrating another, leading to a single operational entity. In a joint venture, risks, investments, and profits are shared between partners, while in an acquisition, the acquiring company assumes full control and financial responsibility. Ownership structure, degree of control, and strategic goals distinctly differ, with joint ventures emphasizing collaboration and acquisitions focusing on consolidation and market expansion.
Strategic Advantages of Joint Ventures
Joint ventures enable companies to share resources, risks, and market expertise, fostering innovation and faster entry into new markets. This collaborative approach retains the unique strengths and autonomy of each partner while leveraging combined capital and operational capabilities. By aligning strategic objectives, joint ventures facilitate sustained growth and adaptability in dynamic business environments.
Strategic Benefits of Acquisitions
Acquisitions provide strategic benefits such as full control over the acquired company's assets, enabling seamless integration of operations, technologies, and market presence. This control accelerates growth by eliminating competition and expanding customer base while leveraging established brand equity and distribution channels. Moreover, acquisitions offer enhanced synergies through cost reduction, improved innovation capacity, and access to new geographic markets.
Risks and Challenges of Joint Ventures
Joint ventures pose risks such as cultural clashes between partner companies, which can hinder decision-making and operational efficiency. Shared control often leads to conflicts over strategic goals and resource allocation, increasing the likelihood of disputes. Additionally, joint ventures face challenges in protecting intellectual property and maintaining confidentiality compared to acquisitions where control is consolidated.
Risks and Challenges of Acquisitions
Acquisitions often involve significant financial risks, including overvaluation of the target company and unforeseen liabilities that can impact the buyer's balance sheet. Cultural integration challenges and resistance from employees may lead to decreased productivity and loss of key talent post-acquisition. Regulatory hurdles and antitrust issues pose legal risks, potentially delaying or blocking the transaction and increasing costs.
Factors to Consider: Choosing Between Joint Venture and Acquisition
Evaluating control over operations is crucial when choosing between a joint venture and an acquisition, as acquisitions offer full ownership while joint ventures involve sharing management with partners. Financial risk tolerance influences the decision, with acquisitions requiring significant capital investment and exposure, whereas joint ventures distribute risk among entities. Compatibility of goals, company culture, and long-term strategic vision determines the best fit, since joint ventures rely on collaboration, while acquisitions enable full integration under one corporate strategy.
Conclusion: Which is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between a joint venture and an acquisition depends on your business goals, risk tolerance, and resource availability. Joint ventures offer shared risk and expertise, ideal for entering new markets or developing innovation collaboratively, while acquisitions provide full control and quicker integration but require significant capital and carry higher risk. Analyzing your company's strategic priorities and financial capacity helps determine whether partnership synergy or outright ownership aligns better with your growth objectives.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com