Effective corporate finance strategies are essential for maximizing shareholder value and ensuring sustainable business growth. By understanding financial planning, capital structure, and investment analysis, your organization can make informed decisions that drive profitability and manage risks. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to optimize your corporate finance practices for long-term success.
Table of Comparison
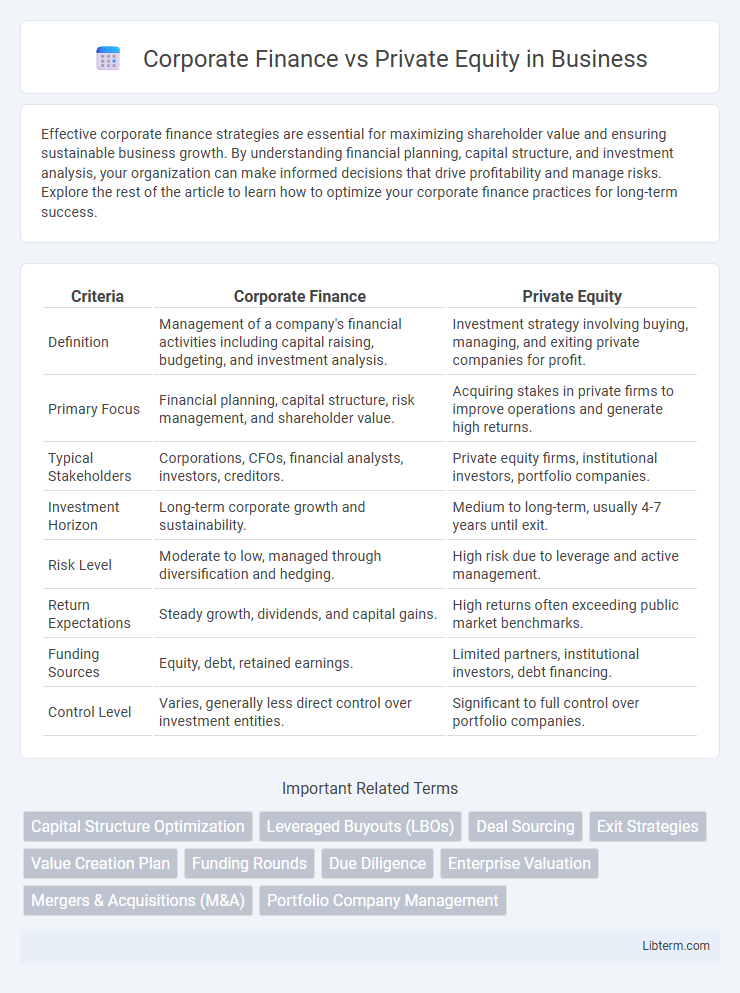
| Criteria | Corporate Finance | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of a company's financial activities including capital raising, budgeting, and investment analysis. | Investment strategy involving buying, managing, and exiting private companies for profit. |
| Primary Focus | Financial planning, capital structure, risk management, and shareholder value. | Acquiring stakes in private firms to improve operations and generate high returns. |
| Typical Stakeholders | Corporations, CFOs, financial analysts, investors, creditors. | Private equity firms, institutional investors, portfolio companies. |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term corporate growth and sustainability. | Medium to long-term, usually 4-7 years until exit. |
| Risk Level | Moderate to low, managed through diversification and hedging. | High risk due to leverage and active management. |
| Return Expectations | Steady growth, dividends, and capital gains. | High returns often exceeding public market benchmarks. |
| Funding Sources | Equity, debt, retained earnings. | Limited partners, institutional investors, debt financing. |
| Control Level | Varies, generally less direct control over investment entities. | Significant to full control over portfolio companies. |
Introduction to Corporate Finance and Private Equity
Corporate finance involves managing a company's capital structure, investment decisions, and funding strategies to maximize shareholder value, often focusing on debt and equity financing, risk management, and financial planning. Private equity refers to investment funds that acquire equity ownership in private companies or take public companies private, aiming to improve operations and profitability before exiting through a sale or IPO. While corporate finance centers on managing financial activities within a corporation, private equity emphasizes external investment and value creation through active ownership and strategic restructuring.
Key Concepts in Corporate Finance
Corporate finance centers on managing a company's capital structure, investment decisions, and funding strategies to maximize shareholder value. Key concepts include capital budgeting, risk management, capital raising through debt and equity, and dividend policy. Understanding the time value of money, cost of capital, and financial statements analysis plays a crucial role in effective corporate financial management.
Core Principles of Private Equity
Private equity centers on acquiring ownership stakes in private companies to drive value creation through active management, strategic guidance, and operational improvements. Core principles include rigorous due diligence, aligning interests through equity incentives, and leveraging capital structures to enhance returns. Unlike traditional corporate finance, private equity emphasizes long-term value enhancement, hands-on governance, and exit strategies such as IPOs or strategic sales.
Differences in Capital Structure Approaches
Corporate finance primarily utilizes a mix of debt and equity financing to optimize a firm's capital structure for long-term growth and operational stability. Private equity firms typically employ leveraged buyouts, using high levels of debt to acquire companies, aiming to enhance returns through operational improvements and strategic restructuring. The difference lies in corporate finance's balanced risk approach versus private equity's aggressive use of leverage to maximize investment returns.
Investment Strategies: Corporate Finance vs Private Equity
Corporate finance investment strategies prioritize optimizing capital structure and managing financial resources within corporations to support growth and operational efficiency. Private equity strategies focus on acquiring equity stakes in private companies, leveraging restructuring, and operational improvements to achieve high returns over a defined investment horizon. Both approaches rely on financial analysis but differ in their risk profiles, investment timelines, and value creation mechanisms.
Risk Management in Corporate Finance and Private Equity
Risk management in Corporate Finance centers on optimizing capital structure, maintaining liquidity, and mitigating market, credit, and operational risks to ensure sustainable growth and financial stability. Private Equity risk management emphasizes thorough due diligence, portfolio diversification, active monitoring, and exit strategy planning to maximize returns while minimizing investment and market risks. Both domains employ advanced financial modeling and scenario analysis, but Private Equity involves higher risk tolerance due to leveraged buyouts and illiquid asset investments.
Roles of Financial Professionals in Each Sector
Financial professionals in corporate finance primarily manage capital structure, budgeting, and financial planning to support a company's operational growth and value maximization. In private equity, financial experts focus on evaluating investment opportunities, conducting due diligence, and driving portfolio company improvements to generate high returns for investors. Both sectors require strong analytical skills, but corporate finance emphasizes internal financial management, while private equity centers on investment analysis and active value creation.
Typical Transactions and Deal Structures
Corporate finance transactions typically involve debt and equity financing for mergers, acquisitions, and capital raising, focusing on structured deals like leveraged buyouts, IPOs, and bond issuances. Private equity deals concentrate on acquiring controlling stakes in private companies through buyouts, growth capital investments, or venture funding, often employing preferred equity, mezzanine debt, and management incentive plans. Deal structures in corporate finance emphasize balancing risk and return for shareholders, whereas private equity structures prioritize value creation, exit strategies, and alignment of interests between investors and management teams.
Career Paths: Corporate Finance vs Private Equity
Career paths in corporate finance often lead to roles such as financial analyst, finance manager, or chief financial officer, emphasizing budgeting, forecasting, and internal financial strategy within established companies. Private equity careers typically involve positions like associate, vice president, or partner, focusing on investment analysis, deal structuring, and portfolio management for acquiring and improving companies. Both fields require strong financial modeling skills, but private equity demands deeper expertise in valuation and negotiation, offering potentially higher returns with greater risk exposure.
Future Trends in Corporate Finance and Private Equity
Future trends in corporate finance emphasize digital transformation, with increased adoption of AI-powered financial analytics and blockchain for secure transactions and transparency. Private equity is expected to focus on ESG-driven investments, leveraging data analytics to identify sustainable and socially responsible opportunities that generate long-term value. Both sectors will increasingly prioritize agility and innovation to adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes and global economic shifts.
Corporate Finance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com