Conversion rights grant investors the option to convert preferred shares or convertible securities into common stock, enhancing flexibility and potential returns. These rights protect investors during financing rounds by allowing participation in equity growth while maintaining downside protection. Explore the full article to understand how conversion rights can impact your investment strategy and shareholder value.
Table of Comparison
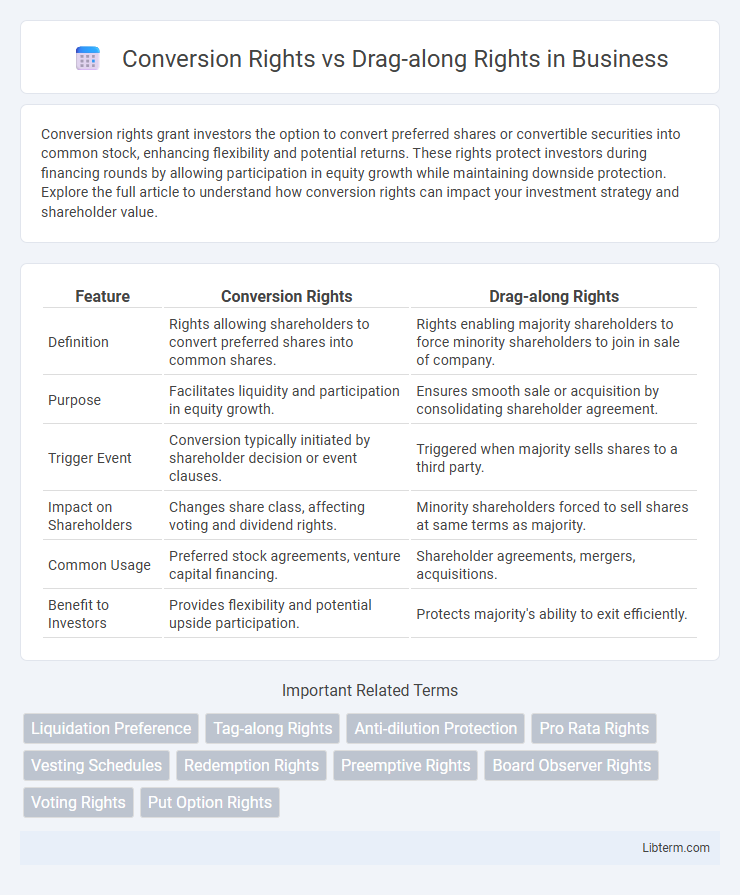
| Feature | Conversion Rights | Drag-along Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rights allowing shareholders to convert preferred shares into common shares. | Rights enabling majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in sale of company. |
| Purpose | Facilitates liquidity and participation in equity growth. | Ensures smooth sale or acquisition by consolidating shareholder agreement. |
| Trigger Event | Conversion typically initiated by shareholder decision or event clauses. | Triggered when majority sells shares to a third party. |
| Impact on Shareholders | Changes share class, affecting voting and dividend rights. | Minority shareholders forced to sell shares at same terms as majority. |
| Common Usage | Preferred stock agreements, venture capital financing. | Shareholder agreements, mergers, acquisitions. |
| Benefit to Investors | Provides flexibility and potential upside participation. | Protects majority's ability to exit efficiently. |
Understanding Conversion Rights: An Overview
Conversion rights allow investors or shareholders to convert preferred shares into common shares, providing flexibility to participate in the company's equity upside. This mechanism is crucial during financing rounds or initial public offerings (IPOs), enabling holders to maximize their returns by choosing the most advantageous share class. Understanding conversion rights helps stakeholders assess their potential influence and exit strategies in corporate governance and investment scenarios.
What Are Drag-along Rights?
Drag-along rights are contractual provisions that allow majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company under the same terms and conditions. These rights ensure that a potential buyer can acquire full control without facing holdout challenges from minority investors. Drag-along rights protect the interests of majority stakeholders by facilitating smoother and more efficient exit transactions.
Key Differences Between Conversion and Drag-along Rights
Conversion rights allow investors to convert preferred shares into common shares, typically to participate in an initial public offering or acquisition at a favorable rate, while drag-along rights enable majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of the company, ensuring a smoother exit. Conversion rights primarily affect the ownership structure and valuation by changing share classes, whereas drag-along rights focus on governance and transaction execution by mandating unified shareholder action during a sale. The key difference lies in conversion rights facilitating share class transformations for liquidity, whereas drag-along rights enforce collective decision-making to prevent holdouts in corporate sales.
Legal Foundations of Conversion Rights
Conversion rights are legally established through corporate charters and shareholder agreements that define the terms under which preferred shares convert into common shares, ensuring investor protection and flexibility in equity structure. These rights are typically grounded in contract law and securities regulations, providing mechanisms to trigger conversion on specific events like IPOs or acquisitions. Legal enforcement of conversion rights helps maintain shareholder equity value and clarifies obligations and entitlements during corporate restructuring or fundraising.
How Drag-along Rights Protect Majority Shareholders
Drag-along rights protect majority shareholders by enabling them to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring the transaction proceeds smoothly without holdouts. These rights prevent minority shareholders from blocking or delaying a lucrative exit, preserving the majority's control over strategic decisions. By aligning all shareholders during sale negotiations, drag-along provisions maximize the sale value and facilitate liquidity for majority stakeholders.
Practical Scenarios for Conversion Rights
Conversion rights allow investors to convert preferred shares into common shares, often triggered during an IPO or acquisition, enabling participation in equity upside. In practical scenarios, these rights provide flexibility when startups pivot or need additional funding, securing investor interests without forcing immediate liquidity. Unlike drag-along rights, which compel minority shareholders to sell stakes during a majority-approved exit, conversion rights primarily protect investment value through strategic equity restructuring.
When Are Drag-along Rights Invoked?
Drag-along rights are typically invoked during the sale of a company when majority shareholders want to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale under the same terms. These rights ensure that the sale process is streamlined by preventing minority shareholders from blocking a deal favored by the majority. Conversion rights, on the other hand, pertain to the ability of shareholders to convert one class of shares into another, mainly impacting control and liquidation preferences rather than sale processes.
Investor Implications: Conversion vs Drag-along
Conversion rights grant investors the option to convert preferred shares into common shares, typically maximizing returns during liquidity events by aligning equity stakes with founders or other shareholders. Drag-along rights enable majority investors to compel minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company, ensuring smoother exit transactions but potentially limiting minority investor control over timing and terms. Investors must weigh conversion rights for flexibility in exit strategy against drag-along rights' impact on shareholder autonomy in exit scenarios.
Negotiating Terms: Conversion and Drag-along Clauses
Negotiating conversion rights requires careful consideration of the conversion price, triggering events, and timing to protect investor interests while maintaining founder incentives. Drag-along rights should be clearly defined to ensure minority shareholders are compelled to sell under fair terms when a majority agrees to a transaction, preventing potential holdouts. Balancing these clauses involves aligning the interests of all parties, minimizing disputes, and safeguarding company valuation during liquidity events.
Best Practices for Balancing Shareholder Interests
Balancing conversion rights and drag-along rights requires clear contractual definitions to protect both minority and majority shareholders while ensuring liquidity and control during exit events. Best practices include setting transparent valuation mechanisms for conversion and establishing drag-along thresholds that prevent abuse but facilitate efficient decision-making in sales or mergers. Regular stakeholder communication and periodic rights reviews help align shareholder interests and maintain corporate governance integrity.
Conversion Rights Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com