Bootstrapping is a method of starting a business using minimal external funding, relying primarily on personal savings and revenue generated from initial sales. This approach helps maintain full control over your company and fosters resourcefulness in managing expenses. Discover key strategies and benefits of bootstrapping in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
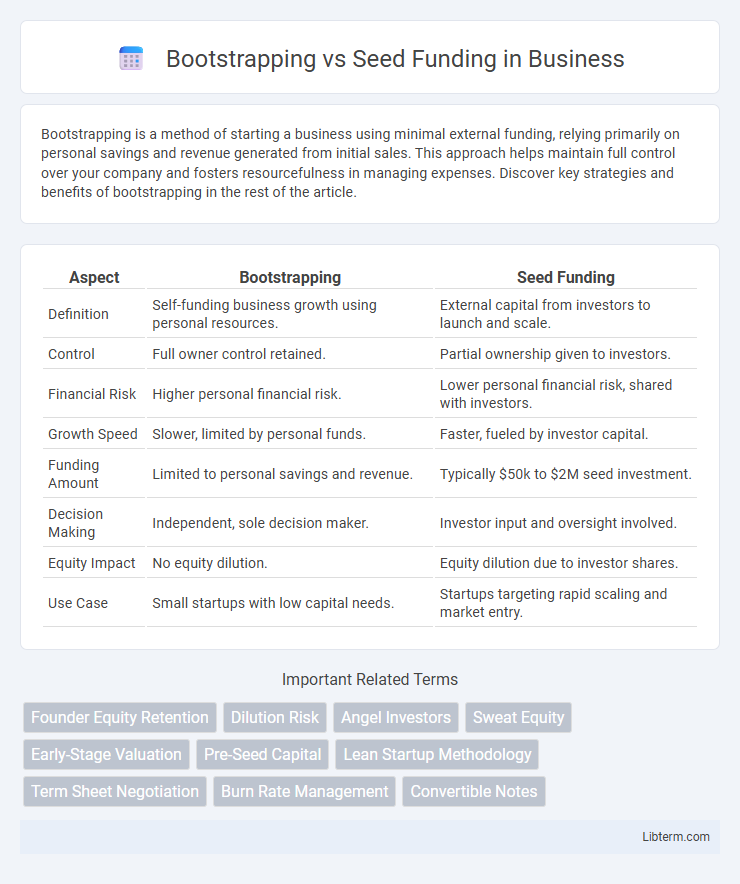
| Aspect | Bootstrapping | Seed Funding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-funding business growth using personal resources. | External capital from investors to launch and scale. |
| Control | Full owner control retained. | Partial ownership given to investors. |
| Financial Risk | Higher personal financial risk. | Lower personal financial risk, shared with investors. |
| Growth Speed | Slower, limited by personal funds. | Faster, fueled by investor capital. |
| Funding Amount | Limited to personal savings and revenue. | Typically $50k to $2M seed investment. |
| Decision Making | Independent, sole decision maker. | Investor input and oversight involved. |
| Equity Impact | No equity dilution. | Equity dilution due to investor shares. |
| Use Case | Small startups with low capital needs. | Startups targeting rapid scaling and market entry. |
Understanding Bootstrapping and Seed Funding
Bootstrapping involves using personal savings and operating revenues to fund a startup, emphasizing financial discipline and gradual growth without external investors. Seed funding refers to the early-stage capital raised from angel investors, venture capitalists, or crowdfunding to accelerate product development and market entry. Choosing between bootstrapping and seed funding depends on the startup's growth strategy, risk tolerance, and control preferences.
Key Differences Between Bootstrapping and Seed Funding
Bootstrapping involves entrepreneurs using personal savings or internal cash flow to finance their startup, while seed funding relies on external investors providing capital in exchange for equity. Bootstrapping offers complete control and ownership but limits resources, whereas seed funding accelerates growth with more substantial financial support but entails equity dilution. The choice impacts risk exposure, decision-making authority, and the startup's ability to scale rapidly.
Pros and Cons of Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping allows entrepreneurs to retain full ownership and control of their startup, fostering resourcefulness and long-term financial discipline. Limited external funding, however, can restrict growth potential and delay product development due to constrained cash flow. This self-funding approach reduces dependency on investors but may increase personal financial risk and limit scalability.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Seed Funding
Seed funding provides startups with essential capital to accelerate product development, marketing, and hiring, enabling faster market entry and competitive advantage. Investors often bring valuable mentorship, industry connections, and credibility, enhancing business growth potential. However, seed funding typically requires equity dilution and may impose pressure for rapid performance, potentially leading to loss of control and strategic direction conflicts.
Financial Control and Equity Ownership
Bootstrapping provides founders full financial control and retains 100% equity ownership, minimizing dilution but limiting funding capacity. Seed funding involves external investors who contribute capital in exchange for equity, reducing founders' ownership percentage and sharing decision-making power. Maintaining financial control often requires balancing equity sacrifices against the benefits of capital influx during early growth stages.
Risks and Rewards in Early-Stage Funding
Bootstrapping in early-stage funding involves using personal resources, which minimizes dilution but increases financial risk for founders if the business fails. Seed funding provides external capital that accelerates growth and market entry but often requires equity exchange, potentially diluting founder control. The choice between bootstrapping and seed funding hinges on founders' risk tolerance, desired growth speed, and long-term control of the company.
Impact on Startup Growth Trajectory
Bootstrapping forces startups to prioritize lean operations and organic growth, often leading to slower but sustainable scaling with strong financial discipline. Seed funding injects capital early, accelerating product development and market entry, which can fast-track growth but may also increase pressure for rapid scaling and higher risk. The choice between bootstrapping and seed funding significantly influences the startup's growth trajectory, strategic flexibility, and long-term viability.
Choosing the Right Funding Path for Your Startup
Bootstrapping enables startups to maintain full control and equity by self-funding through personal savings or revenue, fostering disciplined growth and cost management. Seed funding involves securing external investment from angel investors or venture capitalists, which accelerates product development and market entry but requires equity dilution and shared decision-making. Evaluating business goals, capital needs, growth trajectory, and risk tolerance helps entrepreneurs determine whether bootstrapping's independence or seed funding's capital infusion aligns better with their startup's strategic vision.
Real-World Examples: Bootstrapped vs Seed-Funded Startups
Bootstrapped startups like Mailchimp, which grew to profitability without external funding, demonstrate the potential for organic scalability and control retention. In contrast, seed-funded startups such as Airbnb leveraged early external capital to accelerate product development and market expansion, enabling rapid growth and competitive advantage. These real-world examples highlight the trade-offs between maintaining equity through bootstrapping and pursuing aggressive growth using seed capital.
Factors to Consider Before Deciding
Evaluating bootstrapping versus seed funding requires analyzing factors such as control retention, financial risk, and growth speed. Bootstrapping maintains full ownership and minimizes debt but may limit resource availability and scalability. Seed funding offers capital influx for rapid expansion but often involves equity dilution and investor oversight.
Bootstrapping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com