A savings account offers a secure way to grow your money with interest while keeping funds easily accessible. It provides a low-risk option for managing your finances and building an emergency fund or future savings. Discover how choosing the right savings account can maximize your financial potential by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
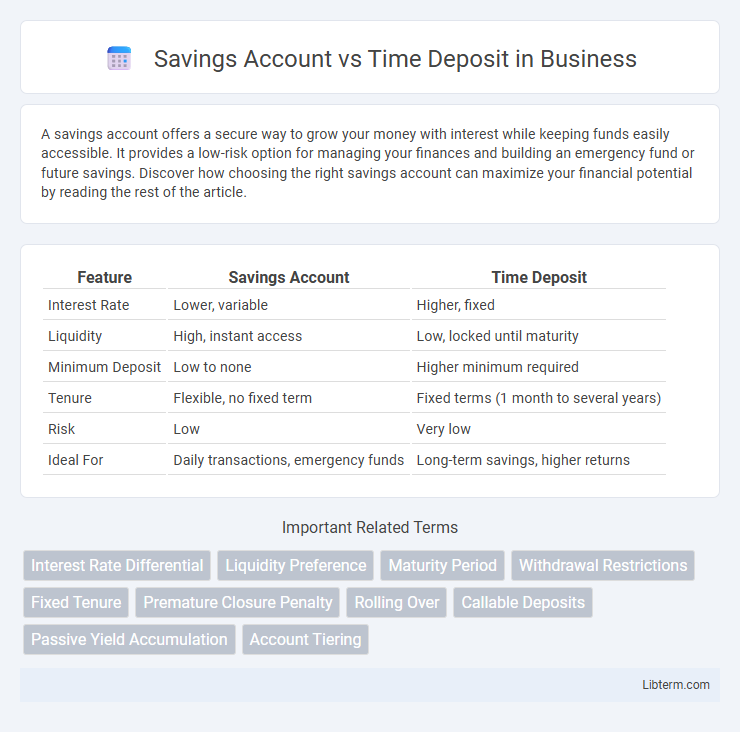
| Feature | Savings Account | Time Deposit |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Lower, variable | Higher, fixed |
| Liquidity | High, instant access | Low, locked until maturity |
| Minimum Deposit | Low to none | Higher minimum required |
| Tenure | Flexible, no fixed term | Fixed terms (1 month to several years) |
| Risk | Low | Very low |
| Ideal For | Daily transactions, emergency funds | Long-term savings, higher returns |
Introduction to Savings Accounts and Time Deposits
Savings accounts offer flexible access to funds with interest earned on deposited money, making them ideal for everyday financial needs and emergency savings. Time deposits, also known as certificates of deposit (CDs), lock in funds for a fixed term with higher interest rates, providing a secure option for long-term savings growth. Both financial instruments cater to different saving strategies, balancing liquidity and interest returns based on depositor goals.
Key Differences Between Savings Accounts and Time Deposits
Savings accounts offer high liquidity with easy access to funds anytime, whereas time deposits lock money for a fixed term, limiting withdrawals until maturity. Interest rates on time deposits are generally higher due to the fixed tenure, providing better returns compared to the typically lower, variable rates of savings accounts. Risk levels differ as savings accounts maintain liquidity and flexibility, while time deposits prioritize higher interest earnings in exchange for restricted access.
Interest Rates Comparison
Savings accounts typically offer lower interest rates, ranging from 0.01% to 1.00% annually, making them suitable for easy access and liquidity. Time deposits, also known as certificates of deposit (CDs), provide higher interest rates between 1.5% and 5.0% per year, depending on the term length, which can range from 3 months to 5 years. The fixed interest rates on time deposits generally yield better returns than variable rates on savings accounts, encouraging longer-term saving commitments.
Accessibility and Withdrawal Flexibility
Savings accounts provide high accessibility with the ability to make frequent withdrawals and deposits without penalties, making them ideal for emergency funds and daily transactions. Time deposits, or fixed deposits, restrict access to funds for a predetermined period, offering limited withdrawal flexibility and often imposing penalties for early withdrawal. Choosing between the two depends on the need for liquidity versus earning higher interest rates through locked-in funds.
Minimum Balance and Initial Deposit Requirements
Savings accounts typically require a low minimum balance, often ranging from $25 to $100, making them accessible for everyday transactions and regular deposits. Time deposits, also known as certificates of deposit (CDs), usually demand a higher initial deposit, commonly starting at $500 or more, which locks funds for a fixed term to earn higher interest rates. Understanding these minimum balance and initial deposit requirements helps determine the best account type based on liquidity needs and savings goals.
Risk and Security Factors
Savings accounts offer higher liquidity with lower minimum balance requirements, providing easy access to funds while maintaining FDIC insurance for security. Time deposits, or certificates of deposit (CDs), lock funds for a fixed term, reducing liquidity but often yielding higher interest rates and the same federal insurance protections. Risk primarily relates to early withdrawal penalties in time deposits, whereas savings accounts carry minimal risk with immediate fund availability.
Penalties and Fees: What to Expect
Savings accounts typically have minimal fees and no penalties for withdrawals, making them highly liquid and flexible, whereas time deposits often impose penalties such as a portion of accrued interest or a fixed fee when funds are withdrawn before the maturity date. Early withdrawal penalties on time deposits can significantly reduce overall returns, emphasizing the importance of commitment to the agreed term for optimal benefits. Understanding these fee structures is essential for choosing the right financial product based on liquidity needs and financial goals.
Ideal Users for Each Account Type
Savings accounts are ideal for individuals seeking easy access to their funds with flexible withdrawals and minimal balance requirements, making them suitable for daily expenses and emergency savings. Time deposits cater to those who can lock away money for a fixed term in exchange for higher interest rates, appealing to investors aiming for predictable returns and long-term financial goals. Choosing between these accounts depends on the user's need for liquidity versus higher interest earnings over a specified period.
Pros and Cons: Savings Accounts vs Time Deposits
Savings accounts offer high liquidity, allowing easy access to funds with minimal restrictions, making them ideal for emergency savings but typically provide lower interest rates compared to time deposits. Time deposits lock funds for a fixed period, offering higher interest earnings suited for long-term goals but impose penalties for early withdrawal, reducing flexibility. Choosing between savings accounts and time deposits depends on balancing the need for accessibility against the desire for higher returns.
How to Choose the Best Option for Your Financial Goals
Evaluate your liquidity needs and interest rate preferences to choose between a savings account and a time deposit. Savings accounts offer flexible access to funds with lower interest rates, ideal for emergency savings and frequent transactions. Time deposits provide higher fixed interest rates in exchange for locking in your money for a specific term, suitable for long-term financial goals and maximizing returns.
Savings Account Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com