A Non-Executive Director (NED) plays a crucial role in overseeing company strategy, providing independent judgment, and ensuring corporate governance without being involved in daily operations. They bring external experience and objectivity to board decisions, safeguarding shareholder interests and enhancing accountability. Explore the full article to understand how a Non-Executive Director can impact Your business success and governance standards.
Table of Comparison
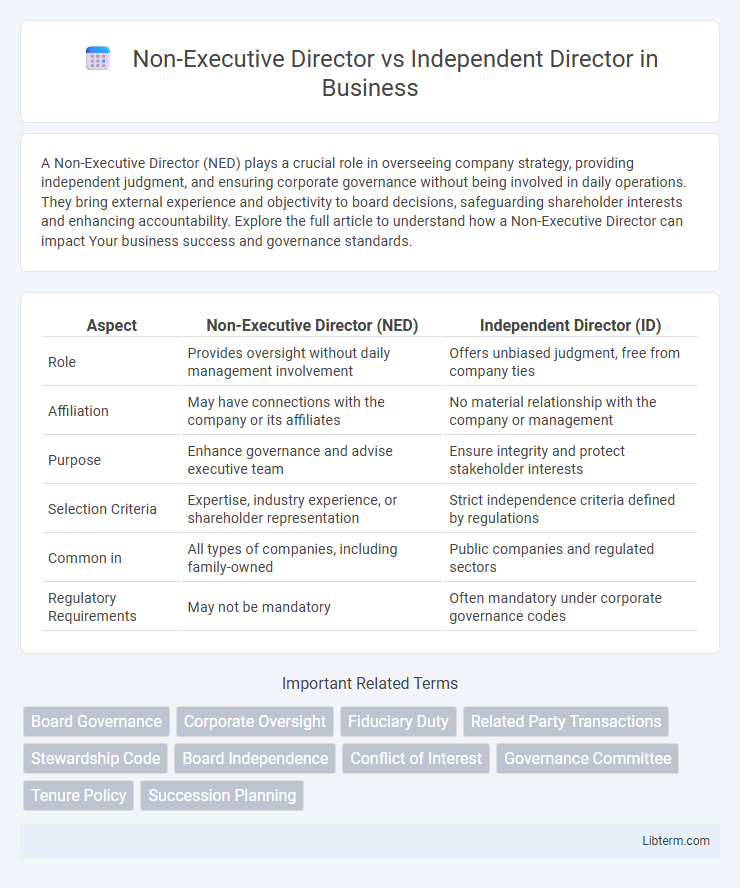
| Aspect | Non-Executive Director (NED) | Independent Director (ID) |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Provides oversight without daily management involvement | Offers unbiased judgment, free from company ties |
| Affiliation | May have connections with the company or its affiliates | No material relationship with the company or management |
| Purpose | Enhance governance and advise executive team | Ensure integrity and protect stakeholder interests |
| Selection Criteria | Expertise, industry experience, or shareholder representation | Strict independence criteria defined by regulations |
| Common in | All types of companies, including family-owned | Public companies and regulated sectors |
| Regulatory Requirements | May not be mandatory | Often mandatory under corporate governance codes |
Introduction to Board Roles
Non-Executive Directors (NEDs) participate in board governance without engaging in daily management, providing oversight and strategic guidance. Independent Directors are a specific type of NED who have no material relationship with the company, ensuring unbiased judgment and protecting shareholder interests. Both roles enhance board effectiveness by balancing executive decision-making with external perspectives.
Defining Non-Executive Directors
Non-Executive Directors (NEDs) serve on a company's board without being part of its executive management team, providing oversight and strategic guidance. They play a crucial role in monitoring executive performance and safeguarding shareholders' interests without engaging in daily operations. Unlike Independent Directors, whose autonomy must be free from any material business or familial relationships, Non-Executive Directors may have some affiliations with the company but still function primarily outside the company's executive structure.
Understanding Independent Directors
Independent Directors are a specific category of Non-Executive Directors characterized by their lack of material relationships or financial ties with the company, ensuring unbiased judgment and objective oversight. Their primary role involves safeguarding shareholders' interests, enhancing corporate governance, and mitigating conflicts of interest through independent decision-making. The presence of Independent Directors is crucial for maintaining board integrity, promoting transparency, and fostering long-term sustainable growth within publicly listed companies.
Key Differences between NEDs and Independent Directors
Non-Executive Directors (NEDs) are members of a company's board who do not engage in daily management but may have relationships with the company, potentially influencing their impartiality. Independent Directors must meet strict criteria ensuring no material ties to the company, enabling unbiased oversight and protecting shareholder interests. The key difference lies in the independence standard: all Independent Directors are NEDs, but not all NEDs qualify as Independent due to possible conflicts of interest or affiliations.
Regulatory Framework and Guidelines
Non-Executive Directors (NEDs) and Independent Directors are governed by distinct regulatory frameworks, where NEDs primarily provide oversight without daily management responsibilities, while Independent Directors must meet stricter criteria of independence to ensure unbiased judgment. The Companies Act 2013 in India and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act in the U.S. emphasize mandatory disclosures, conflict of interest policies, and board composition requirements specifically for Independent Directors to enhance corporate governance. Regulatory guidelines from bodies like SEBI and the UK Corporate Governance Code mandate clear definitions, tenure limits, and performance evaluations for Independent Directors, underscoring their critical role in protecting shareholder interests and maintaining board objectivity.
Qualifications and Appointment Process
Non-Executive Directors (NEDs) typically possess extensive industry experience, leadership skills, and a strong understanding of corporate governance, while Independent Directors must meet strict criteria to ensure no material relationship with the company, preserving impartiality. The appointment process for NEDs often involves board recommendation and shareholder approval, prioritizing expertise relevant to the company's strategic needs. Independent Directors undergo rigorous vetting to confirm their independence and are usually appointed through a nomination committee to maintain objectivity and regulatory compliance.
Roles and Responsibilities
Non-Executive Directors primarily provide strategic oversight and bring external perspectives without engaging in daily management, focusing on governance and stakeholder interests. Independent Directors have the added responsibility of unbiased judgment, ensuring impartiality by not having any material relationship with the company, thereby safeguarding minority shareholders and enhancing board objectivity. Both roles emphasize monitoring management performance, compliance with legal standards, and contributing to risk management, but Independent Directors must strictly avoid conflicts of interest to maintain board independence.
Influence on Corporate Governance
Non-Executive Directors contribute to corporate governance by providing oversight and strategic guidance without being involved in daily operations, ensuring a balance between management and board interests. Independent Directors enhance governance effectiveness by offering unbiased judgment free from management ties, which strengthens accountability and protects shareholder interests. Their combined presence fosters robust checks and balances, promoting transparency and ethical decision-making within the boardroom.
Challenges and Conflicts of Interest
Non-Executive Directors (NEDs) face challenges in balancing oversight responsibilities while maintaining strategic alignment without being involved in daily operations, which can create potential conflicts of interest with executive management. Independent Directors, selected for their lack of material relationships with the company, confront difficulties in accessing comprehensive information and influencing board decisions without bias, enhancing corporate governance but heightening scrutiny over their impartiality. Both roles require managing conflicts of interest related to competing personal, professional, or financial connections, ensuring decisions serve shareholder interests and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Director for Your Board
Selecting the right director for your board hinges on understanding the distinctions between Non-Executive Directors (NEDs) and Independent Directors. Non-Executive Directors bring valuable external expertise and oversight but may have affiliations with the company, whereas Independent Directors provide unbiased judgment free from business or personal ties. Opting for a balanced mix enhances governance by combining insider knowledge with impartial scrutiny, ensuring robust strategic decision-making and compliance.
Non-Executive Director Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com