Strategic alliances enable companies to combine resources, expertise, and market access, driving innovation and competitive advantage. Collaborating with the right partners can unlock new opportunities and accelerate growth in dynamic markets. Discover how your business can leverage strategic alliances for success by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
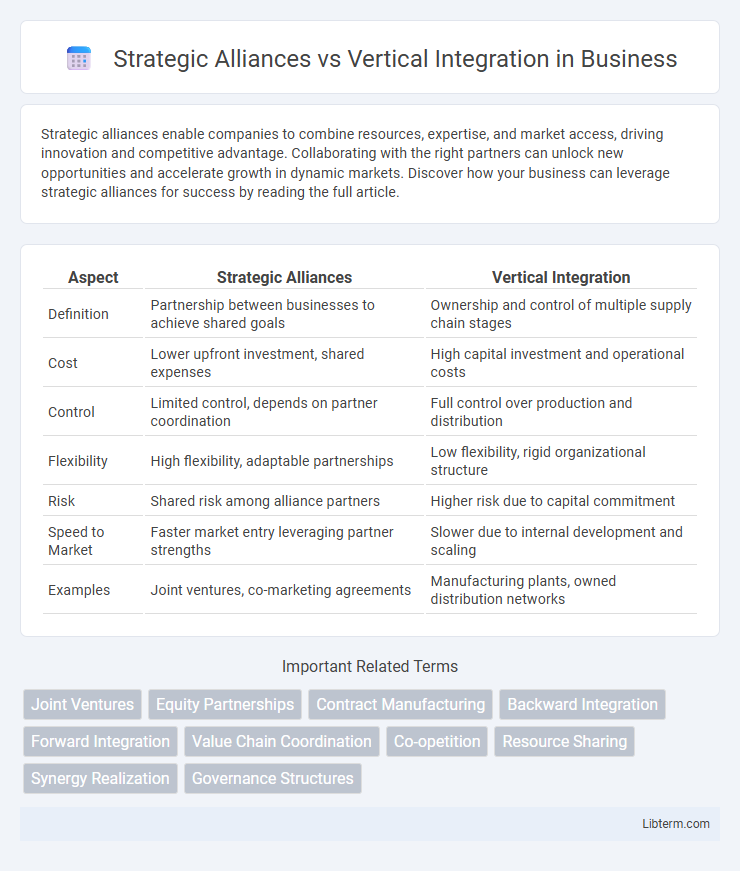
| Aspect | Strategic Alliances | Vertical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between businesses to achieve shared goals | Ownership and control of multiple supply chain stages |
| Cost | Lower upfront investment, shared expenses | High capital investment and operational costs |
| Control | Limited control, depends on partner coordination | Full control over production and distribution |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, adaptable partnerships | Low flexibility, rigid organizational structure |
| Risk | Shared risk among alliance partners | Higher risk due to capital commitment |
| Speed to Market | Faster market entry leveraging partner strengths | Slower due to internal development and scaling |
| Examples | Joint ventures, co-marketing agreements | Manufacturing plants, owned distribution networks |
Introduction to Strategic Alliances and Vertical Integration
Strategic alliances involve partnerships between companies to share resources, knowledge, and capabilities for mutual benefit without full ownership integration. Vertical integration occurs when a company expands its operations within its supply chain by acquiring or controlling upstream suppliers or downstream distributors. Both strategies aim to enhance competitive advantage but differ in commitment level and operational control.
Defining Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances involve collaborative agreements between independent companies to achieve shared objectives while maintaining their autonomy, enabling resource sharing, risk reduction, and market expansion. These partnerships often focus on complementary strengths such as technology, distribution channels, or research and development without full ownership transfer. Unlike vertical integration, which consolidates operations within a single company by acquiring suppliers or distributors, strategic alliances foster flexibility and innovation through cooperative interaction across organizational boundaries.
Understanding Vertical Integration
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations into different stages of production within its supply chain, either through backward integration into suppliers or forward integration into distribution. This strategy enhances control over resources, reduces dependency on external partners, and can lead to cost savings and improved coordination across the value chain. Companies like Apple and Tesla use vertical integration to streamline production processes and secure critical components, boosting efficiency and competitive advantage.
Key Differences Between Strategic Alliances and Vertical Integration
Strategic alliances involve collaboration between independent firms to achieve mutual goals without ownership changes, while vertical integration entails a company owning multiple stages of its supply chain. Strategic alliances offer flexibility and shared resources, whereas vertical integration provides greater control over production processes and cost efficiencies. Key differences include the level of control, investment risk, and operational integration, with alliances emphasizing cooperation and vertical integration focusing on consolidation and internal coordination.
Advantages of Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances offer companies flexibility and access to new markets without the high capital investment associated with vertical integration. They enable firms to leverage complementary strengths, share risks, and accelerate innovation through collaborative partnerships. This approach enhances scalability and responsiveness to market changes, improving competitive advantage while maintaining operational focus.
Benefits of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances control over the supply chain, reducing dependency on external suppliers and minimizing production delays. It enables cost savings through economies of scale and improved coordination across production stages. Firms can also protect proprietary technologies and enhance market power by directly controlling multiple levels of the value chain.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Strategic alliances can face risks such as lack of control, cultural clashes, and misaligned objectives, which may lead to conflicts and reduced collaboration effectiveness. Vertical integration presents challenges including high capital investment, reduced flexibility, and potential inefficiencies from managing diverse operations internally. Both strategies require careful risk assessment and management to ensure alignment with long-term business goals and market conditions.
Industry Examples and Case Studies
Strategic alliances allow companies like Starbucks and PepsiCo to leverage complementary strengths, expanding market reach through partnerships without full ownership, demonstrated in their joint development of ready-to-drink beverages. Vertical integration is exemplified by Tesla's control over its battery production and vehicle assembly, enhancing efficiency and reducing dependence on suppliers. Case studies reveal that strategic alliances suit dynamic industries like technology, while vertical integration excels in manufacturing sectors where supply chain control is critical.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Selecting between strategic alliances and vertical integration hinges on your business goals, resource availability, and market conditions. Strategic alliances enable access to complementary skills and markets while minimizing investment risk and maintaining flexibility. Vertical integration offers greater control over the supply chain, cost reductions, and improved coordination but requires substantial capital and operational expertise.
Future Trends in Strategic Alliances and Vertical Integration
Future trends in strategic alliances emphasize collaborative innovation, leveraging digital platforms and AI to enhance real-time data sharing and joint value creation across industries. Vertical integration continues evolving with automation and blockchain technologies enabling greater transparency, efficiency, and control over supply chains. Hybrid models combining strategic alliances and vertical integration emerge, optimizing agility and competitive advantage in dynamic global markets.
Strategic Alliances Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com