Subscription rights grant existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares before the company offers them to the public, helping you maintain your proportional ownership and avoid dilution. These rights are often issued during a new stock offering or capital increase to protect shareholder interests. Explore the full article to understand how subscription rights impact your investment strategy and shareholder value.
Table of Comparison
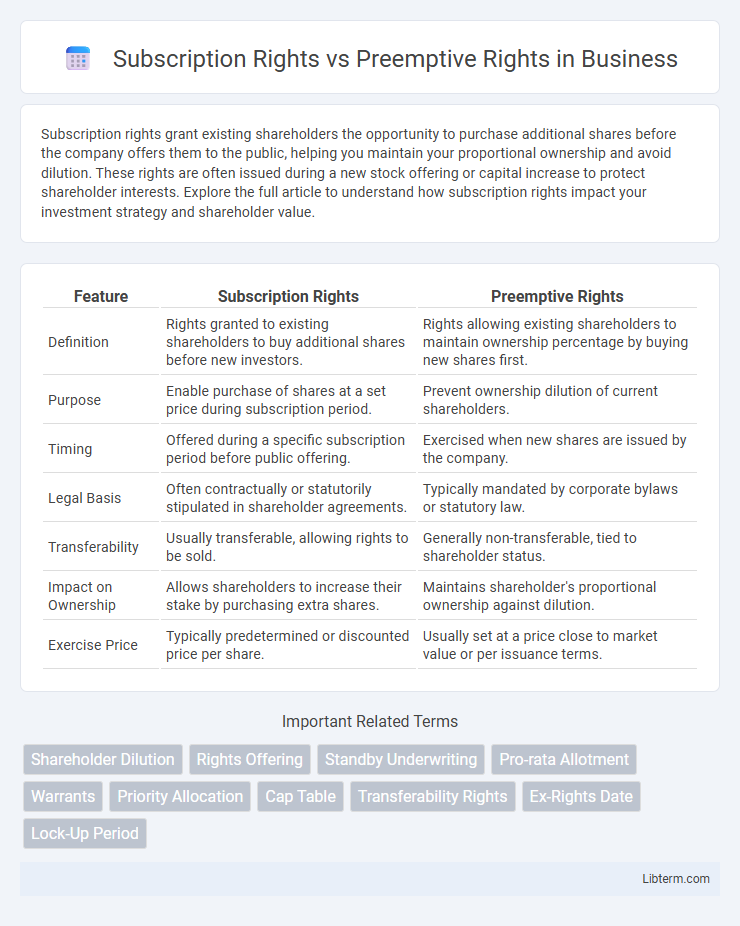
| Feature | Subscription Rights | Preemptive Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rights granted to existing shareholders to buy additional shares before new investors. | Rights allowing existing shareholders to maintain ownership percentage by buying new shares first. |
| Purpose | Enable purchase of shares at a set price during subscription period. | Prevent ownership dilution of current shareholders. |
| Timing | Offered during a specific subscription period before public offering. | Exercised when new shares are issued by the company. |
| Legal Basis | Often contractually or statutorily stipulated in shareholder agreements. | Typically mandated by corporate bylaws or statutory law. |
| Transferability | Usually transferable, allowing rights to be sold. | Generally non-transferable, tied to shareholder status. |
| Impact on Ownership | Allows shareholders to increase their stake by purchasing extra shares. | Maintains shareholder's proportional ownership against dilution. |
| Exercise Price | Typically predetermined or discounted price per share. | Usually set at a price close to market value or per issuance terms. |
Introduction to Subscription Rights and Preemptive Rights
Subscription rights and preemptive rights both serve to protect existing shareholders from dilution during new stock issuances. Subscription rights allow current shareholders to purchase additional shares in proportion to their holdings, typically at a discounted price and within a specified time frame. Preemptive rights legally obligate companies to offer new shares to existing shareholders first, ensuring their ownership percentage remains intact before shares are offered to outsiders.
Defining Subscription Rights
Subscription rights grant existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares in a new stock issuance, typically at a discounted price, before the shares are offered to the public. These rights are designed to protect investors from dilution of their ownership percentage by allowing them to maintain their proportional equity. Often issued as part of a rights offering, subscription rights have a limited duration and must be exercised within a specified timeframe.
Understanding Preemptive Rights
Preemptive rights grant existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares in a new issuance before the company offers them to the public, protecting their ownership percentage from dilution. These rights are often outlined in a corporation's charter or bylaws and ensure that current investors maintain proportional control. In contrast, subscription rights allow shareholders to buy shares at a discount during a limited period but do not always guarantee the right to maintain ownership percentage.
Key Similarities Between Subscription and Preemptive Rights
Subscription rights and preemptive rights both grant existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares before they are offered to the public, thereby preventing ownership dilution. These rights ensure shareholders maintain proportional equity and voting power in the company during new stock issuances. Both mechanisms are crucial for protecting investor interests and maintaining corporate control balance.
Major Differences: Subscription Rights vs Preemptive Rights
Subscription rights grant existing shareholders the option to purchase additional shares at a specified price before the company offers them to the public, primarily to raise new capital. Preemptive rights ensure shareholders maintain their proportional ownership by allowing them to buy a proportional number of new shares in any future issuance, preventing dilution. The key difference lies in subscription rights being tied to warrants or specific share offerings, while preemptive rights are a broader protective mechanism embedded in corporate bylaws or charters.
Legal Framework Governing Rights Issues
The legal framework governing subscription rights and preemptive rights is primarily established under corporate law statutes and securities regulations, ensuring shareholder protection during rights issues. Subscription rights grant existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares before new investors, while preemptive rights are statutory or contractual entitlements preventing dilution of ownership by allowing shareholders to maintain proportional equity stakes. Jurisdiction-specific regulations, including the U.S. Securities Act and the European Union's Prospectus Regulation, delineate disclosure requirements and procedural safeguards in rights offerings.
Importance for Shareholders
Subscription rights provide shareholders the privilege to purchase additional shares before the public offering, enabling them to maintain or increase their ownership percentage and prevent dilution. Preemptive rights specifically protect existing shareholders by allowing them to buy new shares in proportion to their current holdings, thus preserving their voting power and control in the company. Both rights are crucial in safeguarding shareholders' equity and influence during capital increases, ensuring their investments are not unfairly diluted.
Impact on Corporate Governance
Subscription rights empower existing shareholders to purchase additional shares proportionate to their holdings, maintaining ownership balance and preventing dilution, which supports shareholder control and alignment with management. Preemptive rights give shareholders first priority to buy new shares before the company offers them to outsiders, safeguarding their influence and voting power in corporate decisions. Both rights enhance corporate governance by protecting shareholder interests and promoting transparent equity issuance policies.
Risks and Benefits to Investors
Subscription rights offer investors the benefit of purchasing additional shares at a fixed price before the general public, reducing dilution risk and maintaining ownership percentage, but may require immediate capital outlay. Preemptive rights protect investors by allowing proportional participation in new stock issuances, ensuring control retention and minimizing voting power dilution, though exercising these rights can limit portfolio diversification. Both rights carry risks of financial commitment and potential loss if the stock value declines post-exercise, while providing strategic advantages in safeguarding investment value and influence.
Choosing Between Subscription and Preemptive Rights
Choosing between subscription rights and preemptive rights involves evaluating the company's financing goals and shareholder preferences. Subscription rights allow shareholders to purchase additional shares at a fixed price before the public offering, providing a direct opportunity to increase ownership. Preemptive rights protect existing shareholders from dilution by granting priority to buy new shares proportionate to their current holdings during future issuances.
Subscription Rights Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com