Brand licensing allows companies to expand their market presence by permitting others to use their brand name, logo, or intellectual property for a fee. This strategy generates additional revenue streams while boosting brand recognition without the need for direct investment in new product lines. Discover how brand licensing can transform your business and create valuable partnerships by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
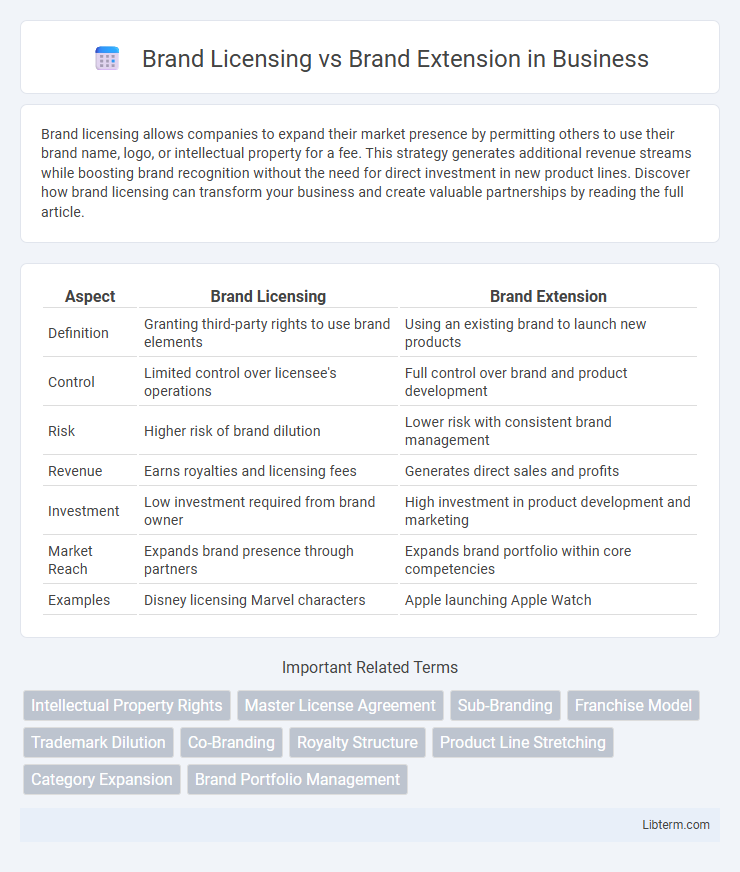
| Aspect | Brand Licensing | Brand Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Granting third-party rights to use brand elements | Using an existing brand to launch new products |
| Control | Limited control over licensee's operations | Full control over brand and product development |
| Risk | Higher risk of brand dilution | Lower risk with consistent brand management |
| Revenue | Earns royalties and licensing fees | Generates direct sales and profits |
| Investment | Low investment required from brand owner | High investment in product development and marketing |
| Market Reach | Expands brand presence through partners | Expands brand portfolio within core competencies |
| Examples | Disney licensing Marvel characters | Apple launching Apple Watch |
Understanding Brand Licensing
Brand licensing involves granting permission to a third party to use a brand's trademark, logo, or intellectual property in exchange for royalties or fees, helping brands expand their market presence without direct product development. This strategy allows licensors to leverage established brand equity while licensees gain immediate brand recognition, reducing their marketing costs and enhancing trust with consumers. Understanding brand licensing is crucial for companies seeking to maximize brand value through partnerships while maintaining control over brand image and quality standards.
Defining Brand Extension
Brand extension involves leveraging an established brand name to introduce new products or categories, enhancing market reach without creating a new brand identity. This strategy capitalizes on existing brand equity, consumer trust, and recognition to facilitate acceptance of new offerings. Successful brand extensions maintain consistency with the parent brand's core values while meeting customer expectations in the target category.
Key Differences Between Brand Licensing and Brand Extension
Brand licensing involves a legal agreement where a brand owner allows another company to use its brand name, logo, or intellectual property for a specific product or service, generating royalties without direct product development. Brand extension refers to a company leveraging its existing brand name to introduce new products or services within the same market, maintaining control over production and marketing. Key differences include brand licensing's reliance on third-party partnerships and royalty income versus brand extension's direct brand control and market expansion.
Benefits of Brand Licensing
Brand licensing enables companies to generate additional revenue streams by allowing third parties to use their established trademarks, enhancing brand visibility without the need for extensive capital investment. It reduces risks associated with product development and market entry, as licensees typically handle production and distribution. This strategy also fosters brand awareness across new markets and customer segments while maintaining brand integrity through controlled usage agreements.
Advantages of Brand Extension
Brand extension leverages the established brand equity to introduce new products, reducing marketing costs and accelerating consumer trust in unfamiliar categories. This strategy enhances brand visibility and broadens market reach without diluting the core brand identity when executed carefully. Companies benefit from higher profit margins and increased shelf presence by capitalizing on existing customer loyalty and brand recognition.
Risks and Challenges in Brand Licensing
Brand licensing involves permitting another company to use a brand's name or trademark, posing risks such as loss of brand control, inconsistent product quality, and potential damage to brand reputation if licensees fail to meet standards. Challenges include managing complex legal agreements and ensuring compliance with brand guidelines across diverse markets, which can strain resources and oversight capabilities. Unlike brand extension, where the original company maintains direct control, brand licensing requires vigilant monitoring to prevent brand dilution and protect intellectual property.
Potential Pitfalls of Brand Extension
Brand extension carries potential pitfalls such as brand dilution, where the original brand's identity weakens due to inconsistent or inappropriate product associations. Consumer confusion can arise when the extension fails to align with the core brand values, leading to decreased customer loyalty. Poorly executed brand extensions risk damaging the brand's reputation and decreasing overall market equity.
Strategic Considerations for Brands
Strategic considerations for brand licensing involve leveraging an established brand's equity to enter new markets or product categories while minimizing investment and risk, allowing for rapid expansion through partnerships with licensees. In contrast, brand extension requires careful evaluation of compatibility between the parent brand's core values and the new product to maintain brand integrity and avoid consumer confusion. Both strategies demand rigorous market research and alignment with long-term brand positioning goals to enhance brand equity and ensure sustainable growth.
Real-World Examples: Licensing vs Extension
Brand licensing involves allowing another company to use a trademark or brand on their products, like Disney licensing its characters for apparel and toys, while brand extension means a company leverages its own brand to enter new product categories, exemplified by Apple branching from computers to smartphones and wearables. Licensing provides quick market access and revenue with lower risk, whereas extension demands investment and risks dilution but offers more control over brand image. Real-world cases show Lego's successful brand extension into video games contrasts with its licensing deals for movie tie-in merchandise that expand reach without direct production involvement.
Choosing the Right Growth Strategy for Your Brand
Selecting the appropriate growth strategy for your brand requires understanding the distinction between brand licensing and brand extension. Brand licensing allows third parties to use your brand's intellectual property, generating revenue with lower risk and capital investment, while brand extension involves leveraging your existing brand equity to enter new product categories, strengthening brand recognition and customer loyalty. Evaluating factors such as market fit, control over quality, financial goals, and long-term brand positioning ensures choosing a strategy that maximizes growth and maintains brand integrity.
Brand Licensing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com