A green tariff allows you to support renewable energy by opting to pay a premium on your electricity bill that guarantees your power comes from renewable sources like wind or solar. This eco-friendly option helps reduce carbon emissions while promoting the growth of clean energy infrastructure. Discover how choosing a green tariff can positively impact your energy consumption and the environment in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
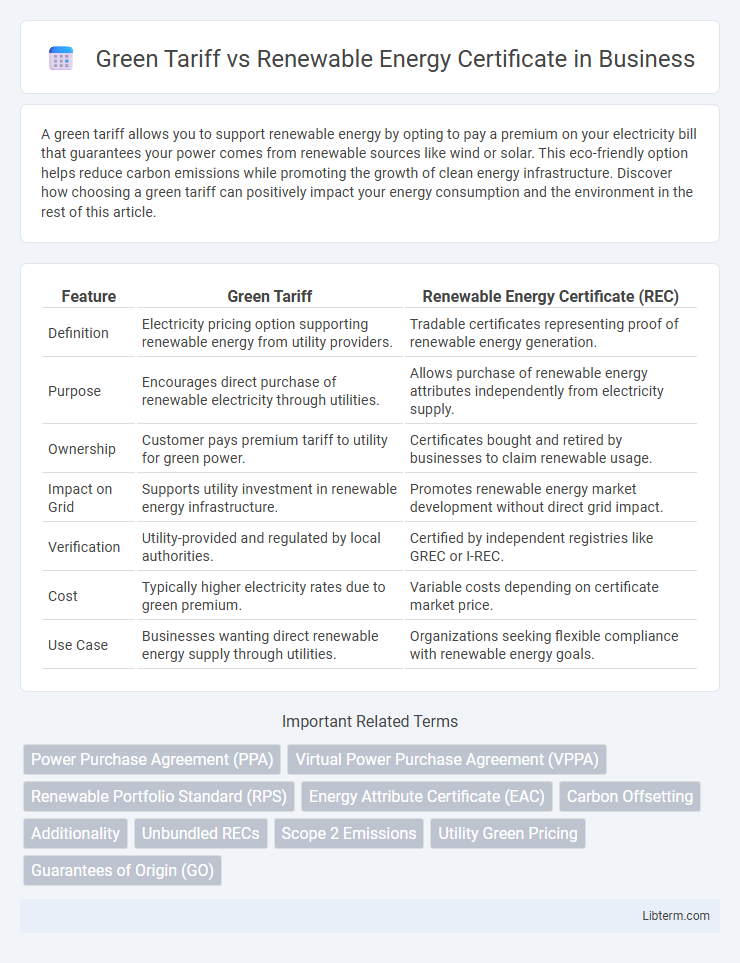
| Feature | Green Tariff | Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electricity pricing option supporting renewable energy from utility providers. | Tradable certificates representing proof of renewable energy generation. |
| Purpose | Encourages direct purchase of renewable electricity through utilities. | Allows purchase of renewable energy attributes independently from electricity supply. |
| Ownership | Customer pays premium tariff to utility for green power. | Certificates bought and retired by businesses to claim renewable usage. |
| Impact on Grid | Supports utility investment in renewable energy infrastructure. | Promotes renewable energy market development without direct grid impact. |
| Verification | Utility-provided and regulated by local authorities. | Certified by independent registries like GREC or I-REC. |
| Cost | Typically higher electricity rates due to green premium. | Variable costs depending on certificate market price. |
| Use Case | Businesses wanting direct renewable energy supply through utilities. | Organizations seeking flexible compliance with renewable energy goals. |
Introduction to Green Tariffs and Renewable Energy Certificates
Green Tariffs allow consumers to support renewable energy generation by paying a premium on their electricity bills, directly funding new renewable projects within their utility's service area. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that one megawatt-hour of electricity was generated from a renewable energy resource, enabling companies and individuals to claim renewable energy usage without physically consuming the energy. Both mechanisms enhance the growth of clean energy but operate through distinct accounting and contractual frameworks.
How Green Tariffs Work
Green tariffs enable utility customers to support renewable energy generation by paying a premium for electricity sourced from wind, solar, or other green power projects directly through their utility provider. These tariffs are structured as opt-in programs where consumers can choose to purchase a specific portion or all of their electricity as renewable, contributing to the expansion of clean energy infrastructure without owning the generation asset. The utility then matches these green tariff purchases by procuring renewable energy or renewable energy certificates (RECs), ensuring that the environmental benefits align with consumer demand.
Understanding Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that one megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity was generated from a renewable energy source and fed into the grid, serving as a market-based instrument to promote clean energy. Unlike Green Tariffs, which involve a direct contractual agreement between consumers and utilities to purchase renewable energy, RECs can be bought and sold independently of the actual energy consumption, allowing businesses to meet sustainability goals flexibly. Understanding RECs helps organizations verify their renewable energy usage without requiring physical delivery, supporting renewable energy development and regulatory compliance.
Key Differences Between Green Tariffs and RECs
Green Tariffs provide consumers direct access to renewable energy through their utility's green pricing program, ensuring a specific portion of their electricity comes from renewable sources. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) represent proof that one megawatt-hour of electricity was generated from a renewable energy resource, allowing businesses and individuals to claim renewable energy use indirectly. The key difference lies in Green Tariffs delivering renewable energy through utility contracts, while RECs offer flexible, tradable credits that decouple renewable energy generation from consumption location.
Pros and Cons of Green Tariffs
Green Tariffs offer businesses and consumers a straightforward way to support renewable energy by purchasing electricity that is directly sourced from renewable projects, ensuring clear environmental impact and consistent pricing. However, they may come with higher costs compared to standard rates and sometimes lack flexibility in energy sourcing or contract terms. Unlike Renewable Energy Certificates, which represent proof of green energy generation that can be traded separately from actual energy usage, Green Tariffs provide a bundled solution that simplifies renewable energy procurement but can limit market participation options.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Renewable Energy Certificates
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) offer a flexible method for businesses and individuals to support renewable energy generation by purchasing certificates that represent proof of renewable power production. The benefits of RECs include verifiable tracking of renewable energy credits, market-driven pricing, and the ability to offset carbon emissions without needing on-site renewable installations. However, drawbacks include potential market volatility, risk of double counting if REC systems are not rigorously monitored, and limited direct impact on increasing new renewable energy capacity compared to Green Tariffs, which provide guaranteed sourcing of renewable power.
Environmental Impact: Green Tariffs vs RECs
Green Tariffs and Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) both support environmental goals but differ in impact clarity; Green Tariffs represent direct procurement of renewable energy from utilities, ensuring increased renewable generation on the grid. RECs signify proof that one megawatt-hour of renewable electricity has been generated but can be purchased separately from actual energy use, potentially allowing continued reliance on fossil fuels. Consequently, Green Tariffs generally offer a more transparent and tangible environmental benefit by driving new renewable projects, while RECs provide flexible but less direct support for renewable energy development.
Cost Comparison: Green Tariffs vs Renewable Energy Certificates
Green Tariffs typically involve a fixed premium on utility bills, ranging from 1 to 5 cents per kilowatt-hour, offering a straightforward cost structure for consumers seeking renewable energy. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) vary widely in price depending on market demand, geographic region, and certificate vintage, with prices generally between $1 and $5 per megawatt-hour. While Green Tariffs provide price predictability and easier budgeting, RECs allow more flexible and potentially lower-cost options for businesses and individuals aiming to offset their carbon footprint.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Organization
Choosing between a Green Tariff and Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) depends on your organization's sustainability goals and operational needs. Green Tariffs offer a direct contract with utilities to source renewable energy, ensuring a consistent energy supply linked to clean power generation, while RECs provide flexibility by allowing companies to purchase certificates representing renewable energy generation independent of their electricity provider. Organizations seeking long-term energy price stability and tangible impact may prefer Green Tariffs, whereas those valuing cost-effectiveness and customizable renewable sourcing often lean toward RECs.
Future Trends in Clean Energy Procurement
Green Tariffs and Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are increasingly shaping the future of clean energy procurement by offering scalable options for businesses to meet sustainability goals. Emerging trends indicate a growing preference for bundled Green Tariff programs that provide direct access to renewable energy alongside the flexibility of RECs, enhancing transparency and cost-effectiveness. Advances in blockchain technology and real-time tracking systems are expected to further streamline RECs management, driving higher adoption rates and stronger corporate commitments to carbon neutrality.
Green Tariff Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com