A well-designed licensing model defines how your software or product can be used, distributed, and monetized, ensuring legal protection and revenue generation. Choosing the right type of license--whether open-source, proprietary, or hybrid--can significantly impact your business strategy and customer reach. Explore the rest of the article to discover the best licensing model tailored to your needs.
Table of Comparison
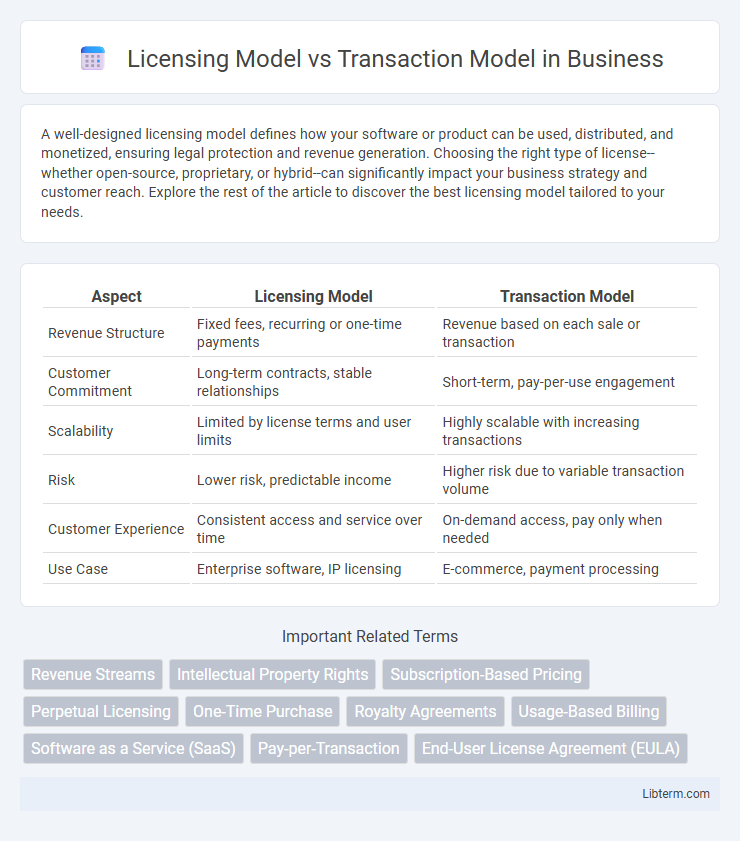
| Aspect | Licensing Model | Transaction Model |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Structure | Fixed fees, recurring or one-time payments | Revenue based on each sale or transaction |
| Customer Commitment | Long-term contracts, stable relationships | Short-term, pay-per-use engagement |
| Scalability | Limited by license terms and user limits | Highly scalable with increasing transactions |
| Risk | Lower risk, predictable income | Higher risk due to variable transaction volume |
| Customer Experience | Consistent access and service over time | On-demand access, pay only when needed |
| Use Case | Enterprise software, IP licensing | E-commerce, payment processing |
Understanding the Licensing Model
The Licensing Model involves granting permission to use intellectual property or software under defined terms, often based on duration, number of users, or usage scope. This model provides predictable revenue streams for companies and legal protections for both licensors and licensees by clearly outlining rights and restrictions. Understanding the Licensing Model requires recognizing its emphasis on control, compliance, and recurring fees compared to the pay-per-use structure of the Transaction Model.
Defining the Transaction Model
The transaction model defines a business framework where revenue is generated through individual sales or exchanges of goods and services, emphasizing payment per transaction rather than a fixed fee. This model facilitates flexibility, allowing customers to pay only for what they use, making it ideal for scalable or usage-based offerings. Transaction models ensure transparency in pricing and can drive higher customer engagement by aligning cost with actual consumption.
Key Differences Between Licensing and Transaction Models
The Licensing Model grants rights to use intellectual property or software under specific terms for a defined period, often involving recurring fees or royalties. The Transaction Model entails a one-time sale where ownership or usage rights transfer immediately without ongoing obligations. Key differences include the payment structure, duration of access, and control retention, with licensing providing continued revenue streams and transactional allowing a single, complete transfer.
Revenue Streams: Licensing vs Transaction
The licensing model generates revenue through upfront fees or periodic payments granting rights to use a product or service, creating predictable and recurring income streams. In contrast, the transaction model produces revenue by charging fees or commissions per individual sale or interaction, resulting in variable income tied directly to customer activity. Understanding these distinct revenue streams helps businesses align their monetization strategies with their operational goals and customer behavior patterns.
Cost Structure and Profit Margins
The Licensing Model typically incurs lower variable costs with fixed fees paid upfront or periodically, resulting in stable profit margins driven by licensing rates and renewal volumes. The Transaction Model involves variable costs tied to each sale or usage, allowing for scalable revenue but fluctuating profit margins depending on transaction volume and processing fees. Companies favor the Licensing Model for predictable revenue streams, while the Transaction Model is preferred for growth potential and flexibility in pricing strategies.
Customer Relationship Dynamics
The licensing model fosters long-term customer relationships through ongoing support and updates, encouraging brand loyalty and sustained engagement. In contrast, the transaction model centers on one-time purchases, leading to more sporadic interactions and less emphasis on customer retention. Businesses leveraging licensing models benefit from recurring revenue streams and deeper customer insights, enhancing personalized service and satisfaction.
Scalability and Growth Potential
The Licensing Model offers predictable revenue through fixed fees, supporting steady scalability limited by market reach and license renewals. The Transaction Model drives higher growth potential by enabling variable, usage-based revenue that scales directly with customer activity and volume. Scalability in the Transaction Model benefits from network effects and increasing transaction frequency, often resulting in faster revenue expansion compared to the Licensing Model.
Industry Suitability for Each Model
The licensing model suits industries with stable, long-term software needs, such as healthcare and manufacturing, where upfront investment in software ownership ensures consistent access and control. The transaction model fits sectors like retail and digital services, where pay-per-use flexibility aligns with variable demand and frequent updates. Both models cater to different operational scales and budgeting preferences, optimizing software deployment based on industry-specific workflows and financial structures.
Risk Factors and Legal Considerations
The Licensing Model exposes licensors to risks such as intellectual property infringement, contract disputes, and compliance with jurisdiction-specific regulations, necessitating thorough legal review and robust contractual protections. The Transaction Model involves transactional risks like payment defaults, fraud, and consumer protection issues, requiring clear terms of sale and adherence to e-commerce laws. Both models demand careful risk assessment and legal strategies to mitigate liabilities and ensure regulatory compliance in domestic and international markets.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Selecting the right revenue model depends on your business goals, customer behavior, and industry standards. Licensing models provide predictable recurring income by granting usage rights, ideal for software or intellectual property businesses aiming for long-term client relationships. Transaction models generate revenue through per-sale fees, better suited for marketplaces or businesses with high sales volume and variable customer interactions.
Licensing Model Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com