A business model defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value through its products or services. Understanding your business model is essential for identifying revenue streams, target customers, and competitive advantages. Explore the rest of this article to discover key components and examples that can help refine your business strategy.
Table of Comparison
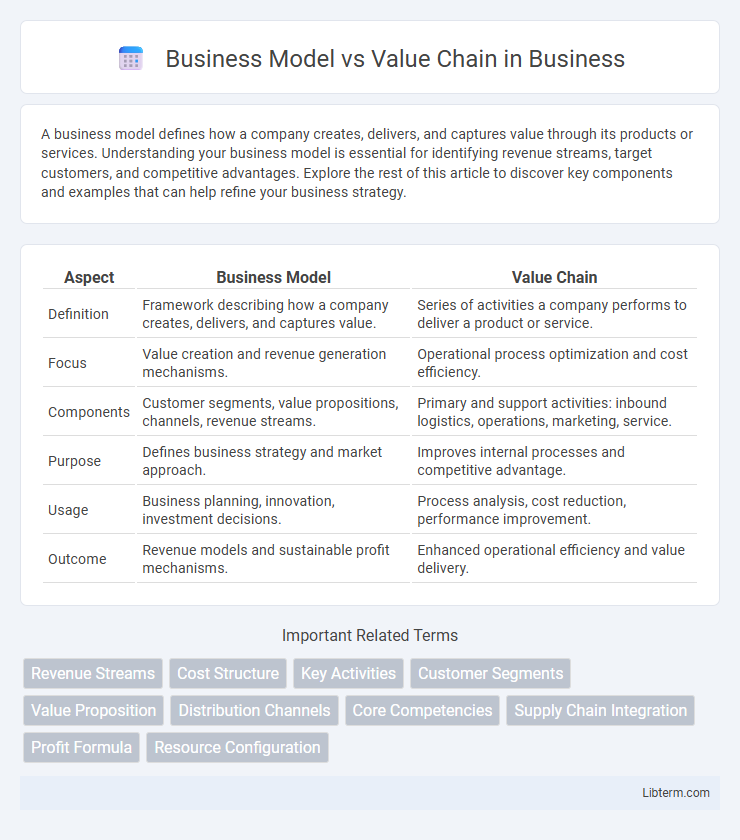
| Aspect | Business Model | Value Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework describing how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. | Series of activities a company performs to deliver a product or service. |
| Focus | Value creation and revenue generation mechanisms. | Operational process optimization and cost efficiency. |
| Components | Customer segments, value propositions, channels, revenue streams. | Primary and support activities: inbound logistics, operations, marketing, service. |
| Purpose | Defines business strategy and market approach. | Improves internal processes and competitive advantage. |
| Usage | Business planning, innovation, investment decisions. | Process analysis, cost reduction, performance improvement. |
| Outcome | Revenue models and sustainable profit mechanisms. | Enhanced operational efficiency and value delivery. |
Introduction to Business Model and Value Chain
A business model defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value through its products or services, outlining key components such as target customers, revenue streams, and cost structures. The value chain represents the sequence of activities a business performs to design, produce, market, deliver, and support its product, emphasizing operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Understanding both concepts is essential for aligning strategic objectives with practical execution to maximize profitability and market positioning.
Defining Business Model: Core Concepts
A business model outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value through its core operations, revenue streams, customer segments, and value propositions. It provides a strategic framework that defines the company's approach to market positioning, competitive advantage, and profit generation. Understanding the business model's components, such as key activities, resources, and partnerships, is essential for aligning organizational goals with customer needs and industry dynamics.
Understanding the Value Chain Framework
The value chain framework analyzes a company's internal activities to identify areas of competitive advantage by mapping primary and support activities that create value for customers. It complements the business model by breaking down how value is delivered and costs are incurred at each stage, from inbound logistics to after-sales service. Understanding the value chain helps businesses optimize operations, enhance efficiencies, and align resources with strategic goals for sustainable profitability.
Key Components of a Business Model
Key components of a business model include customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure. These elements define how a company creates, delivers, and captures value within its market. In contrast, the value chain focuses on the internal processes and activities that transform inputs into final products or services, emphasizing operational efficiency and value creation at each step.
Primary and Support Activities in the Value Chain
The Business Model defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, while the Value Chain breaks down the internal activities that support this process into Primary and Support Activities. Primary Activities include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, all directly involved in producing and delivering products. Support Activities such as procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of Primary Activities, optimizing the overall business performance.
Differences Between Business Model and Value Chain
The business model defines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, focusing on customer segments, revenue streams, and value propositions. The value chain analyzes internal activities and processes that create competitive advantage through primary and support activities like inbound logistics and marketing. Unlike the business model's broad strategic framework, the value chain provides a detailed operational perspective emphasizing efficiency and cost management.
How Business Models Influence Value Chains
Business models define the framework through which a company creates, delivers, and captures value, directly shaping the structure and activities of its value chain. By determining core processes such as production, marketing, and distribution, business models influence how resources are allocated and optimized across the value chain. This alignment ensures competitive advantage by enhancing efficiency, customer satisfaction, and innovation within the entire value creation process.
Aligning Value Chain Activities with Business Strategy
Aligning value chain activities with business strategy ensures that each operational step--from inbound logistics to after-sales service--directly supports the company's competitive positioning and customer value proposition. This alignment enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and drives differentiation by optimizing resource allocation and process integration across procurement, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution. Effective synchronization between the business model and value chain fosters sustainable competitive advantage through coherent strategic execution and value creation.
Case Studies: Business Model and Value Chain in Action
Case studies such as Apple's integration of its business model and value chain highlight the critical interplay between innovative product design, strategic supplier relationships, and seamless distribution channels to create competitive advantage. Amazon's value chain focuses on efficient logistics and customer-centric services within its business model, optimizing inventory management and personalized recommendations to drive sales growth. Tesla's approach demonstrates how aligning sustainable energy business models with vertically integrated value chains accelerates innovation and reduces costs in the electric vehicle market.
Choosing the Right Approach for Business Success
Selecting between a business model and a value chain approach depends on the company's strategic goals and industry context. The business model outlines how a company creates, delivers, and captures value, focusing on customer segments, revenue streams, and key partnerships. The value chain emphasizes internal activities to optimize operational efficiency and competitive advantage through inbound logistics, operations, marketing, and service.
Business Model Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com