Norms shape behavior and establish expectations within social groups, guiding interactions and maintaining order. Understanding the different types of norms--such as folkways, mores, and laws--can help you navigate social environments more effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how norms influence everyday life and social cohesion.
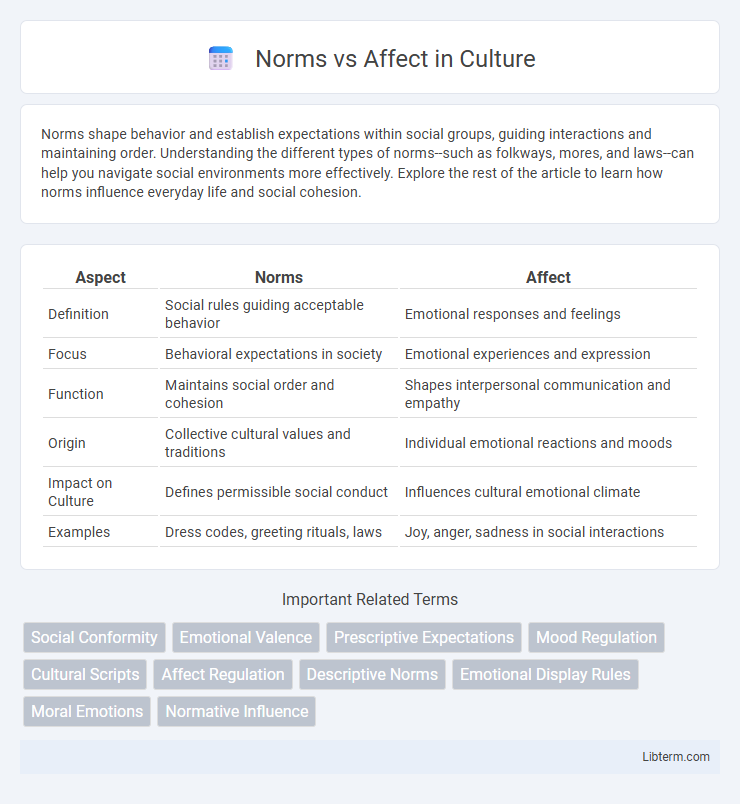
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Norms | Affect |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social rules guiding acceptable behavior | Emotional responses and feelings |
| Focus | Behavioral expectations in society | Emotional experiences and expression |
| Function | Maintains social order and cohesion | Shapes interpersonal communication and empathy |
| Origin | Collective cultural values and traditions | Individual emotional reactions and moods |
| Impact on Culture | Defines permissible social conduct | Influences cultural emotional climate |
| Examples | Dress codes, greeting rituals, laws | Joy, anger, sadness in social interactions |
Understanding Norms: Definition and Types
Norms represent shared expectations and rules guiding behavior within a group or society, encompassing types such as descriptive norms, which describe typical behavior, and injunctive norms, which indicate approved or disapproved actions. Understanding norms involves recognizing their role in shaping social order and influencing individual and collective conduct. These behavioral guidelines are critical for predicting social interactions and maintaining cultural cohesion.
What is Affect? Emotional Responses Explained
Affect refers to the automatic and immediate emotional responses triggered by stimuli, encompassing feelings such as happiness, anger, fear, or sadness. Unlike norms, which are socially constructed rules guiding behavior, affect is rooted in neurobiological processes that influence attention, decision-making, and interpersonal interactions. Understanding affect is crucial in psychology and behavioral science as it drives motivation and emotional regulation in individuals.
The Interplay Between Norms and Affect
Norms and affect interact dynamically, where social norms influence emotional responses and affect shapes adherence to these norms. Emotional experiences such as fear, pride, or guilt can reinforce or challenge normative behaviors within groups. Understanding this interplay is crucial for predicting behavior change and designing interventions in social psychology and behavioral economics.
Cultural Influences on Norms and Emotional Expression
Cultural influences strongly shape social norms, dictating acceptable behaviors and emotional expressions within a community. Collectivist cultures often emphasize harmony and restraint in affect, promoting emotional expression that aligns with group cohesion, while individualistic cultures encourage open and authentic emotional displays. These cultural norms impact interpersonal communication, emotional regulation, and social expectations, highlighting the dynamic relationship between societal rules and affective experiences.
How Norms Shape Emotional Behaviors
Social norms profoundly shape emotional behaviors by dictating acceptable expressions of feelings within different contexts. These unwritten rules influence how individuals regulate emotions, such as displaying happiness, anger, or sadness, to align with cultural expectations and maintain social harmony. Research in social psychology shows that adherence to norms can both enhance emotional intelligence and suppress genuine emotional responses, affecting interpersonal relationships and group dynamics.
Affect’s Role in Reinforcing or Challenging Norms
Affect plays a crucial role in reinforcing or challenging social norms by shaping emotional responses that guide behavior within a group. Positive emotions like pride and belonging often strengthen adherence to established norms, while feelings such as anger or dissatisfaction can motivate individuals to question or resist these rules. Emotional experiences act as powerful signals that validate or undermine normative structures, influencing social cohesion and change.
Socialization: Learning Norms and Emotional Responses
Socialization involves acquiring both societal norms and emotional responses, which are essential for effective social interaction and cohesion. Norms guide expected behaviors, while affect shapes emotional reactions, enabling individuals to understand and respond appropriately within social contexts. The interplay between learned norms and affective processes facilitates adaptive social functioning and cultural integration.
Breaking Norms: Emotional Consequences and Reactions
Breaking social norms often elicits strong emotional reactions such as guilt, shame, or anxiety due to internalized societal expectations. Individuals may experience discomfort or fear of social rejection when violating established norms, highlighting the powerful influence of affect on norm adherence. Emotional consequences serve as internal regulators, reinforcing conformity and deterring deviant behavior in social contexts.
Norms, Affect, and Group Dynamics
Norms serve as unwritten rules that guide group behavior, shaping collective expectations and influencing individual actions within social settings. Affect, encompassing emotions and feelings, interacts with norms by reinforcing conformity or resistance through emotional responses. In group dynamics, the interplay between norms and affect determines cohesion, decision-making, and the regulation of social conduct.
Implications for Social Change and Emotional Well-being
Norms shape collective behavior by establishing shared expectations, while affect influences individual emotional responses and motivation. Understanding their interplay helps design effective social change interventions that align group standards with positive emotional experiences, promoting sustained engagement. Integrating affective insights into norm-based strategies enhances emotional well-being and fosters resilient, adaptive communities.
Norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com