Cultural assimilation involves the process through which individuals or groups adopt the cultural traits of another group, often leading to the loss of their original cultural identity. This transformation can impact social integration, identity formation, and community dynamics. Explore the detailed effects and challenges of cultural assimilation in the rest of the article.
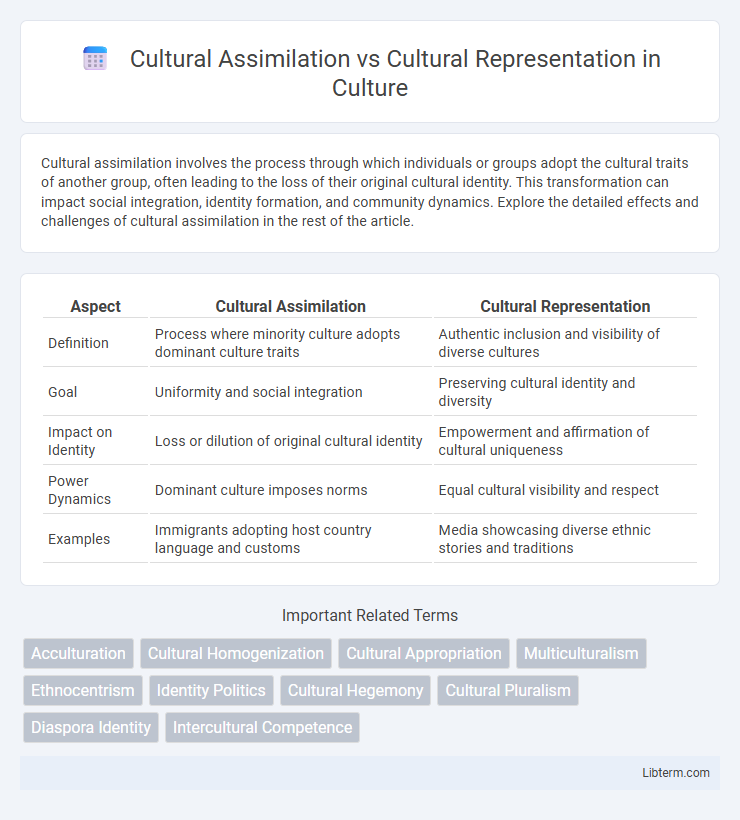
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cultural Assimilation | Cultural Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where minority culture adopts dominant culture traits | Authentic inclusion and visibility of diverse cultures |
| Goal | Uniformity and social integration | Preserving cultural identity and diversity |
| Impact on Identity | Loss or dilution of original cultural identity | Empowerment and affirmation of cultural uniqueness |
| Power Dynamics | Dominant culture imposes norms | Equal cultural visibility and respect |
| Examples | Immigrants adopting host country language and customs | Media showcasing diverse ethnic stories and traditions |
Understanding Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation involves the process by which individuals or groups adopt the customs, values, and behaviors of a dominant culture, often leading to the loss of their original cultural identities. This phenomenon typically occurs through social integration mechanisms such as language acquisition, education, and media exposure, which pressure minority groups to conform to mainstream norms. Understanding cultural assimilation is crucial for recognizing the challenges faced by marginalized communities and the importance of preserving cultural diversity.
Defining Cultural Representation
Cultural representation refers to the accurate and respectful portrayal of diverse cultural identities, customs, and values within media, literature, and social institutions. It emphasizes the importance of visibility and voice for marginalized groups, ensuring their perspectives are authentically depicted rather than stereotyped or erased. Unlike cultural assimilation, which involves the absorption of minority cultures into a dominant culture, cultural representation seeks to preserve and celebrate cultural uniqueness and diversity.
Historical Contexts of Assimilation and Representation
Historical contexts reveal cultural assimilation as a process often enforced by dominant powers to erase indigenous identities, seen in examples like Native American boarding schools and colonial language policies. Cultural representation emerged as a counter-movement, emphasizing the preservation and visibility of marginalized groups' traditions, customs, and narratives in media, education, and public discourse. The tension between assimilation and representation reflects ongoing struggles over identity, power, and cultural survival within historical frameworks.
Key Differences Between Assimilation and Representation
Cultural assimilation involves individuals or groups adopting the dominant culture's traits, often leading to the loss of original cultural identities, whereas cultural representation emphasizes the accurate and respectful portrayal of diverse cultural identities within media, institutions, or society. Assimilation pressures conformity and integration into the majority culture, while representation ensures visibility, inclusivity, and recognition of cultural uniqueness. Key differences include assimilation's impact on cultural erasure versus representation's role in preserving and validating cultural diversity.
The Impact of Cultural Assimilation on Identity
Cultural assimilation often leads to the erosion of individual and community identities as dominant cultural norms overshadow traditional beliefs and practices. This process can diminish the visibility of minority cultures, causing a loss of linguistic diversity and heritage. The struggle to maintain cultural representation becomes crucial for preserving unique identities and fostering a sense of belonging within multicultural societies.
The Role of Media in Shaping Cultural Representation
Media plays a crucial role in shaping cultural representation by framing narratives and highlighting diverse voices, which influences public perception and social norms. Through selective portrayal and storytelling, media can either perpetuate cultural assimilation by promoting dominant cultural values or foster authentic representation by valuing multicultural identities. The power of media platforms in disseminating content widely makes them a key factor in determining whether cultural diversity is celebrated or homogenized.
Benefits and Challenges of Cultural Assimilation
Cultural assimilation fosters social cohesion and facilitates communication by encouraging individuals to adopt the dominant culture's language and customs, promoting unity within diverse societies. However, it can lead to the loss of unique cultural identities and traditions, causing minority groups to experience marginalization and identity conflicts. Balancing the benefits of integration with the preservation of cultural heritage remains a significant challenge in multicultural communities.
Importance of Authentic Cultural Representation
Authentic cultural representation fosters inclusivity and respect by accurately portraying diverse traditions and experiences. It combats stereotypes and preserves cultural identity, allowing communities to see themselves reflected truthfully in media and society. Emphasizing genuine cultural narratives enhances social cohesion and promotes understanding across different cultures.
Case Studies: Assimilation vs Representation in Society
Case studies of cultural assimilation versus cultural representation reveal contrasting societal impacts, with assimilation often leading to the erosion of minority identities and representation promoting cultural diversity and recognition. For example, indigenous groups in Canada face assimilation pressures in education systems, whereas initiatives like New Zealand's Te Reo Maori revitalization highlight successful cultural representation. These examples demonstrate how representation strengthens social inclusion and preserves cultural heritage, while assimilation risks homogenizing communities and marginalizing unique cultural narratives.
Moving Toward Inclusive Cultural Practices
Inclusive cultural practices prioritize cultural representation by honoring diverse identities and traditions instead of forcing cultural assimilation, which can erase unique cultural expressions. Emphasizing authentic representation in education, media, and public policy promotes respect and equity for marginalized communities. Shifting toward inclusivity enriches social cohesion by valuing multiplicity rather than uniformity in cultural narratives.
Cultural Assimilation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com