Literary culture shapes society by preserving stories, ideas, and values through written and oral traditions that inspire creativity and critical thinking. It fosters a shared identity and encourages diverse perspectives, enriching your understanding of human experience. Explore the rest of the article to discover how literary culture influences both individual growth and collective heritage.
Table of Comparison
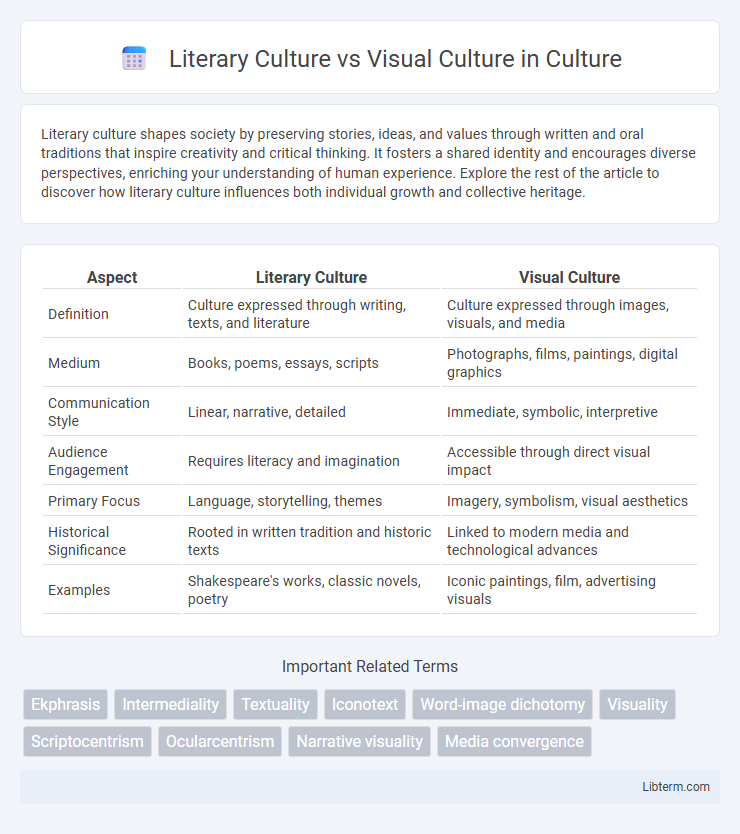
| Aspect | Literary Culture | Visual Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Culture expressed through writing, texts, and literature | Culture expressed through images, visuals, and media |
| Medium | Books, poems, essays, scripts | Photographs, films, paintings, digital graphics |
| Communication Style | Linear, narrative, detailed | Immediate, symbolic, interpretive |
| Audience Engagement | Requires literacy and imagination | Accessible through direct visual impact |
| Primary Focus | Language, storytelling, themes | Imagery, symbolism, visual aesthetics |
| Historical Significance | Rooted in written tradition and historic texts | Linked to modern media and technological advances |
| Examples | Shakespeare's works, classic novels, poetry | Iconic paintings, film, advertising visuals |
Defining Literary Culture and Visual Culture
Literary culture encompasses the traditions, practices, and values centered around written and spoken language, including genres such as poetry, novels, and essays, emphasizing narrative structures and linguistic expression. Visual culture involves the creation, interpretation, and consumption of visual images and media, such as painting, photography, film, and digital graphics, shaping perception through visual representation. Both cultures influence cognitive processes and societal norms, but literary culture relies on text-based communication while visual culture prioritizes imagery and spatial aesthetics.
Historical Evolution of Literary and Visual Traditions
The historical evolution of literary and visual traditions reveals distinct yet intertwined trajectories shaped by technological advancements and cultural shifts. Literary culture originated with oral storytelling, evolving through manuscript production to printed books, fundamentally transforming knowledge dissemination and literacy rates. Visual culture progressed from prehistoric cave paintings to digital media, reflecting changes in societal communication methods and the expanding role of imagery in everyday life.
Modes of Expression: Text vs. Image
Literary culture emphasizes the written word, using complex syntax, narrative structures, and metaphor to convey meaning, engaging readers through imagination and interpretive thought. Visual culture relies on images, symbols, and spatial compositions to communicate messages quickly and universally, often evoking immediate emotional responses. Text demands sequential decoding and deep cognitive processing, whereas images provide simultaneous perception and contextual cues.
Cognitive Impact: Reading Words vs. Seeing Images
Reading words engages the brain's language centers, fostering deep cognitive processing, critical thinking, and imagination by requiring interpretation and visualization. Visual culture activates the brain's visual and spatial regions, offering immediate comprehension and emotional impact through imagery, which can enhance memory retention and pattern recognition. The cognitive impact of literary culture promotes analytical skills and abstract thought, whereas visual culture emphasizes sensory experience and intuitive understanding.
Narrative Structures: Linear Texts and Visual Storytelling
Literary culture relies heavily on linear texts that follow structured narrative arcs with clear beginnings, middles, and ends, emphasizing sequential comprehension and detailed character development. Visual culture, in contrast, utilizes visual storytelling techniques such as montage, spatial composition, and non-linear timelines to convey complex narratives through imagery and symbolism. The integration of visual elements challenges traditional narrative structures by enabling multi-layered interpretations that transcend linear progression.
The Role of Technology in Shaping Cultural Modes
Technological advancements have transformed literary culture by enabling digital publishing, e-books, and interactive narratives that expand traditional reading experiences. Visual culture has been shaped by innovations such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and high-definition imaging, which enhance visual storytelling and audience engagement. The integration of artificial intelligence and social media platforms further influences both literary and visual modes, fostering new forms of cultural expression and consumption.
Literacy and Visual Literacy: Skills for Understanding
Literacy involves decoding written language, comprehension, and critical analysis of texts, essential for navigating literary culture. Visual literacy encompasses interpreting, analyzing, and evaluating visual media, crucial for engaging with visual culture. Mastery of both literacy and visual literacy equips individuals with comprehensive skills to understand diverse communication forms in contemporary society.
Influence on Society and Identity Formation
Literary culture shapes society and identity through the transmission of narratives, language, and historical consciousness, fostering critical thinking and empathy by engaging readers in complex textual analysis. Visual culture influences identity formation via immediate, sensory experiences in media, art, and popular culture, emphasizing symbolism and emotional impact that can transcend linguistic barriers. Both cultures interact dynamically, with literature providing depth and reflection, while visual culture offers accessibility and visceral connectivity, collectively molding societal values and individual self-perception.
Intersections and Hybrid Forms in Contemporary Media
Contemporary media increasingly blurs the boundaries between literary culture and visual culture, creating hybrid forms such as graphic novels, multimedia storytelling, and interactive digital narratives. These intersections facilitate immersive experiences where textual elements merge with visual aesthetics, enhancing meaning through multimodal engagement. Platforms like webcomics and virtual reality literature exemplify how literary narratives adapt to visual culture, fostering innovative ways of knowledge transmission and emotional resonance.
Future Trends: Integration or Divergence of Cultures
Future trends indicate a growing integration of literary and visual cultures through multimedia platforms and digital storytelling, enhancing narrative experiences via augmented reality and interactive e-books. Advances in AI and virtual reality technologies enable immersive environments that blend textual and visual elements, creating hybrid cultural forms that appeal to diverse audiences. However, certain sectors may witness divergence as purists in literature and visual arts emphasize traditional mediums, prompting parallel evolution rather than complete convergence.
Literary Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com