Technological advancement drives innovation across industries, enhancing efficiency and transforming everyday life with cutting-edge tools and solutions. It shapes the future by enabling smarter communication, automation, and sustainable development. Discover how these breakthroughs can impact your world by reading the rest of the article.
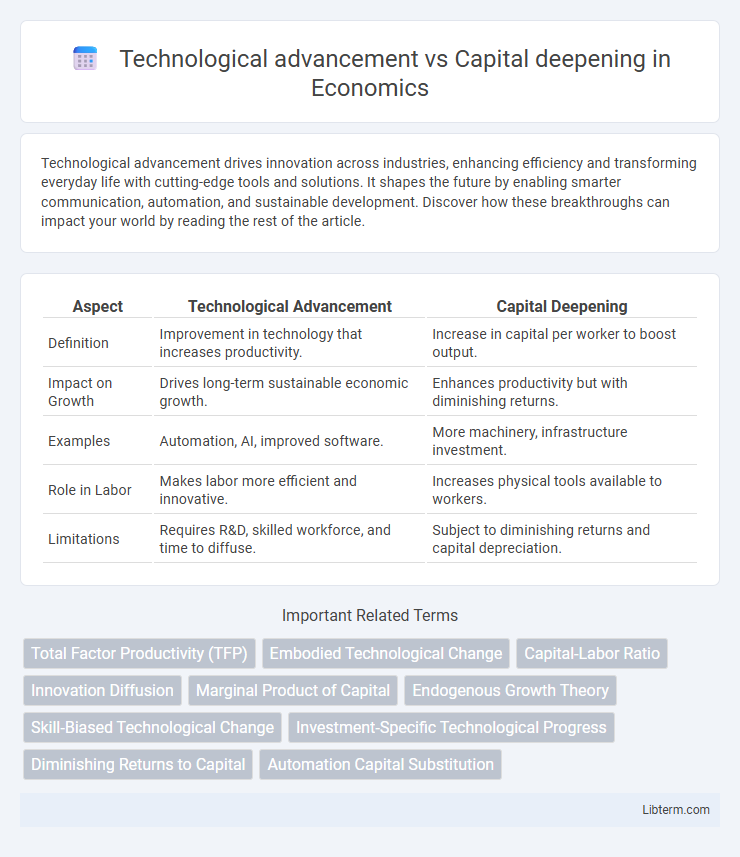
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Technological Advancement | Capital Deepening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Improvement in technology that increases productivity. | Increase in capital per worker to boost output. |
| Impact on Growth | Drives long-term sustainable economic growth. | Enhances productivity but with diminishing returns. |
| Examples | Automation, AI, improved software. | More machinery, infrastructure investment. |
| Role in Labor | Makes labor more efficient and innovative. | Increases physical tools available to workers. |
| Limitations | Requires R&D, skilled workforce, and time to diffuse. | Subject to diminishing returns and capital depreciation. |
Defining Technological Advancement and Capital Deepening
Technological advancement refers to the process of developing and implementing new technologies, innovations, and improvements that increase productivity and efficiency in economic activities. Capital deepening involves an increase in the amount of capital per worker, enhancing labor productivity through more intensive use of physical assets such as machinery, tools, and infrastructure. Both concepts are crucial in driving economic growth, with technological advancement focusing on innovation and capital deepening emphasizing the accumulation of physical capital.
Historical Perspectives on Economic Growth Drivers
Technological advancement and capital deepening have played distinct but complementary roles in shaping economic growth throughout history. During the Industrial Revolution, breakthroughs in machinery and production techniques dramatically enhanced productivity, marking technological progress as a primary growth driver. In contrast, periods of intensified capital deepening, characterized by increased investment in physical assets like infrastructure and equipment, also stimulated growth by expanding the economy's productive capacity and supporting sustained technological adoption.
The Role of Technology in Boosting Productivity
Technological advancement significantly enhances productivity by introducing innovative tools, automation, and processes that streamline operations and reduce labor intensity. Capital deepening, which involves increasing the amount of capital per worker, supports productivity growth but often depends on the underlying technology integrated into the capital assets. Efficient technology adoption amplifies the returns on capital investments, driving sustainable economic growth by improving output quality and operational efficiency.
Capital Deepening: Investing in Tools and Infrastructure
Capital deepening involves increasing the amount of capital per worker, enhancing productivity through investment in tools, machinery, and infrastructure. This approach allows businesses to utilize advanced equipment and modern facilities, leading to more efficient production processes and higher output levels. Empirical studies show that sustained capital deepening significantly boosts economic growth by expanding the productive capacity of labor.
Comparative Impacts on Labor Markets
Technological advancement drives labor market transformation by automating tasks and creating demand for high-skill jobs, often leading to job displacement in routine occupations. Capital deepening enhances labor productivity by increasing physical capital per worker, which can raise wages but does not fundamentally change the skill composition of labor demand. Studies show technological change has a more pronounced effect on wage inequality and employment polarization compared to capital deepening, highlighting its critical role in shaping future labor market dynamics.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Growth Strategies
Technological advancement drives economic growth by enhancing productivity through innovation and automation, as seen in South Korea's shift to high-tech industries. Capital deepening, involving increased investment in physical capital per worker, played a crucial role in China's rapid industrialization by boosting labor efficiency. Global case studies reveal that balanced integration of technology and capital deepening creates sustainable growth trajectories in emerging and developed economies alike.
Interplay Between Technology Adoption and Capital Investment
Technological advancement drives productivity by enhancing the efficiency and capabilities of capital assets, making capital deepening more impactful when firms adopt cutting-edge innovations. Capital investment facilitates the implementation of new technologies by providing updated machinery and infrastructure necessary for technology integration and optimized production processes. The interplay between technology adoption and capital deepening creates a synergistic effect, where investments in advanced technology amplify returns on capital, accelerating economic growth and competitive advantage.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Technological advancement faces challenges such as high research and development costs, rapid obsolescence of innovations, and the need for skilled labor to implement new technologies effectively. Capital deepening encounters limitations including diminishing returns to additional capital, increased operational costs, and potential underutilization of equipment during economic downturns. Both approaches require substantial investment and strategic planning to balance productivity gains with sustainable growth.
Policy Implications for Sustainable Economic Development
Technological advancement drives productivity by introducing innovative methods and processes, while capital deepening enhances worker efficiency through increased investment in physical assets. Policy implications emphasize balanced investment in R&D to foster innovation alongside infrastructure development to support capital accumulation. Sustainable economic development requires integrating technology adoption policies with capital deepening strategies to ensure long-term growth without depleting environmental resources.
Future Trends in Growth: Integrating Technology and Capital Deepening
Future economic growth increasingly depends on the integration of technological advancement and capital deepening, where investments in cutting-edge technologies enhance capital productivity and efficiency. Emerging trends highlight the synergy between digital transformation, automation, and smart infrastructure as key drivers that amplify capital intensity and foster sustained long-term growth. Strategies prioritizing AI adoption, advanced robotics, and IoT-enabled assets will redefine capital deepening by accelerating innovation cycles and optimizing resource allocation across industries.
Technological advancement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com