Dynamic stability refers to the ability of a system or structure to maintain its equilibrium under changing conditions or external forces, ensuring continuous performance without failure. It is essential in engineering, aerospace, and vehicle design to prevent oscillations or instabilities that could lead to catastrophic outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to understand how dynamic stability impacts your projects and everyday life.
Table of Comparison
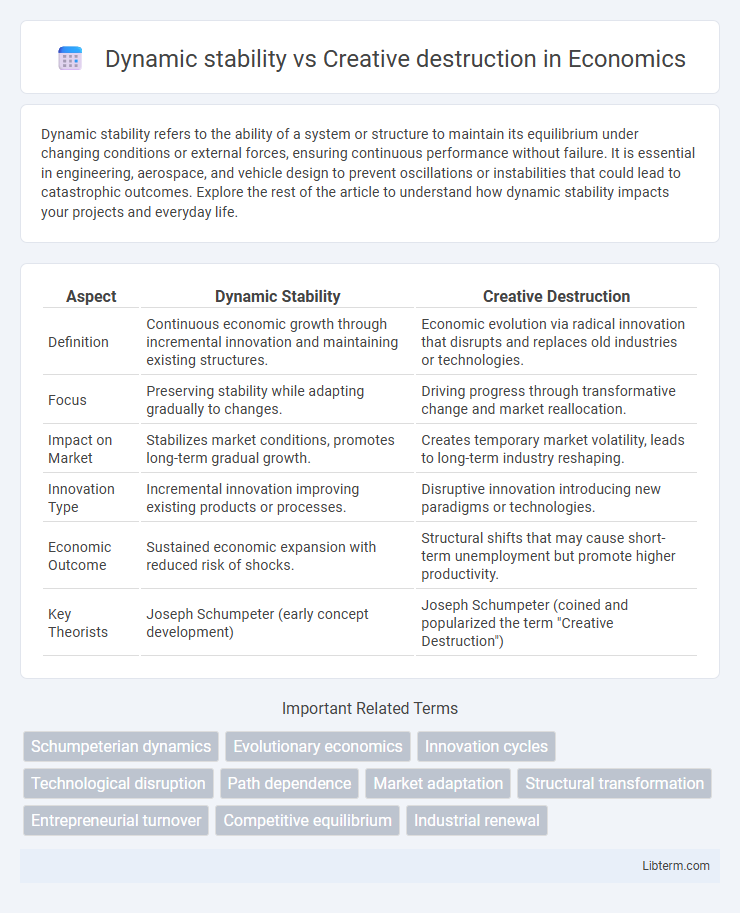
| Aspect | Dynamic Stability | Creative Destruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous economic growth through incremental innovation and maintaining existing structures. | Economic evolution via radical innovation that disrupts and replaces old industries or technologies. |
| Focus | Preserving stability while adapting gradually to changes. | Driving progress through transformative change and market reallocation. |
| Impact on Market | Stabilizes market conditions, promotes long-term gradual growth. | Creates temporary market volatility, leads to long-term industry reshaping. |
| Innovation Type | Incremental innovation improving existing products or processes. | Disruptive innovation introducing new paradigms or technologies. |
| Economic Outcome | Sustained economic expansion with reduced risk of shocks. | Structural shifts that may cause short-term unemployment but promote higher productivity. |
| Key Theorists | Joseph Schumpeter (early concept development) | Joseph Schumpeter (coined and popularized the term "Creative Destruction") |
Understanding Dynamic Stability in Economics
Dynamic stability in economics refers to a system's ability to maintain equilibrium despite ongoing changes, ensuring sustainable growth and adaptive responses to market fluctuations. It contrasts with creative destruction, where outdated industries are replaced by innovation-driven transformations, often causing short-term instability. Understanding dynamic stability involves analyzing feedback mechanisms, adaptive expectations, and regulatory frameworks that support continuous economic resilience and long-term prosperity.
The Principles of Creative Destruction
The principles of creative destruction emphasize the continuous innovation cycle where new technologies and business models disrupt existing market structures, fostering economic growth and industrial evolution. This process contrasts with dynamic stability, which seeks to maintain equilibrium and steady progress within an economy by adapting to changes without fundamental upheaval. Creative destruction drives transformational change by replacing outdated industries, while dynamic stability prioritizes incremental improvement and risk management to sustain long-term economic resilience.
Historical Context: Evolution of Market Systems
Dynamic stability in market systems emphasizes gradual adaptation and incremental innovation to maintain economic balance, often seen in post-industrial economies during the 20th century. Creative destruction, introduced by economist Joseph Schumpeter, highlights the disruptive process where new innovations replace outdated technologies and business models, driving capitalist evolution since the Industrial Revolution. Historical shifts from agrarian economies to industrial and digital markets illustrate the interplay between preserving system stability and fostering transformation through entrepreneurial innovation.
Dynamic Stability vs Creative Destruction: A Comparative Overview
Dynamic stability emphasizes gradual innovation and continuous improvement to maintain equilibrium within markets, ensuring long-term sustainability and resilience. Creative destruction drives transformative shifts by dismantling outdated structures and fostering radical innovations, often resulting in industry disruption and economic evolution. Comparing both reveals that dynamic stability supports incremental growth with minimal market volatility, while creative destruction accelerates progress through cyclical renewal and competitive upheaval.
Key Drivers of Dynamic Stability
Dynamic stability is driven primarily by adaptive innovation, steady resource allocation, and continuous process improvements that maintain equilibrium within evolving markets. Key drivers include resilient organizational structures, feedback mechanisms for rapid problem-solving, and sustained investment in human capital to foster incremental advancements. These factors contrast with creative destruction's emphasis on disruptive innovation and radical market shifts.
Catalysts and Consequences of Creative Destruction
Creative destruction acts as a powerful catalyst in economic evolution by dismantling outdated structures and fostering innovation, leading to increased market efficiency and technological advancement. This process generates both opportunities and challenges, driving entrepreneurial activity while causing short-term job displacement and sectoral shifts. The consequences of creative destruction include accelerated economic growth, enhanced competitive dynamics, and transformation of industries, contrasting with the steady-state equilibrium emphasized in dynamic stability.
Innovation: The Connecting Thread
Dynamic stability fosters continuous innovation by maintaining a balance between preserving existing capabilities and integrating new knowledge, ensuring steady growth and adaptation. Creative destruction drives innovation through disruptive transformation, replacing outdated technologies and business models with novel solutions that redefine industries. Both concepts underscore innovation as the connecting thread that fuels economic evolution, where dynamic stability supports incremental improvements while creative destruction enables radical breakthroughs.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures in Market Adaptation
Dynamic stability in market adaptation emphasizes continuous incremental improvements to maintain competitive advantage, as demonstrated by Toyota's lean manufacturing, which sustained profitability over decades. Creative destruction involves radical innovation that disrupts existing markets, illustrated by Kodak's failure to adapt to digital photography, leading to bankruptcy despite prior dominance. Tesla exemplifies successful creative destruction by revolutionizing the automotive industry with electric vehicles, significantly altering market dynamics.
Policy Implications and Strategic Approaches
Dynamic stability emphasizes policies that balance incremental innovation with economic resilience, fostering steady growth through continuous improvement of existing industries. Creative destruction advocates for strategic approaches that encourage disruptive innovation, enabling rapid resource reallocation and market adaptation despite transitional instability. Policymakers must design frameworks that support both the protection of stable economic structures and the facilitation of transformative technological shifts to sustain long-term competitiveness.
Future Trends: Navigating Change in a Dynamic Economy
Dynamic stability ensures continuous innovation and adaptation within industries, fostering sustainable growth while maintaining core economic structures. Creative destruction accelerates transformative shifts by dismantling outdated systems, allowing novel technologies and business models to emerge rapidly. Future trends emphasize the balance between preserving economic resilience through dynamic stability and embracing disruptive innovation driven by creative destruction to navigate volatility and drive long-term prosperity.
Dynamic stability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com