Hedging involves using financial instruments or strategies to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in assets, providing a safeguard against market volatility. By understanding and applying hedging techniques, you can protect your investments and stabilize your portfolio's performance. Dive into the rest of this article to explore effective hedging methods and how they can benefit your financial planning.
Table of Comparison
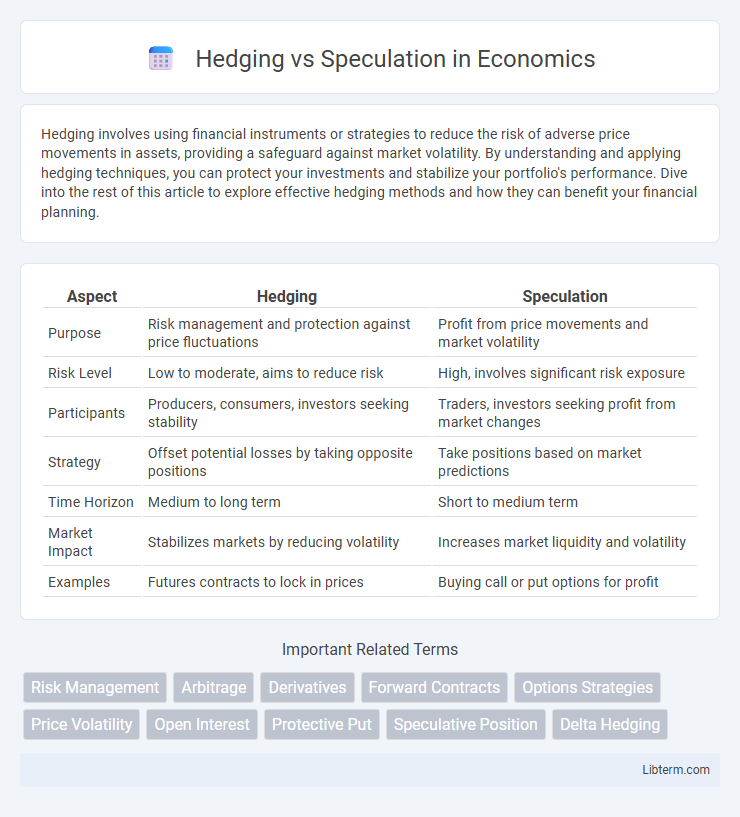
| Aspect | Hedging | Speculation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Risk management and protection against price fluctuations | Profit from price movements and market volatility |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate, aims to reduce risk | High, involves significant risk exposure |
| Participants | Producers, consumers, investors seeking stability | Traders, investors seeking profit from market changes |
| Strategy | Offset potential losses by taking opposite positions | Take positions based on market predictions |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long term | Short to medium term |
| Market Impact | Stabilizes markets by reducing volatility | Increases market liquidity and volatility |
| Examples | Futures contracts to lock in prices | Buying call or put options for profit |
Introduction to Hedging and Speculation
Hedging is a risk management strategy used by investors and businesses to protect against potential losses from market fluctuations by taking opposite positions in related assets. Speculation involves taking on higher risk with the goal of profiting from price changes in financial instruments such as stocks, commodities, or currencies. Both strategies are fundamental in financial markets, with hedging aimed at minimizing risk and speculation focused on capitalizing on market volatility.
Defining Hedging: Purpose and Process
Hedging is a risk management strategy used to protect investments or business operations from adverse price movements in assets or commodities. The process involves taking an offsetting position in a related security, such as futures contracts or options, to minimize potential losses. Its primary purpose is to provide financial stability by reducing exposure to market volatility rather than seeking profit.
Understanding Speculation in Financial Markets
Speculation in financial markets involves actively buying and selling assets to profit from price fluctuations, often taking higher risks compared to hedging. Speculators analyze market trends, economic indicators, and events to forecast price movements and capitalize on short-term opportunities. Unlike hedgers who aim to minimize risk and protect assets, speculators accept volatility to achieve potentially higher returns.
Key Differences Between Hedging and Speculation
Hedging involves mitigating risk by taking an offsetting position in a related asset to protect against adverse price movements, whereas speculation aims to profit from price fluctuations by taking on higher risk. Hedgers prioritize risk reduction and capital preservation, typically using derivatives like futures, options, or swaps to lock in prices or rates. Speculators seek to maximize returns by forecasting market trends and are willing to accept potential losses, with strategies often involving leveraged positions and higher market exposure.
Common Strategies Used in Hedging
Common strategies used in hedging include forward contracts, futures contracts, options, and swaps, each designed to mitigate risk by locking in prices or rates. Forward contracts create customized agreements to buy or sell assets at predetermined prices, reducing exposure to market volatility. Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to trade at specified prices, offering flexible risk management without the requirement to execute the transaction.
Popular Techniques in Speculation
Popular techniques in speculation include leveraging derivatives such as options, futures, and swaps to capitalize on price fluctuations in various asset classes, including commodities, stocks, and currencies. Speculators often employ margin trading to amplify potential returns, accepting higher risk by borrowing funds to increase their market exposure. Technical analysis and algorithmic trading systems are widely used to identify short-term price trends and execute rapid trades, aiming for profit maximization in volatile markets.
Risk Management in Hedging versus Speculation
Hedging involves strategies designed to minimize or eliminate the risk of adverse price movements in assets by taking offsetting positions, providing stability and protection for investors and businesses. Speculation, on the other hand, accepts higher risk with the aim of achieving significant profits based on market fluctuations, often involving leveraged positions that can result in substantial gains or losses. Risk management in hedging prioritizes preserving capital and reducing uncertainty, whereas speculation emphasizes capitalizing on price volatility for potential financial reward.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Hedging
Hedging helps reduce financial risk by using instruments like futures, options, or swaps to protect against price fluctuations, providing businesses and investors with greater stability and predictability. However, it can limit potential profits and incur costs such as premiums and fees, which may reduce overall returns. While hedging minimizes losses in volatile markets, it requires expertise and may lead to over-hedging, resulting in missed opportunities for gains.
Pros and Cons of Speculation
Speculation in financial markets offers the potential for high returns by taking advantage of price volatility and market inefficiencies, allowing traders to profit from short-term movements in assets like stocks, commodities, and currencies. However, speculation carries significant risks, including the possibility of substantial financial losses due to unpredictable market fluctuations and the reliance on accurate market timing. Unlike hedging, which aims to minimize risk exposure, speculation involves exposing capital to higher uncertainty and requires advanced market knowledge and risk management strategies.
Choosing the Right Approach: Hedging or Speculation?
Choosing the right approach between hedging and speculation depends on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and market knowledge. Hedging aims to minimize potential losses by taking offsetting positions in related assets, making it ideal for risk-averse investors and businesses seeking stability. Speculation involves taking higher risks to achieve greater returns, requiring thorough market analysis and a willingness to accept potential losses for profit opportunities.
Hedging Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com