Time rate wage refers to the payment method where employees are compensated based on the number of hours worked, typically receiving a fixed amount per hour. This system ensures predictable earnings and straightforward wage calculations for both employers and employees. Explore the full article to understand how time rate wages impact labor productivity and employee motivation.
Table of Comparison
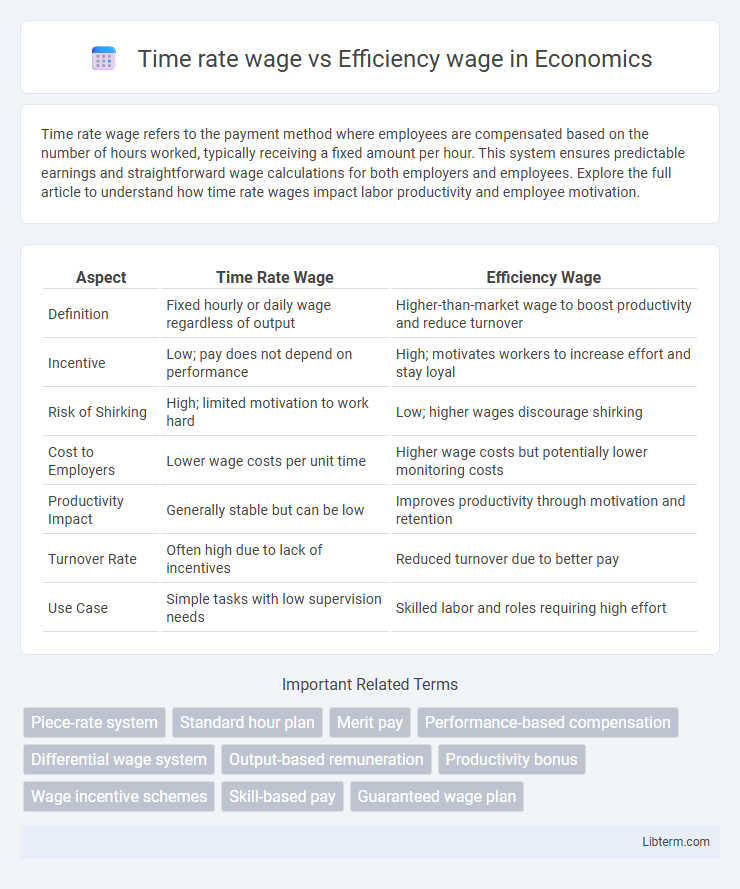
| Aspect | Time Rate Wage | Efficiency Wage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixed hourly or daily wage regardless of output | Higher-than-market wage to boost productivity and reduce turnover |
| Incentive | Low; pay does not depend on performance | High; motivates workers to increase effort and stay loyal |
| Risk of Shirking | High; limited motivation to work hard | Low; higher wages discourage shirking |
| Cost to Employers | Lower wage costs per unit time | Higher wage costs but potentially lower monitoring costs |
| Productivity Impact | Generally stable but can be low | Improves productivity through motivation and retention |
| Turnover Rate | Often high due to lack of incentives | Reduced turnover due to better pay |
| Use Case | Simple tasks with low supervision needs | Skilled labor and roles requiring high effort |
Understanding Time Rate Wage: Definition and Basics
Time rate wage refers to a fixed amount of pay awarded to employees based on the total hours worked, regardless of output level or productivity. Common in hourly wage systems, it provides income stability but may not incentivize increased efficiency or higher performance. Understanding the basic principles of time rate wage clarifies its role in labor cost management and employee compensation structures.
Efficiency Wage Explained: Concept and Principles
Efficiency wage theory posits that employers pay wages above the market-clearing level to increase worker productivity, reduce turnover, and attract higher-quality employees. This strategy aims to align employee incentives with organizational goals, improving efficiency and output, unlike the time rate wage system where pay is based solely on hours worked. By offering higher wages, firms encourage greater effort, lower shirking, and foster loyalty, which can lead to overall cost savings despite increased wage expenses.
Key Differences Between Time Rate Wage and Efficiency Wage
Time rate wage compensates employees based on the number of hours worked, providing a fixed payment regardless of output, while efficiency wage links pay to productivity, incentivizing higher performance. Time rate wage offers predictable labor costs but may lead to lower motivation, whereas efficiency wage can enhance worker efficiency and reduce shirking by rewarding higher output. Employers using efficiency wages often experience improved employee retention and increased overall productivity compared to those relying solely on time rate wages.
Advantages of Time Rate Wage System
The Time Rate Wage system offers predictable and stable income, enhancing worker satisfaction and reducing turnover by providing consistent pay regardless of output fluctuations. It simplifies payroll administration and fosters teamwork, as employees are not incentivized to compete for higher individual productivity. This wage structure also supports quality control by allowing workers to focus on task accuracy without the pressure for speed-driven errors.
Benefits of Efficiency Wage for Employers and Employees
Efficiency wage offers employers increased worker productivity by motivating employees to exert higher effort and reduce shirking, leading to improved overall output and lower supervision costs. Employees benefit from higher-than-market wages that enhance job satisfaction, reduce turnover, and promote better health and morale, creating a more stable and committed workforce. This wage strategy fosters mutual gains by aligning interests and increasing economic efficiency beyond the limitations of time rate wages.
Disadvantages of Time Rate Wage: Challenges and Limitations
Time rate wage systems can lead to reduced worker motivation due to lack of direct incentive for higher productivity, often resulting in decreased efficiency and output quality. Fixed wages regardless of performance may encourage minimal effort, absenteeism, and difficulty in distinguishing high performers from low performers. Such limitations pose significant challenges for businesses seeking to enhance operational efficiency and workforce engagement.
Drawbacks of Efficiency Wage: Potential Downsides
Efficiency wages can lead to increased labor costs, which may reduce a firm's competitiveness in price-sensitive markets. Paying above-market wages might cause resentment among workers whose productivity does not match the premium pay, potentially reducing morale. There is also a risk of inefficiency if employees become complacent, relying on higher wages rather than maintaining consistent performance.
Impact on Productivity: Time Rate Wage vs Efficiency Wage
Time rate wage offers consistent pay regardless of output, which can result in lower employee motivation and reduced productivity due to lack of performance incentives. Efficiency wage, by paying above-market rates, motivates workers to increase effort and reduce shirking, leading to higher productivity and improved work quality. Empirical studies show firms adopting efficiency wage models experience significant gains in output and employee retention compared to those relying solely on time rate wages.
Suitability for Different Industries and Job Roles
Time rate wage systems are highly suitable for industries with repetitive, standardized tasks, such as manufacturing and assembly lines, where output is consistent and easily measured over fixed hours. Efficiency wage models fit knowledge-intensive or creative sectors like technology and research, incentivizing higher productivity and innovation by linking pay to performance and skill levels. Service industries benefit from hybrid approaches, balancing stable hourly pay with performance bonuses to accommodate variable workload and customer interaction dynamics.
Choosing the Right Wage System: Factors to Consider
When choosing between time rate wage and efficiency wage systems, consider factors such as the nature of the job, employee motivation, and productivity measurement. Time rate wage suits standardized, repetitive tasks with easily quantifiable hours, while efficiency wage incentivizes higher output by tying pay to performance, reducing turnover and promoting effort. Firms must balance labor cost control with the need to stimulate productivity and retain skilled workers to select the optimal wage structure.
Time rate wage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com