Open-economy macroeconomic policy focuses on managing a country's economic interactions with the global market through tools such as exchange rates, trade regulations, and capital flows to stabilize growth and inflation. Effective policies help balance trade deficits, attract foreign investment, and maintain currency stability, directly influencing Your nation's economic resilience. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these policies shape global economic dynamics and impact Your economic environment.
Table of Comparison
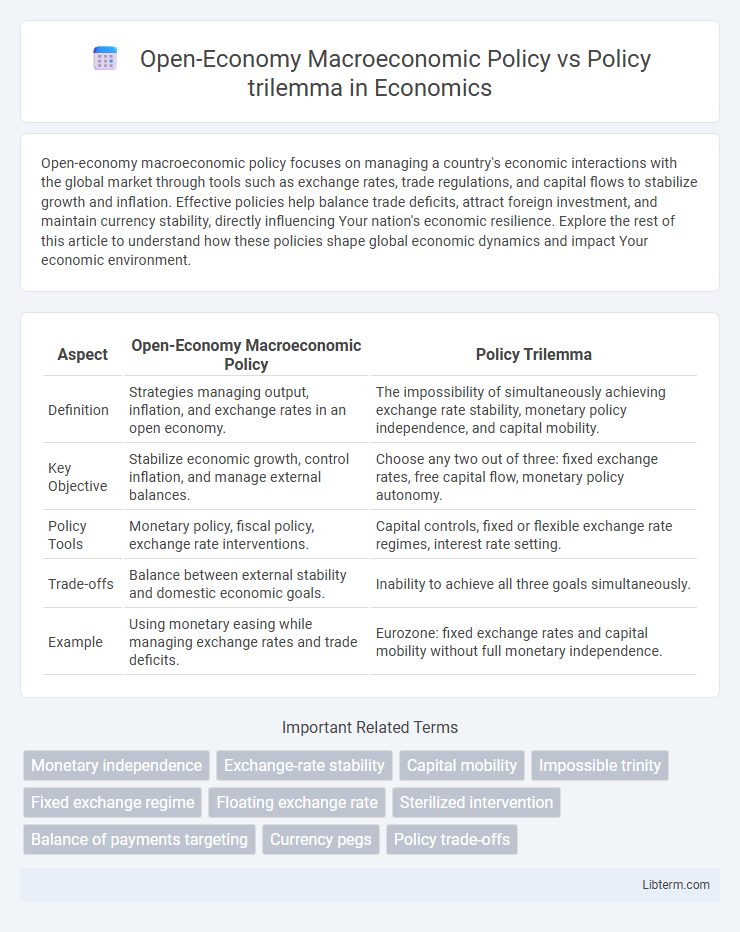
| Aspect | Open-Economy Macroeconomic Policy | Policy Trilemma |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategies managing output, inflation, and exchange rates in an open economy. | The impossibility of simultaneously achieving exchange rate stability, monetary policy independence, and capital mobility. |
| Key Objective | Stabilize economic growth, control inflation, and manage external balances. | Choose any two out of three: fixed exchange rates, free capital flow, monetary policy autonomy. |
| Policy Tools | Monetary policy, fiscal policy, exchange rate interventions. | Capital controls, fixed or flexible exchange rate regimes, interest rate setting. |
| Trade-offs | Balance between external stability and domestic economic goals. | Inability to achieve all three goals simultaneously. |
| Example | Using monetary easing while managing exchange rates and trade deficits. | Eurozone: fixed exchange rates and capital mobility without full monetary independence. |
Understanding Open-Economy Macroeconomic Policy
Open-Economy Macroeconomic Policy navigates the balance between exchange rate stability, monetary autonomy, and capital mobility known as the policy trilemma. Policymakers must prioritize two of these three objectives, influencing inflation control, trade competitiveness, and capital flow regulation. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for designing strategies that promote economic growth while maintaining financial stability in an interconnected global market.
The Concept of the Policy Trilemma
The policy trilemma in open-economy macroeconomic policy states that a country cannot simultaneously achieve fixed exchange rates, free capital mobility, and an independent monetary policy. Policymakers must choose two of these three objectives, sacrificing the third to maintain economic stability. This concept highlights the trade-offs governments face in managing currency stability, capital flows, and domestic economic conditions.
Exchange Rate Regimes and Their Implications
Exchange rate regimes play a critical role in open-economy macroeconomic policy, influencing a country's ability to balance monetary autonomy, exchange rate stability, and capital mobility as described by the policy trilemma. Fixed exchange rate regimes provide exchange rate stability but limit independent monetary policy due to the need to maintain currency pegs, often requiring capital controls to prevent speculative attacks. Conversely, flexible exchange rate regimes allow for monetary policy autonomy and free capital flows, yet expose economies to exchange rate volatility and potential trade imbalances.
Monetary Independence in a Globalized World
Monetary independence in an open-economy macroeconomic policy framework faces significant challenges due to the policy trilemma, which states that countries can only simultaneously achieve two out of three goals: monetary independence, exchange rate stability, and free capital movement. In a globalized world with high capital mobility, sustaining autonomous monetary policy becomes difficult without sacrificing either exchange rate stability or capital controls. Empirical studies show that many advanced economies prioritize monetary independence by adopting floating exchange rates to respond effectively to domestic economic conditions.
Free Capital Mobility: Opportunities and Challenges
Free capital mobility in open-economy macroeconomic policy enables efficient allocation of resources and fosters cross-border investment, boosting economic growth and financial integration. However, according to the policy trilemma, countries must choose between free capital mobility, fixed exchange rates, and autonomous monetary policy, making it impossible to achieve all three simultaneously. The challenge lies in balancing capital flows to prevent financial instability and sudden capital flight while maintaining economic sovereignty and exchange rate stability.
The Impossible Trinity: Trade-offs and Constraints
The Impossible Trinity, or policy trilemma, highlights the trade-offs between three macroeconomic policy goals: fixed exchange rates, free capital movement, and independent monetary policy in an open economy. Policymakers must choose only two of these objectives simultaneously, as pursuing all three leads to inherent economic constraints and instability. This trilemma forces countries to strategically balance exchange rate stability, capital mobility, and monetary autonomy, shaping open-economy macroeconomic policy decisions.
Policy Tools for Open Economies
Open-economy macroeconomic policy utilizes tools such as monetary policy adjustments, fiscal measures, and exchange rate interventions to manage economic stability amid global capital flows and trade dynamics. The policy trilemma, or impossible trinity, highlights the trade-offs between exchange rate stability, monetary autonomy, and capital mobility, forcing policymakers to prioritize two out of the three objectives. Effective policy tools in open economies must balance these constraints to foster sustainable growth, control inflation, and maintain external balance without triggering financial instability.
Case Studies: Navigating the Policy Trilemma
Open-economy macroeconomic policy faces the policy trilemma, which states that a country cannot simultaneously maintain fixed exchange rates, free capital movement, and an independent monetary policy. Case studies like China's managed float system and Eurozone countries illustrate different trade-offs: China maintains exchange rate stability and monetary control by restricting capital flows, while Eurozone members embrace capital mobility and fixed exchange rates under the euro but forfeit independent monetary policy. These examples highlight strategic choices countries make to navigate the constraints imposed by the policy trilemma, balancing economic stability and integration within global markets.
Lessons from Emerging and Advanced Economies
Emerging economies often face heightened challenges balancing exchange rate stability, monetary policy independence, and capital mobility, revealing the constraints of the policy trilemma in open-economy macroeconomic management. Advanced economies, with deeper financial markets and stronger institutional frameworks, demonstrate more effective navigation of policy trade-offs, emphasizing the role of credible monetary policy and flexible exchange rate regimes. These lessons highlight the importance of tailored macroeconomic strategies that consider financial integration levels and institutional capacity in achieving sustainable growth and stability.
Future Directions for Open-Economy Macro Policies
Future directions for open-economy macroeconomic policy emphasize balancing exchange rate stability, capital mobility, and monetary autonomy amid increasing global financial integration. Emerging tools like digital currencies and enhanced macroprudential regulations aim to mitigate risks inherent in the policy trilemma framework. Embracing flexible policy frameworks and international coordination can improve resilience against external shocks and foster sustainable economic growth.
Open-Economy Macroeconomic Policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com