Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency that uses cryptography for secure transactions and operates independently of a central bank. Blockchain technology ensures transparency and immutability, making it a popular choice for investors and businesses seeking decentralized financial solutions. Discover how cryptocurrency can impact your financial future in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
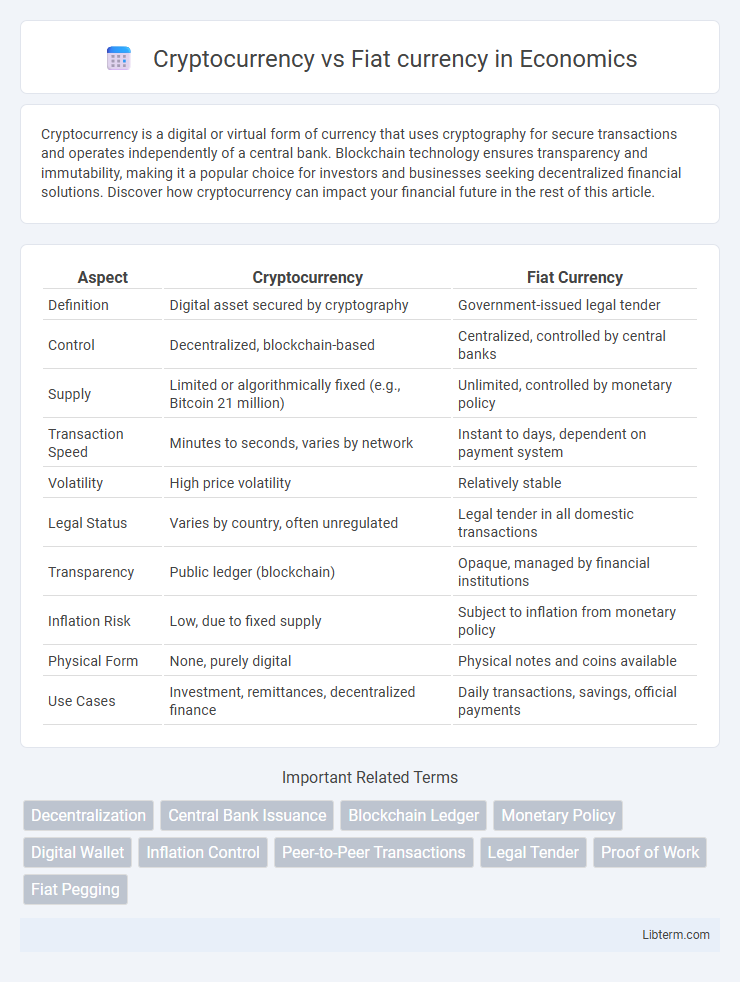
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency | Fiat Currency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital asset secured by cryptography | Government-issued legal tender |
| Control | Decentralized, blockchain-based | Centralized, controlled by central banks |
| Supply | Limited or algorithmically fixed (e.g., Bitcoin 21 million) | Unlimited, controlled by monetary policy |
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to seconds, varies by network | Instant to days, dependent on payment system |
| Volatility | High price volatility | Relatively stable |
| Legal Status | Varies by country, often unregulated | Legal tender in all domestic transactions |
| Transparency | Public ledger (blockchain) | Opaque, managed by financial institutions |
| Inflation Risk | Low, due to fixed supply | Subject to inflation from monetary policy |
| Physical Form | None, purely digital | Physical notes and coins available |
| Use Cases | Investment, remittances, decentralized finance | Daily transactions, savings, official payments |
Introduction to Cryptocurrency and Fiat Currency
Cryptocurrency is a decentralized digital asset secured by cryptography, operating on blockchain technology that enables peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Fiat currency, issued and regulated by governments, serves as the legal tender for everyday transactions and central banks control its supply to maintain economic stability. Unlike fiat money, cryptocurrencies offer transparency, limited supply through algorithms, and resistance to inflation, reshaping the global financial landscape.
Fundamental Differences Between Cryptocurrency and Fiat Currency
Cryptocurrency operates on decentralized blockchain technology, ensuring transparency and security through cryptographic validation, whereas fiat currency is centralized and regulated by government authorities and central banks. The supply of cryptocurrencies is often algorithmically capped, limiting inflation risk, while fiat currencies can be subject to inflation due to government monetary policies and unlimited issuance. Transactions with cryptocurrency enable peer-to-peer exchanges without intermediaries, contrasting with fiat currency's reliance on banking institutions and financial infrastructures.
How Each Currency Type Is Created and Managed
Cryptocurrency is created through decentralized blockchain protocols using processes like mining or staking, ensuring transparency and security without central authority control. Fiat currency is issued and regulated by central banks and governments, which manage supply through monetary policies such as interest rates and quantitative easing to maintain economic stability. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrency contrasts with the centralized management of fiat, impacting control, inflation, and trust mechanisms in financial systems.
Security and Fraud Protection
Cryptocurrency leverages blockchain technology, offering decentralized security features such as cryptographic encryption and immutable transaction records that reduce risks of fraud and unauthorized access. Fiat currency depends on centralized financial institutions and government regulations for security, which can be vulnerable to counterfeiting, identity theft, and fraud through intermediaries. Advanced encryption protocols and consensus mechanisms in cryptocurrencies enhance fraud protection compared to traditional fiat systems reliant on regulatory frameworks and manual oversight.
Transaction Speed and Accessibility
Cryptocurrency transactions often complete within minutes or seconds due to blockchain technology, bypassing traditional banking delays associated with fiat currency transfers that can take several days. Digital wallets and global internet access improve the accessibility of cryptocurrencies, allowing users to send and receive funds anywhere without relying on centralized financial institutions. In contrast, fiat currency transactions require intermediaries like banks or payment processors, which may limit accessibility and increase processing times, especially in cross-border payments.
Inflation and Value Stability
Cryptocurrency offers limited inflation risk due to fixed supply mechanisms like Bitcoin's 21 million cap, resulting in potential value appreciation over time. Fiat currency, controlled by central banks, faces inflationary pressures through monetary policy adjustments, often leading to decreased purchasing power. Investors seeking value stability must weigh cryptocurrency's volatility against fiat currency's susceptibility to inflation-driven depreciation.
Global Acceptance and Usability
Cryptocurrency offers increasing global acceptance through decentralized blockchain networks enabling borderless transactions without intermediaries, while fiat currency remains the dominant medium due to government backing and widespread institutional support across nearly all countries. Major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are accepted by numerous online merchants and international platforms, yet fiat currencies maintain superior usability for everyday transactions, regulatory compliance, and access to financial services worldwide. The ongoing development of digital wallets and payment gateways aims to enhance cryptocurrency usability, but fiat currency's entrenched infrastructure continues to facilitate seamless global commerce.
Regulatory Environment and Legal Considerations
Cryptocurrency operates within a rapidly evolving regulatory environment characterized by varying global standards on taxation, anti-money laundering (AML), and consumer protection, often leading to legal ambiguity and compliance challenges. Fiat currency regulation is well-established through central banks and government monetary policies, providing clear legal frameworks for issuance, circulation, and anti-counterfeiting measures. Regulatory bodies such as the SEC, FATF, and FINRA actively monitor cryptocurrency to enforce securities laws and prevent illicit activities, contrasting with the stable oversight mechanisms governing traditional fiat money.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Currency
Cryptocurrency offers advantages such as decentralization, lower transaction fees, and enhanced privacy, but faces challenges including price volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and limited merchant acceptance. Fiat currency provides stability, widespread acceptance, and governmental backing, yet suffers from inflation risk, central control, and slower international transfers. Both currencies serve distinct financial needs, with cryptocurrency excelling in borderless, digital transactions and fiat currency favored for everyday, regulated use.
Future Outlook: Cryptocurrency vs Fiat Currency
Cryptocurrency is projected to reshape the future financial landscape with its decentralized, blockchain-based technology promising increased security and lower transaction costs compared to fiat currency. Central banks worldwide are exploring Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) to combine the stability of fiat with the innovation of digital currency, indicating a hybrid future. Market adoption, regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements will critically determine whether cryptocurrency surpasses or coexists alongside traditional fiat money.
Cryptocurrency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com