Sustainable innovation focuses on developing new products, processes, or services that minimize environmental impact while promoting economic and social benefits. This approach integrates renewable resources, energy efficiency, and waste reduction to create long-term value. Discover how your business can leverage sustainable innovation to drive growth and responsibility by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
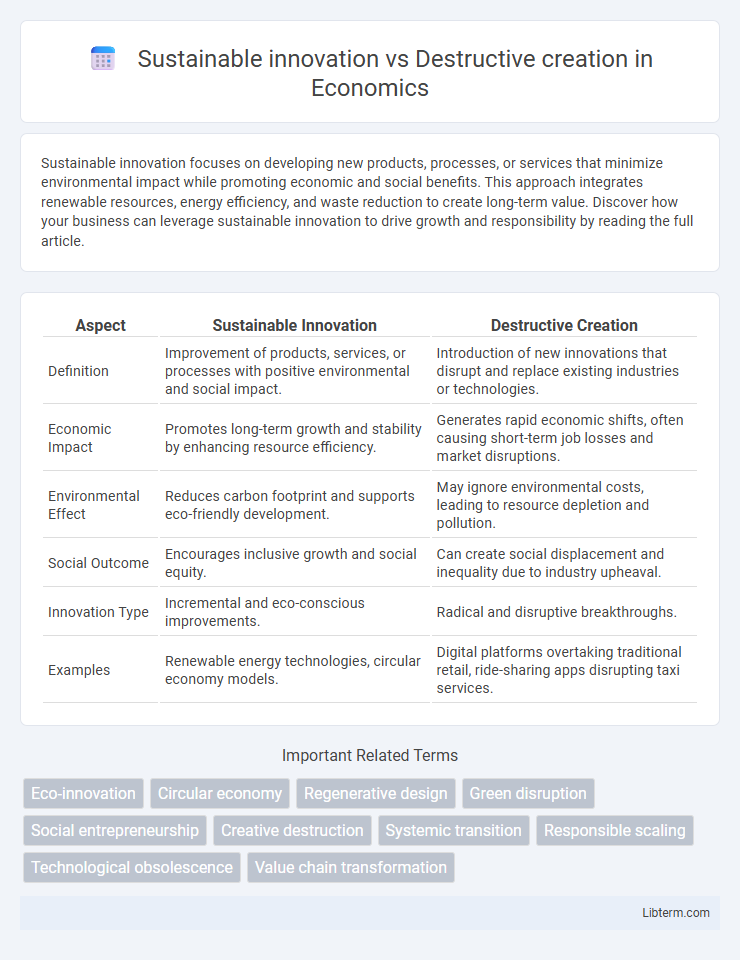
| Aspect | Sustainable Innovation | Destructive Creation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Improvement of products, services, or processes with positive environmental and social impact. | Introduction of new innovations that disrupt and replace existing industries or technologies. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes long-term growth and stability by enhancing resource efficiency. | Generates rapid economic shifts, often causing short-term job losses and market disruptions. |
| Environmental Effect | Reduces carbon footprint and supports eco-friendly development. | May ignore environmental costs, leading to resource depletion and pollution. |
| Social Outcome | Encourages inclusive growth and social equity. | Can create social displacement and inequality due to industry upheaval. |
| Innovation Type | Incremental and eco-conscious improvements. | Radical and disruptive breakthroughs. |
| Examples | Renewable energy technologies, circular economy models. | Digital platforms overtaking traditional retail, ride-sharing apps disrupting taxi services. |
Understanding Sustainable Innovation
Sustainable innovation prioritizes long-term environmental, social, and economic benefits by developing products, services, and processes that minimize negative impacts on natural resources and communities. Understanding sustainable innovation requires recognizing its role in driving circular economies, reducing carbon footprints, and promoting ethical supply chains that support resilience and equity. Companies that integrate sustainable innovation can achieve competitive advantage while addressing global challenges such as climate change and resource depletion.
The Concept of Destructive Creation
Destructive creation refers to the process of innovation that fundamentally disrupts existing systems, products, or industries by destroying old paradigms to make way for new ones. This concept highlights the trade-off between innovation and preservation, where transformative advances may result in economic and social upheaval as established practices and jobs become obsolete. In contrast to sustainable innovation, destructive creation often involves higher risk and uncertainty but can drive radical progress and long-term competitive advantage.
Key Differences: Sustainable Innovation vs Destructive Creation
Sustainable innovation prioritizes long-term environmental, economic, and social benefits by integrating renewable resources and ethical practices into product development, reducing negative ecological impacts. Destructive creation, in contrast, emphasizes rapid growth and profit often at the expense of natural resources, causing environmental degradation and social harm. Key differences include the approach to resource management, with sustainable innovation advocating for circular economy models, while destructive creation follows linear, waste-intensive processes.
Environmental Impact: Building vs Breaking
Sustainable innovation emphasizes eco-friendly materials, renewable energy, and circular economy principles, reducing carbon footprints and preserving natural resources during development. Destructive creation often causes habitat loss, pollution, and resource depletion through extractive processes and wasteful manufacturing. Prioritizing building strategies supports biodiversity and long-term environmental resilience, while breaking approaches increase ecological damage and hinder sustainability goals.
Economic Outcomes of Each Approach
Sustainable innovation drives long-term economic growth by fostering resource efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing brand reputation, leading to increased market competitiveness and job creation. Destructive creation, while potentially generating short-term profits through disruptive market entry or replacing obsolete technologies, often incurs social costs, environmental degradation, and volatile economic cycles. Economic outcomes of sustainable approaches tend to be more resilient and inclusive, supporting stable development and stakeholder value over time.
Social Implications and Responsibilities
Sustainable innovation prioritizes long-term social well-being by creating technologies and systems that enhance community resilience, equity, and environmental health without depleting resources or exacerbating social inequalities. In contrast, destructive creation often leads to short-term gains at the expense of vulnerable populations, increasing social fragmentation and environmental degradation. Ethical responsibility in innovation demands proactive engagement with stakeholders to ensure inclusive benefits, transparency, and accountability in addressing social challenges.
Drivers Behind Sustainable Innovation
Drivers behind sustainable innovation include growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, increasing regulatory pressure for environmental compliance, and advancements in green technologies that reduce resource consumption and waste. Companies prioritize sustainability to enhance brand reputation and achieve long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and circular economy practices. Collaboration between governments, businesses, and research institutions further accelerates development of sustainable solutions that minimize environmental impact and foster social responsibility.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Tesla's sustainable innovation in electric vehicles revolutionized the automotive industry by prioritizing renewable energy and reducing emissions, demonstrating significant global market growth and environmental impact. Conversely, the Deepwater Horizon oil spill exemplifies destructive creation, where risky offshore drilling led to catastrophic environmental damage and economic loss. These case studies highlight the critical importance of aligning innovation with sustainability to ensure long-term success and minimize harmful consequences.
Transition Strategies for Businesses
Transition strategies for businesses prioritize sustainable innovation by integrating circular economy principles, reducing carbon footprints, and investing in renewable energy sources to ensure long-term viability. Embracing sustainable innovation minimizes environmental impact while enhancing brand reputation and meeting evolving regulatory standards. Conversely, destructive creation often leads to resource depletion and ecological harm, undermining corporate resilience and stakeholder trust.
The Future of Responsible Innovation
Sustainable innovation prioritizes eco-friendly technologies and ethical practices that promote long-term environmental health and social equity. Destructive creation, by contrast, often leads to resource depletion and irreversible ecological damage, undermining future generations' well-being. The future of responsible innovation depends on integrating circular economy principles and adopting transparent governance to balance economic growth with planetary boundaries.
Sustainable innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com